
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
David Jiles
This is a test
- 626 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
David Jiles
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
A long overdue update, this edition of Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials is a complete revision of its predecessor. While it provides relatively minor updates to the first two sections, the third section contains vast updates to reflect the enormous progress made in applications in the past 15 years, particularly in magnetic recordin
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials di David Jiles in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Sciences physiques e Matière condensée. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Section II
Magnetism in Materials
Magnetic Phenomena on the Microscopic Scale
5 Magnetic Properties
We will now look at the causes of hysteresis in ferromagnets and how the variation of magnetization with magnetic field can be quantified in restricted cases such as at low field and in the approach to saturation. High-resolution measurements of the variation of M with H indicate that there are discontinuities. This is known as the Barkhausen effect. We will also consider the change in length of a ferromagnet as it is magnetized, that is, the magnetostriction, and discuss anisotropy in relation to magnetostriction.
We have shown in the previous chapter that most of the important macroscopic magnetic properties of ferromagnets can be represented on a B-H plot or hysteresis loop. From this, the magnetization can be calculated at every point on the hysteresis curve using the general formula B = μ0(H + M). As the magnetization curve is traversed, there are discontinuous, irreversible changes in the magnetization known as the Barkhausen effect after its discoverer. In recent years, the Barkhausen effect has become an important tool for investigating the microstructural properties of ferromagnetic materials.
One important bulk property of interest, which is not contained in the hysteresis plot, is the magnetostriction. This is the change in length of a material either as a result of a magnetic order (spontaneous magnetostriction) or under the action of a magnetic field (field-induced magnetostriction). This will also be discussed in this chapter.
5.1 HYSTERESIS AND RELATED PROPERTIES
5.1.1 INFORMATION FROM THE HYSTERESIS CURVE
Which are the most important macroscopic magnetic properties of ferromagnets?
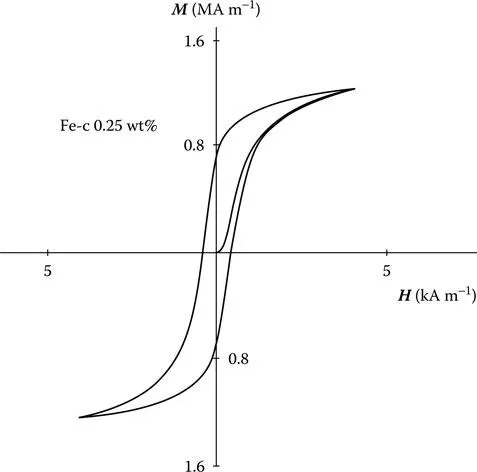
From the hysteresis curve such as the one shown in Figure 5.1, we can define a number of magnetic properties of the material, which can be used to characterize the hysteresis loop. A question immediately arises: How many degrees of freedom are there in a hysteresis loop? Or to put the question another way: How many parameters are needed to characterize a hysteresis loop? Clearly, there is no general answer to this, but for the commonly encountered sigmoid-shaped hysteresis loop such as the one in Figure 5.1, we can start to enumerate the important properties and thereby make an estimate.
5.1.2 PARAMETRIC CHARACTERIZATION OF HYSTERESIS
Which are the parameters that can be used to define hysteresis?
First of all, the saturation magnetization M0 will give us an upper limit to the magnetization that can be achieved. At temperatures well below the Curie point, the technical saturation Ms can be used instead. The width of the loop across the H axis, which is twice the coercivity Hc, is also an independent parameter since this can be altered by heat treatment and hence is not dependent on Ms. The height of the curve along the B-axis, that is, the remanence is also an independent parameter since it is not wholly dependent on Ms and Hc. The orientation of the hysteresis curve on the B-H plane, which can be represented by , the slope of the curve at the coercive point, is also independent of the other parameters.
The hysteresis loss WH may also be an independent parameter as may the initial permeability . Finally, the curvature of the sides of the hysteresis loop, which although not immediately obvious as an independent parameter, is clearly not dependent on factors such ...