
eBook - ePub
Linear Algebra
Reg Allenby
This is a test
- 240 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Linear Algebra
Reg Allenby
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
As the basis of equations (and therefore problem-solving), linear algebra is the most widely taught sub-division of pure mathematics. Dr Allenby has used his experience of teaching linear algebra to write a lively book on the subject that includes historical information about the founders of the subject as well as giving a basic introduction to the mathematics undergraduate. The whole text has been written in a connected way with ideas introduced as they occur naturally. As with the other books in the series, there are many worked examples.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Linear Algebra è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Linear Algebra di Reg Allenby in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Mathématiques e Théorie des nombres. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
MathématiquesCategoria
Théorie des nombres1
Systems of Simultaneous Linear Equations
Solutions of systems of simultaneous linear equations (also called linear systems) arise in very many real life situations; for just a couple of instances see the Applications at the end of the chapter. Here we show how to solve such systems (much as a computer would) by simplifying them in a systematic way. We shall also see how to interpret the results we obtain geometrically.
In 1849 the French mathematician Joseph Alfred Serret (30 August 1819–2 March 1885) wrote: ‘Algebra is, properly speaking, the analysis of equations.’ (This is no longer an accurate statement – although the motivating factor behind the theory of groups was the investigation of the solutions of polynomial equations.) Accordingly, linear algebra should (amongst other things) involve the study of linear equations – that is, equations involving the ‘unknowns’ (or ‘indeterminates’ or ‘variables’) x, y, z,… from which terms such as √x, xy, xy3z2, ex, sin x, 1/x, log x, etc. which are not of degree 1 in the variables, are excluded. The prefix ‘linear’ derives from the fact that such equations can, at least in the case of two and three unknowns, be represented geometrically by straight lines and planes in 2- and 3-dimensional space. In particular, linear algebra is much concerned with finding the solutions to a given system of simultaneous linear equations. We will begin by looking at some simple examples.
• Example 1
Solve
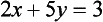
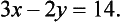
Recall that, to ‘solve’ the pair of equations (1.1) and (1.2) simultaneously, we must find all possible (pairs of) values of x and y which make both (1.1) and (1.2) true at the same time.
To obtain the full solution to Example 1 we may eliminate x, say, from equation (1.2). We can do this by taking twice equation (1.2) from three times equation (1.1) - in brief 3x(1.1)-2x(1.2) – which gives
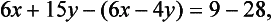
that is,
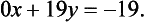
Thus equations (1.1) and (1.2) are replaced by the pair
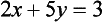
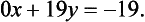
Equation (1.3) tells us at once that y = −1 and then (1.1) can be used to deduce that x = 4.
As an example (with somewhat more adventurous coefficients!) let us try the following.
Example 2
Solve
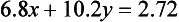
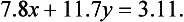
Proceeding as in Example 1, we obtain a new third equation by forming 7.8x(1.4)-6.8x(1.5).
This gives (!)
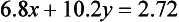
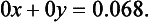
Since there are no numbers x and y satisfying (1.6) we infer that the given pair of equations can have no (simultaneous) solution.
As a final example consider the (almost identical) equations in the following.
Example 3
Solve
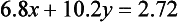
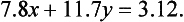
This time 7.8x(1.4)-6.8x(1.7) leads to
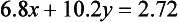
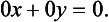
Here equation (1.8) imposes no restrictions whatsoever on x and y and so it can be ignored. Indeed the pair of equations (1.4) and (1.7) is see...