![]()
Contents
Illustrations
Maps
Timeline
Introduction
1 The Rebranding of Rome
2 Augustus: God and First Citizen
3 Alexandria: Gods in the City
4 The African Goddess-Queen
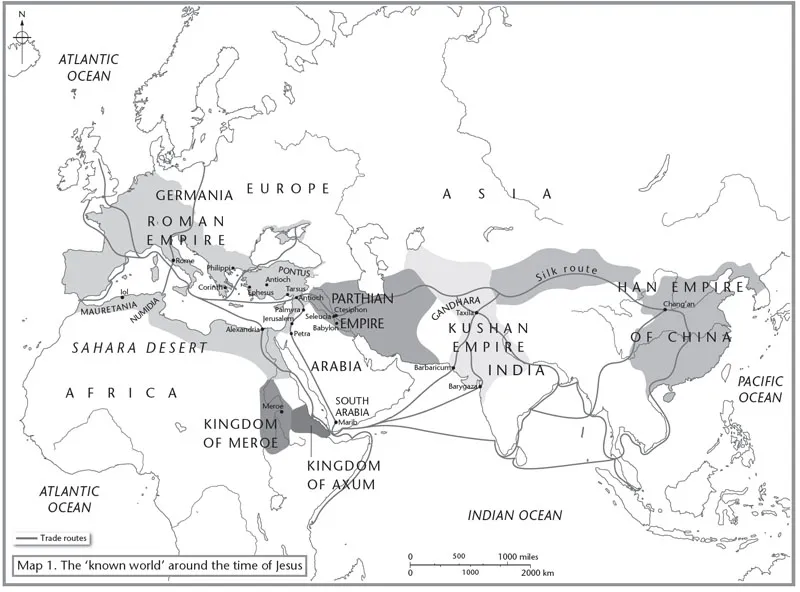
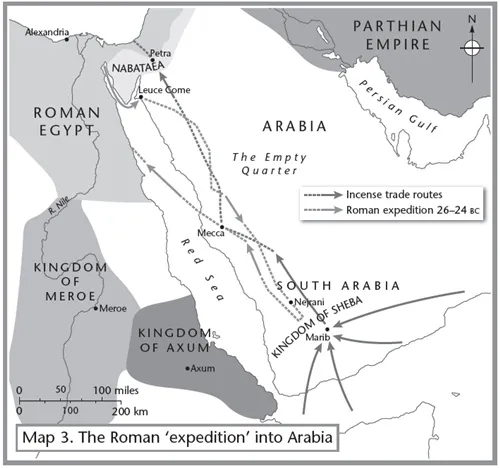
5 The Mirage of Arabia: Rome’s Fiasco
6 How Herod and the Pharisees Radicalized the Jews
7 Galilee: Jesus and the Messiah-Bandits
8 Castrating Priests and Trading Gods in Palmyra
9 Political and Religious Chaos in Parthia
10 A ‘Pagan Christ’ in Babylon
11 India: Brahmins versus Monks
13 Confucius’ Religion for Civil Servants
14 Wang Mang the Pious Usurper
15 The Dragon Who Flew Too High
16 Recalcitrant Spirits: The German Resistance
17 Rome: The Emperor Becomes God
19 And Paul Created Christ
Notes
Select Bibliography
Index
A Note on the Author
![]()
Illustrations
Frontispiece: Isis and Horus. Wellcome Library, London
1. Apollonius. ©2006 Alinari / TopFoto
2. Livia. Giovanni Dall’Orto / Wikimedia Commons
3. House in Marib. Prisma Bildagentur AG / Alamy
4. Maecenas. ©2006 Alinari / TopFoto
5. Agrippa. akg-images
6. Tiberius. akg-images
7. Josephus. akg-images
8. The Kiosk at Naqa. © Nigel Pavitt/JAI/Corbis
9. Suren. Aytakin / Wikimedia Commons
10. Banqueters, Palmyra. Lessing Photo Archive
11. Temple of Bel. De Agostini / Getty
12. Kushan prince. akg-images / RIA Novosti
13. King Juba. De Agostini / Getty
14. St Paul. Leemage / Getty
15. Coin of Varus. INTERFOTO / Sammlung Rauch / Mary Evans
16. Coin of Gondophares. World Imaging / Wikimedia Commons
17. Antonia fortress. deror avi / Wikimedia Commons
18. Augustus. Alinari via Getty Images
19. Seated Buddha. akg-images
20. Queen Mother of the West. The Granger Collection / TopFoto
![]()
![]()
Timeline
Note: Many of these dates are approximate
BC
1500–1000 Aryan (Indo-Iranian) tribesmen from the steppes of southern Russia move into the Indus Valley – in present-day Pakistan and north-west India – and begin to compile the hymns of the Rig Veda, the oldest sacred text of Hinduism
1200 The Aryan priest Zoroaster has a vision of the first supreme god Ahura Mazda and begins preaching in ancient Iran
1070 Egypt loses control of Meroe – present-day southern Egypt and Sudan – and it becomes an independent kingdom
1070–AD 350 EMPIRE OF MEROE
753 Legendary date for the founding of the city of Rome by Romulus and Remus
744–609 Assyrian (NEO-ASSYRIAN) EMPIRE
—Originally a kingdom of northern Mesopotamia – modern-day northern Iraq – Assyria acquires a vast territory and has its capital at Nineveh on the banks of the Tigris River
727 Meroite King Pye invades Egypt and founds the twenty-fifth dynasty of pharaohs which rules Egypt 727–653
727–653 Twenty-fifth dynasty of Egypt
722 Assyria conquers northern Israel and Jews are deported
700 Construction of Marib Dam in South Arabia
—Towards the end of the 7th century Rome becomes an organized city-state
626 The kingdom of Babylonia in southern Mesopotamia – part of modern Iraq – defeats Assyria
626–539 BABYLONIAN (NEO-BABYLONIAN) EMPIRE
587–537 Captivity of the Jews in the city of Babylon – near present-day Baghdad – under Nebuchadnezzar
586 Babylonia conquers southern Israel (the kingdom of Judah)
563–483 The life of Siddhãrtha Gautama, the Buddha
558–479 The life of Confucius
540 Babylonian (Neo-Babylonian) Empire falls to the Persian King Cyrus
540–331 PERSIAN (ACHAEMENID) EMPIRE
539 Cyrus allows the Jews to return home
510 The last king of Rome is expelled; Etruscan rule ends and the Republic is established at Rome
510–27 Roman Republic
497–425 Vardhamana Mahavira, the son of a chieftain in the Indian kingdom of Magadha, in north-east India, establishes the central tenets of Jainism
396 Rome begins its conquest of Italy
341–270 Life of Epicurus, founder of Epicureanism
335–263 Life of Zeno, founder of Stoicism
334–328 Alexander of Macedonia defeats Darius and conquers the Persian Empire
334–328 EMPIRE OF ALEXANDER THE GREAT
328 At Alexander’s death his general Seleucus ‘inherits’ the eastern part of the Persian Empire
312–204 SELEUCID EMPIRE
321 Chandragupta Maurya founds India’s first and greatest empire; his chief minister Kautilya writes the Arthashastra
321–185 BC MAURYAN EMPIRE
269–232 Reign of Ashoka Maurya, first Buddhist emperor of the Indian subcontinent
264 The first of the Punic Wars between Carthage – in present-day Tunisia – and Rome; Rome’s conquest of Sicily signals the beginning of its imperial expansion beyond the borders of peninsular Italy
250 Parni nomads from Central Asia settle in Parthia – in present-day Iran – and begin their conquest of the Seleucid Empire
250 BC–AD 224 PARTHIAN (ARSACID) EMPIRE
220 Qín Shi Huáng, king of the state of Qin in western China, defeats rival warring states and becomes the first emperor of a unified China; he extends the Great Wall, begun in the 4th century BC, to keep out invading nomads
220–AD 1912 CHINESE EMPIRE
218–202 The Carthaginian general Hannibal invades Italy but is eventually defeated by Scipio
206–AD 9 FORMER (WESTERN) HAN DYNASTY (CHINA)
146 Greece reduced to a Roman province
135–132 Slave revolt in Sicily led by Eunus, a Syrian slave inspired by the mystery cult of Atargatis
63 Pompey captures Jerusalem; Palestine becomes a client state of Rome
53 Parthians defeat the Romans at the Battle of Carrhae
50 Yuezhi/Kushan tribesmen from western China push into India
44 Julius Caesar is assassinated
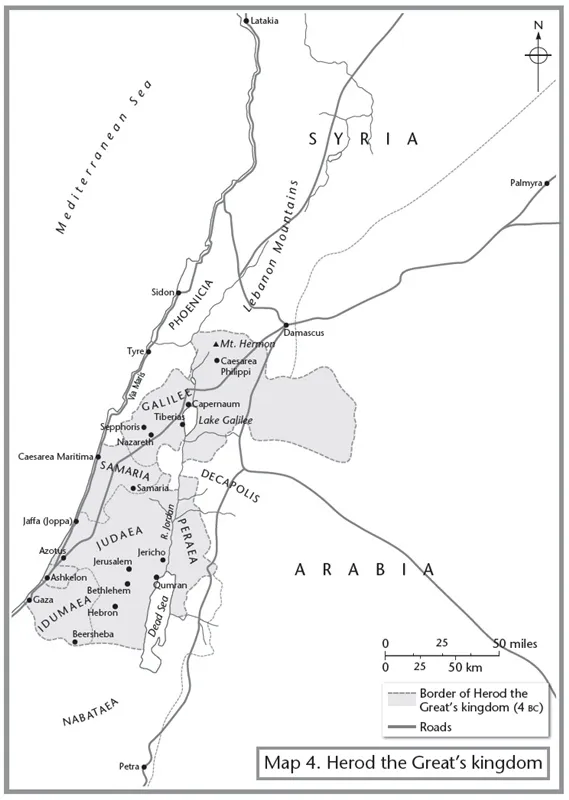
37–4 Reign of Herod the Great
31 Octavian/Augustus, great-nephew of Julius Caesar, defeats Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium
27 The Senate bestow on Octavian the title of ‘Augustus’, the revered one
27–AD 14 Reign of Augustus, the first Roman emperor
27–AD 476/1453 ROMAN EMPIRE
The Western part of the empire collapses in AD 476 and the Eastern part – the Byzantine Empire – with the fall of Constantinople in AD 1453
26 Aelius Gallus leads disastrous Roman ‘expedition’ into South Arabia
25 Juba installed as King of Mauretania – part of present-day Algeria and Morocco
—Queen Amanirenas of Meroe leads her army against Roman-controlled Egypt
20 Peace treaty between Augustus and Queen Amanirenas settles the border disputes between Roman Egypt and Meroe – present-day southern Egypt and Sudan
4 Jewish students in Jerusalem smash the golden eagle erected by Herod the Great on one of the Temple gates
—Death of Herod the Great
—Most likely date for the birth of Jesus
4/2 Former slave-girl Musa murders her husband and becomes co-ruler of Parthia with her son/new husband Phraataces
3 Cult of the Queen Mother of the West sweeps through China
2 Augustus is proclaimed pater patriae (‘father of the fatherland’)
AD
2 Parthians and Romans celebrate their peace agreement on the banks of the Euphrates
6 Rome takes direct control of Judaea and orders a census so that the province can be assessed for tax; Judas the Galilean and Zadok call for a mass boycott – this marks the birth of the Zealots, the radical wing of Pharisaism
9 Battle of Teutoburg Forest; German tribesmen, led by Arminius, wipe out almost the whole Roman army of the Rhine
—China’s acting emperor Wang Mang seizes the throne and proclaims the Xin (‘new’) dynasty
9–23 Rule of Wang Mang
14 Augustus dies and is declared to be a god by the Senate
14–37 Tiberius, Augustus’ thirty-year-old stepson, becomes emperor
20–46 Gondophares rules over the kingdom of Gandhara – a vast region in present-day eastern Afghanistan, northern Pakistan and northern India – within the Parthian Empire; whether he rules as a loyal client king or has broken away from Parthia is unclear; his capital city is Taxila, near presentday Islamabad in Pakistan
23 Wang Mang, the usurper of the Han throne, is defeated and killed
24 Pontius Pilate is appointed procurator (governor) of Judaea
25 Emperor Guangwu restores the Chinese Han Dynasty
25-220 LATER (EASTERN) HAN DYNASTY
28/29 John the Baptist baptizes his cousin Jesus
—Jesus begins his mission
—John the Baptist is beheaded
—Many of John’s disciples become followers of Jesus
30–80 Kujula Kadphises, chief of the Yuezhi tribesmen from Central Asia, becomes the first Kushan emperor
First–Third centuries KUSHAN EMPIRE (present-day Central Asia and northern India)
—Kujula and his successors are patrons of a more populist form of Buddhism, Mahayana Buddhism, which they export to China
30 Rome takes control of Palmyra
31/33 Jesus is crucified
32 Paul’s conversion on the road to Damascus
37 Death of Tiberius; his nephew Caligula becomes emperor
38 Pogrom inflicted on the Jewish community of Alexandria; the Roman prefect Aulus Avillius Flaccus forces Jews to live in one area – the world’s first ghetto
—Apollonius, the wandering holy man and miracle worker, visits the Parthian province of Mesopotamia, where the Parthian King Vardanes I is embroiled in a civil war
40 Paul begins his missionary work in the Near East (modern Turkey and the Middle East) and Gree
41 Caligula is assassinated; his uncle, Claudius, becomes emperor
43 Claudius conquers Britain
48 Paul and Barnabas set off on their first missionary journey
—Paul preaches his first recorded sermon at ‘Psidian Antioch’ (in modern Turkey)
49 Claudius imposes martial law on an increasingly violent Palestine, and expels the Jewish community from Rome
—Paul travels to Jerusalem for a conference to try to heal the differences between the ‘party of the circumcision’, led by Jesus’ brother James, and the ‘party of the uncircumcision’, led by Paul
54 Death of Claudius; his stepson Nero becomes emperor
58 Paul returns to Jerusalem, where he is arrested in the Temple; he demands to be tried as a Roman citizen under Roman law and is taken to Rome
60/61 Boudicca, queen of the Iceni, leads a rebellion in Britain against the Romans, but is defeated and commits suicide
64 Great fire of Rome; Nero blames the Christians who are rounded up to be crucified, torn apart by wild beasts, or burned alive; Paul and Peter may have been among the victims
65 Kujula Kadphises and his Central Asian nomadic army conquer Gondophares’ Indo-Parthian kingdom in Gandhara (today’s northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan)
66–73/4 First Jewish Revolt/War against the Romans
68 Nero commits suicide; his death marks the end of the Julio-Claudian dynasty; he is succeeded by Galba
70 The Temple and Jerusalem are razed to the ground by the victorious armies of the Emperor Vespasian’s son Titus
79 Eruption of Vesuvius overwhelms Pompeii
132–135 Second Jewish Revolt / War against the Romans. After the Jews’ defeat Hadrian expels them from Jerusalem and the rest of Judaea
—Jerusalem is renamed Aelia Capitolina
224 The last of the Parthian kings is killed in battle; the succeeding Sasanian dynasty imposes its authority over the empire, adopting Zoroastrianism as the state religion
312 Conversion of Constantine to Christianity
—Constantine defeats Maxentius, his rival as emperor, at the Milvian Bridge in Rome
335 Emperor Ezana of Aksum converts to Christianity, and makes Christianity the official state religion
391 Theodosius bans all non-Christian rites and orders the destruction of all temples, cult images and ancient festivals
—Christianity is established as the official religion of the Roman Empire
395 After th...