![]()
The history of blockchain and cryptocurrency
Before we get started, I just wanted to talk about how excited I am about the potential future of blockchain technology; not just in business, but in every aspect of our daily lives. For the last decade, we have seen technology progress at breakneck speed. The advent of the internet, smartphone technology, video streaming, social media and online businesses have changed the face of the planet. However, there have been some downsides. Online privacy has taken a backseat for the average consumer, in the search of more business. Google and Facebook have decided that the pursuit of more clicks and revenue supersede our personal privacy.
Enter blockchain. Blockchain has the potential to give us more privacy through innovative encryption of our online activities. This could give businesses the info they need while protecting our privacy.
It also has the potential to revolutionize the way that transactions are made; eliminating the need for the middleman to check the authenticity of these transactions.
Now let’s get started!
The Original Problem with Digital Transactions
Most Digital Purchases are Bank Transfers
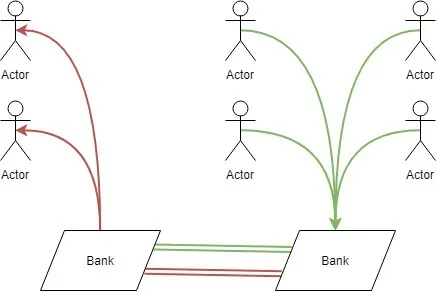
Believe it or not, most digital transactions still occur like a normal bank transfer would nearly three decades ago. The only real difference is that it goes to a middleman before it is approved. You start a transaction since you want to pay for some item, the amount or, rather, the number associated with the amount is then sent to an auction clearing House. This clearing House talks with the associated bank you're giving the amount of money to and ensures there is an account to transfer to. That same clearing house also asks if the bank you're transferring from has an account with the number of the amount associated with it. Once it confirms both sides exist and you have money, it then commits the transaction.
As computers have gotten faster, these transactions have gotten faster as a result and so it's barely noticeable to the average consumer. However, essentially, you are doing a wire transfer every time you use a card, every time you use PayPal, and every time you use something like Google Pay.
Bank Transfers Are Tracked with Physical Items
The way that banks are able to do this is because they have an exchange rate. That is, they have a rate of which items can be exchanged in their program otherwise known as Fiat money. It is not the same exchange rate that is referred to when talking about the value difference between dollars.
What this is talking about is that the bank in question has a certain amount of value in dollars that can be transferred. While money used to be a physical item, it's not anymore, well with a majority of money that there is. Most money is digital because it allows for inflation and deflation of a currency by those who make that money. This actually makes the value of that money much easier to control rather than relying on physical items, but banks still make transfers with physical items.
Usually, at the end of the week, there is a security truck that transfers the amount of money that has been transferred out of that bank going to a depository that will then disperse this money amongst the banks who have claims to it. The bank that sent out the money will also get its own version of a security truck holding money for money that was transferred to that bank. Physical, paper money is still in circulation because of the system as it represents a permanency with the money. You can't copy and paste a dollar bill… well, easily that is.
The Double Spending Riddle
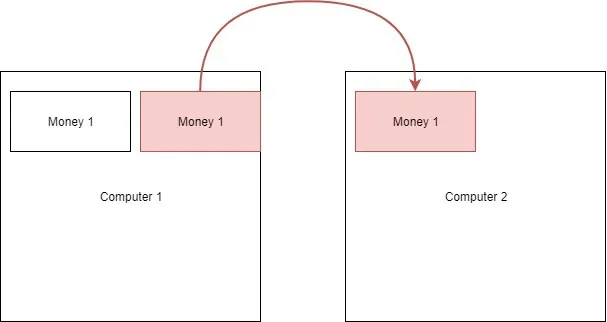
Digital transfers have actually been around for much longer as a concept than they have been in practice. This is because digital currency is a very easy and international way of purchasing items. There was just one problem with doing everything on the computer and that was because of an incredible invention that most of us use in our daily, if not weekly, lives; copy and paste.
When you made a transfer of digital money, how would you go about preventing the ability to copy and paste that money just so you could have a hundred more like it? This was known as the double spending problem. In the beginning of computing history there was virtually no way of preventing the double spending problem and it is only through the internet and encryption that we can truly make our way past this problem, for a temporary amount of time.
Banks Are Prone to Double Spending, You Just Don’t Know
As I noted earlier, you can do a form of copy and paste with Fiat money. Money is just an imaginary thing in that the dollar bill in your hand represents a value everyone created and doesn't actually have a measurable material value beyond the cost it took to make it. Essentially, everybody in society said that this dollar is worth this amount.
Therefore, if you can make something that looks identical to this then you have a double spending problem; it's just not digital. We often refer to this as fraud as it is a term used for trying to lie about something, which means it could be money fraud, wire fraud, or bank fraud amongst the many other types of frauds. Knowing that money could be copied and pasted, those that printed the money took steps to ensure that doing so was incredibly difficult. This is why you have things like special color ink, ridges around the edges, and custom fonts on pieces of cloth as this makes it difficult to copy it unless you have the original printer. Essentially, the first monetary form of encryption.
How to Prevent Double Spending?
Everyone Keeps Track of Everyone
Now, the first thing about the double spending problem was that they needed a way to ensure that double spending couldn't happen between two parties. Let’s say that you decide to make a contract with a company for certain amount of money and then you make a contract, again, with that same company. They are the exact same contract; the only difference is that you get paid twice as much for the same amount of time. How does the company protect itself from contract fraud in this case?
There is actually a position for this and it's known as a notary. A notary has the job of being physically present at the time of signing a contract so that they can say they witnessed this contract happen and then the second contract is invalidated if that notary is not there to sign for the company. Therefore, if you manage to trick a second employee to sign a contract with you, the notary who was there for the first contract signing will know that this second contract is attempted contract fraud. This is essentially how you prevent double spending and we'll get into the details later on.
Worker ID
Now, most systems that keep track of contract invoices will usually have a form of identification. Work at a place long enough and they will give you your own specific workers identification number and this is simply to identify you as the person who you say you are. You often see this in security card keys that are way too vulnerable for most businesses.
sa064t1aMPjmBs2Cd2v-m69YbFmMvpfNt9kt6qC3PF0l8eSV5nof5Yn2hCmS
A cryptocurrency coin has a form of this and this is often known as the worker ID (seen above). The worker ID is often a combination of your specific ID attached to a randomized number that represents your worker on the computer that got the money for you. When you make the transaction, the portion of the worker ID that represents you is actually switched out with the worker ID part that represents the person you're transferring too. This is how identification of coin holders happen.
Coin ID
sa064t1aMPjmBs2Cd2v-m69YbFmMvpfNt9kt6qC3PF0l8eSV5nof5Yn2hCmS
Identifications of coins is a little bit different because the identification number or stream is actually given to you by the algorithm that runs the entire system. This is a mostly randomized stream of letters and numbers partly because there are already coins in the system and those coins clash if there was an identical coin with the same stream. The only difference is that the algorithm that creates this also utilizes techniques so that the coins cannot be created in a linear order but rather an order that matches the function of the algorithm.
Therefore, when you get a coin it is a combination of randomized letters and numbers as well as a sequential combination of those in alignment with the algorithmic function designed to further randomize the coin but in a randomization pattern that can be reversed. This is how coin identification numbers are created so that no two coins have the same identification number attached to them and no one can figure out the next coin and just create the coin on their desktop.
The System Isn’t Complete
The system itself is not very complete and this is why you have so many versions of cryptocurrencies out on the market because there's always someone that either wants the same amount of success they saw out of Bitcoin or someone thinks they've got a better idea for a cryptocurrency. Every year there is an improvement on the technology that exists in this market simply because it is profitable for it to do so.
Not only that, but the system is also still very vulnerable, and this isn't necessarily because of the mechanisms in place used to identify coins and workers. The vulnerability of the system is a two-part problem dealing with encryption and a difference of ideas. Encryption is used at nearly every level until you get to the point where you can earn the coin in the methodology of how that coin is earned.
Encryption is Needed for This to Work
Anyone Can Transfer the Number 1
The primary problem with the double spending problem was the fact that it could be copied and pasted. The easiest way to solve this problem is to simply make it so that it is almost impossible to copy and paste it. You can still copy and paste a blockchain node but, due to encryption, even if you were trying to use it would invalidate the use beyond a single transaction.
Cryptocurrency is not tied to the device but, rather, tied to the encryption of the coin. The encryption algorithm is unknown to anybody that is not the creator of the blockchain. This means that all that needs to happen is the blockchain needs to verify the previously recorded encryption set for both the worker ID and the coin ID. If these are the same, then what happens is that when you transfer the coin the worker ID is changed to the new identified worker. This ID is attached to a wallet and the wallet contains the worker ID that is stamped on every coin that goes into that wallet.
This means that if a person is using a cryptocurrency coin in their wallet and that coin was forcibly placed in their wallet, the blockchain would compare the worker ID to the wallet ID and deny the transaction because they didn't match. This means that if you try to have a fake coin attached to your wallet ID, the same transaction validation will occur. The coin ID will be compared to what is in the blockchain and the worker ID will be compared to the worker ID that's in the blockchain and when the blockchain s...