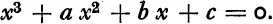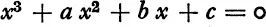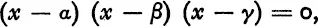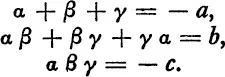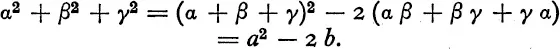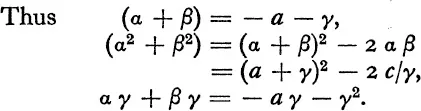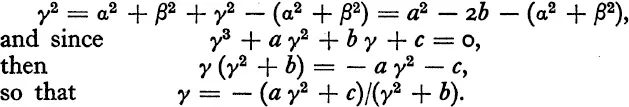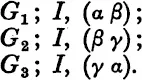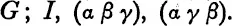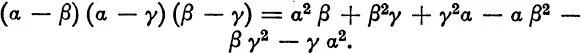![]()
CHAPTER IX
THE GALOIS THEORY OF
EQUATIONS
SUPPOSE that there is given a cubic equation, say
This equation will always have three roots, which will be real or complex numbers, and which we will denote by α, β, γ.
To find α, β, γ it is of course necessary to solve the equation, and this may not be an easy procedure, but there are certain functions of the roots α, β, γ which can be determined easily without solving the equation.
If we are given a function of the roots, say α2 β, we can in general form five other functions, e.g. α2 γ, β2 α, β2 γ, γ2 α, γ2β by taking a different arrangement of the roots α, β, γ, i.e. by operating on the function with a permutation interchanging the roots. The six operations of the symmetric group give six functions which are all distinct in this case.
It may happen that all the operations of the group leave the function unchanged, as, e.g. when the function is (α + β + γ) or α βγ . Such functions are called symmetric functions. Any symmetric function of the roots can be expressed directly in terms of the coefficients in the equation without solving the equation.
Thus the equation
must be exactly the same as the equation
and expanding the latter and comparing the coefficients of the various powers of x,
In terms of these any other symmetric function can be expressed. Thus
Now it may happen that we can find a function of the roots that is changed by some of the permutations but is left unchanged by others. Then the permutations which leave it unchanged will form a subgroup of the symmetric group, and the function is said to belong to this subgroup.
Thus there is a subgroup of order two which contains the identity and the interchange (α β). Examples of functions which belong to this subgroup are (α2 + β2), (α + β), γ, α γ + β γ.
These functions of the roots cannot be expressed in terms of the coefficients a, b, c, without solving the equation, but they have the remarkable property that any one of them can be expressed in terms of any other, with the aid of the coefficients.
To express, say, γ in terms of (α2 + β2) is not so easy, but can nevertheless be accomplished. Thus
This expresses γ in terms of γ2, which in its turn has already been expressed in terms of (α2 + β2).
Now there are three subgroups of the symmetric group, each of order two, and of the same type as the one we are considering. These are:
Any of these subgroups can be transformed into any other by an operation of the symmetric group. They are called conjugate subgroups, and the set of three is a class of conjugate subgroups.
The other subgroup of the symmetric group of order six is the subgroup of order three consisting of the elements
This is different because there is no other subgroup conjugate to it. Every transform of G gives the same subgroup G, and it is called a self conjugate subgroup.
An example of a function of the roots which belongs to this subgroup is
The ratio of the order of the group to the order of the subgroup is called the index of the subgroup.
We will now consider how the properties of these subgroups can be used in the solution of equations.
It is well known that, in general, the solution of an algebraic equation of degree greater than one involves irrational numbers. Hence to find the solution, even of a quadratic, some process must be employed which obtains an irrational number. The simplest process which yields an irrational number is the extraction of roots, that is the finding of the square root, cube root or n-th root of a given number. We say that an equation is solvable if by finding n-th roots of numbers a certain number of times we can reach an expression which satisfies the equation. It is well known that any quadratic equation can be solved by the extraction of one square root. Hence the quadratic equation is solvable.
Now if those functions of the roots of an equation which correspond to a given group H are known, and the group H has a subgroup G of index r, then the functions which belong to the group G can be obtained by solving an equation of degree ...