
- 492 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Gas Well Deliquification
About this book
Gas Well Deliquification, Third Edition, expands upon previous experiences and applies today's more applicable options and technology. Updated to include more information on automation, nodal analysis, and horizontal gas well operations, this new edition provides engineers with key information in one central location. Multiple contributors from today's operators offer their own learned experiences, critical equipment, and rules of thumb for practicality. Covering the entire lifecycle of the well, this book will be an ideal reference for engineers who need to know the right solutions regarding a well's decline curve in their work to continuously optimize assets.- Teaches users how to understand the latest methods of deliquifying gas wells, from nodal analysis, to various forms of artificial lift- Provides an up-to-date reference on automation techniques for today's operations, including horizontal wells- Presents various perspectives contributed from multiple sources, allowing readers to select the best method for a well's lifecycle
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Introduction
Abstract
Keywords
1.1 Introduction

- 1. Newer techniques of rod design and rod protection in deviated wells using sucker rod systems
- 2. New methods for SRP (sucker rod pump) systems to allow deeper intake for the systems in horizontal wells
- 3. Design of gas lift systems for conventional and also declining unconventional wells using conventional gas lift with bracketed valves for anticipated changing rates
- 4. Use of high-pressure gas lift to allow more drawdown initially and to eliminate some downhole equipment
- 5. New techniques of tracking plungers, various forms of plunger lift, new plunger optimization techniques, new equipment, and plungers in horizontal wells
- 6. Use of electric submersible pumps (ESPs) to dewater including design for lower rate wells requiring needed cautions
- 7. Optimization of progressing cavity pumpings (PCPs) that usually operate in shallower wells. Rod protection in deviated and horizontal wells
- 8. The latest in application of foamer chemicals and methods of application
- 9. Details and methods of application for gas separation for all the pumping systems
- 10. New advances in automation are presented in a separate chapter. Automation is a necessity if optimum conditions are to be achieved
1.2 Multiphase flow in a gas well
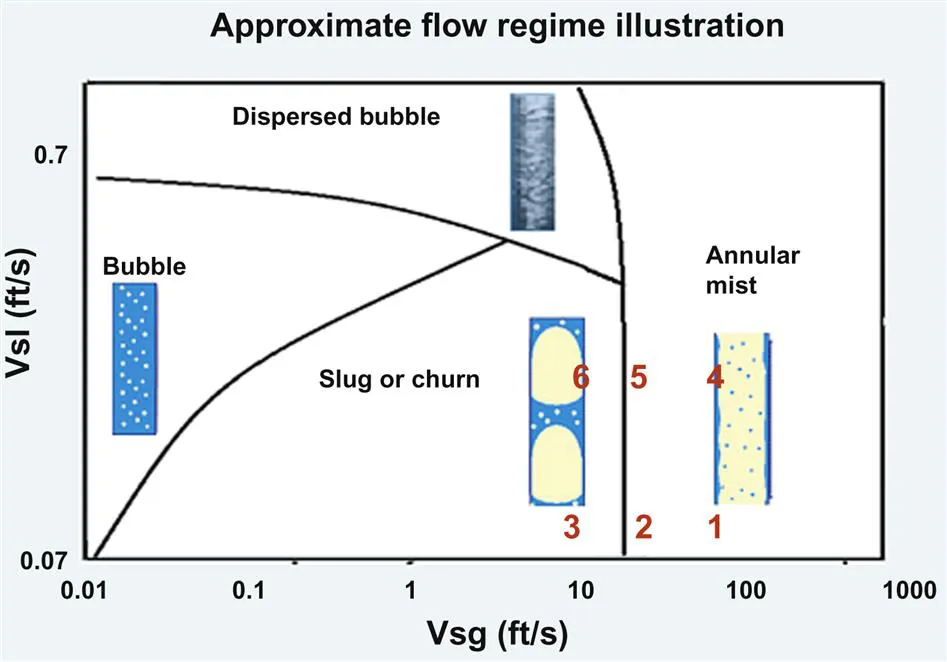
For above what numbers in bold indicate: (all for 2 3/8’s tubing)
1: 88 bbls/Mscf, 50 psi, velocity for 320 Mscf/D, 120°F;
2: 88 bbls/Mscf/100 psi, velocity for 320 Mscf/D, 120°F;
3: 88 bbls/Mscf, 200 psi, velocity for 320 Mscf/D, 120°F;
4: 200 bbls/Mscf, 100 psi, velocity for 320 Mscf/D, 120°F;
5: 200 bbls/Mscf, 50 psi, velocity for 320 Mscf/D, 120°F;
6: 200 bbls/Mscf/50 psi, velocity for 320 Mscf/D, 120°F.
1.3 Liquid loading
1.4 Deliquification techniques
- • Initial high rates (for unconventional well on sharp decline)
Unconventional wells may come in high rates initially which are well above critical rate. For maximum PVP (present value profit) use Nodal to look at flow up casing, flow up casing/tubing annulus and to look at tubing size effect on flow. Some operators are considering annular gas lift and high-pressure gas to boost the high rates. Most of the profits from unconventional ...
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Recognizing symptoms of liquid loading in gas wells
- 3. Critical velocity
- 4. Nodal Analysis: Analyzing loaded wells
- 5. Compression
- 6. Plunger lift
- 7. Hydraulic pumping
- 8. Liquid unloading using chemicals for wells and pipelines
- 9. Progressing cavity pumps
- 10. Use of beam pumps to deliquefy gas wells
- 11. Gas lift
- 12. Electrical submersible pumps
- 13. Coal bed methane (CBM) and shale
- 14. Production automation
- Appendix A. Development of critical velocity equations
- Appendix B. Nodal concepts and stability concerns
- Appendix C. Plunger troubleshooting procedures
- Appendix D. Gas lift terminology
- Index