
eBook - ePub
Thermofluid Modeling for Energy Efficiency Applications
- 360 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Thermofluid Modeling for Energy Efficiency Applications
About this book
Thermofluid Modeling for Sustainable Energy Applications provides a collection of the most recent, cutting-edge developments in the application of fluid mechanics modeling to energy systems and energy efficient technology.
Each chapter introduces relevant theories alongside detailed, real-life case studies that demonstrate the value of thermofluid modeling and simulation as an integral part of the engineering process.
Research problems and modeling solutions across a range of energy efficiency scenarios are presented by experts, helping users build a sustainable engineering knowledge base.
The text offers novel examples of the use of computation fluid dynamics in relation to hot topics, including passive air cooling and thermal storage. It is a valuable resource for academics, engineers, and students undertaking research in thermal engineering.
- Includes contributions from experts in energy efficiency modeling across a range of engineering fields
- Places thermofluid modeling and simulation at the center of engineering design and development, with theory supported by detailed, real-life case studies
- Features hot topics in energy and sustainability engineering, including thermal storage and passive air cooling
- Provides a valuable resource for academics, engineers, and students undertaking research in thermal engineering
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
At the moment all of our mobile-responsive ePub books are available to download via the app. Most of our PDFs are also available to download and we're working on making the final remaining ones downloadable now. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Thermofluid Modeling for Energy Efficiency Applications by Mohammad Masud Kamal Khan,Nur M.S Hassan,Masud Khan in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Fluid Mechanics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Earth Pipe Cooling with Horizontal Piping System
S.F. Ahmed, M.M.K. Khan, M.T.O. Amanullah, M.G. Rasul and N.M.S. Hassan, School of Engineering and Technology, Higher Education Division, Central Queensland University, Rockhampton, QLD, Australia
Earth pipe cooling technology is a building design approach for cooling a room in a passive process without using any customary units. It can reduce energy consumption of the buildings for hot and humid subtropical zones. This chapter investigates the performance of horizontal earth pipe cooling (HEPC) in combination with a green roof system. To measure the performance, a thermal model was developed using Fluent in ANSYS 15.0. Data were collected from three air-conditioning modeled rooms installed at Central Queensland University, Rockhampton, Australia. One of the rooms was connected to a HEPC system, the second to a green roof system, and the third standard room had no cooling system. The effect of air temperature, air velocity, and relative humidity of the hybrid earth pipe cooling performance were assessed. A temperature reduction of 4.26°C is predicted for a combined HEPC and green roof system compared to the standard room, which will assist the inhabitants to achieve thermal comfort and save energy in the buildings.
Keywords
Passive air cooling; earth pipe cooling; horizontal piping system; green roof; air temperature; air velocity
1.1 Introduction
A significant amount of energy is consumed by buildings today and buildings are accountable for about 40% of world annual energy consumption [1]. There has been an enormous increase in energy demand worldwide in recent years due to industrial development and population growth. World energy use is projected to rise from 524 quadrillion Btu in 2010 to 630 quadrillion Btu in 2020 and 820 quadrillion Btu in 2040 as shown in Figure 1.1 [2]. This represents an energy consumption increase of 56% during this period. More than 85% of this growth in global energy demand is predicted to occur among the developing nations outside the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) nations, where demand is driven by strong long-term economic growth and expanding populations. In contrast, the greater part of OECD member countries are now more established energy consumers with slower expected economic growth and particularly no foreseen population growth [3].
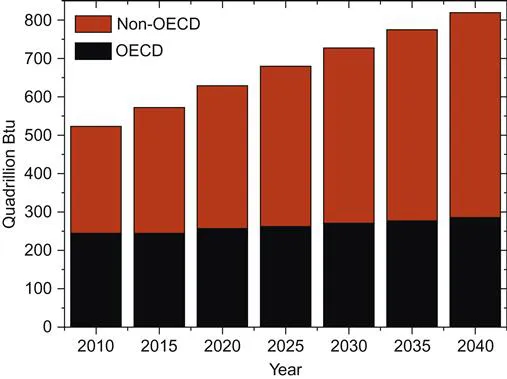
Energy use in non-OECD nations will increase by 85% compared to an increase of 18% for the OECD economies. Country-wise world energy consumption over this period of 2010–2040 is summarized in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1
World energy consumption by country grouping (quadrillion Btu) [2]
| Region | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | 2025 | 2030 | 2035 | 2040 | Average annual change, 2010–2040 (%) |
| OECD | 242 | 244 | 255 | 263 | 269 | 276 | 285 | 0.5 |
| Americas | 120 | 121 | 126 | 130 | 133 | 137 | 144 | 0.6 |
| Europe | 82 | 82 | 85 | 89 | 91 | 93 | 95 | 0.6 |
| Asia | 40 | 41 | 43 | 44 | 45 | 46 | 46 | 0.5 |
| Non-OECD | 282 | 328 | 375 | 418 | 460 | 501 | 535 | 2.2 |
| Europe and Eurasia | 47 | 50 | 53 | 57 | 61 | 65 | 67 | 1.2 |
| Asia | 159 | 194 | 230 | 262 | 290 | 317 | 337 | 2.5 |
| Middle East | 28 | 33 | 37 | 39 | 43 | 46 | 49 | 1.9 |
| Africa | 19 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 27 | 31 | 35 | 2.1 |
| Central and South America | 29 | 31 | 33 | 35 | 39 | 42 | 47 | 1.6 |
| World | 524 | 572 | 630 | 680 | 729 | 777 | 820 | 1.5 |
Almost all of the world population uses energy at some point for their own needs and the greater amount of this energy is used in buildings for cooling, heating, and lighting. The building sector consumes a lot of energy which is responsible for more than 40% of global energy use [4] and 40–50% of the total delivered energy in the United Kingdom and the United States [5,6]. In 2010, the sector accounted for more than one-fifth of global energy consumption [2]. Ventilation, cooling, and heating in buildings can be responsible for as much as 70% of the total energy use in buildings [7]. This growth, along with unprecedented changes in the underlying living standards and economic conditions, will make developments within the building sector. Total world delivered energy demand for buildings shown in Figure 1.2 increases from 81 quadrillion Btu in 2010 to nearly 131 quadrillion Btu in 2040 at an average annual growth rate of 1.6%.
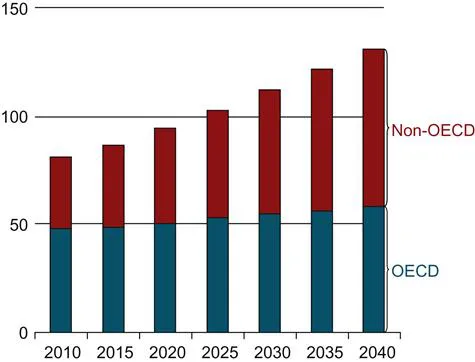
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- List of Contributors
- Preface
- Chapter 1. Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Earth Pipe Cooling with Horizontal Piping System
- Chapter 2. Thermal Efficiency Modeling in a Subtropical Data Center
- Chapter 3. Natural Convection Heat Transfer in the Partitioned Attic Space
- Chapter 4. Application of Nanofluid in Heat Exchangers for Energy Savings
- Chapter 5. Effects of Perforation Geometry on the Heat Transfer Performance of Extended Surfaces
- Chapter 6. Numerical Study of Flow Through a Reducer for Scale Growth Suppression
- Chapter 7. Parametric Analysis of Thermal Comfort and Energy Efficiency in Building in Subtropical Climate
- Chapter 8. Residential Building Wall Systems: Energy Efficiency and Carbon Footprint
- Chapter 9. Cement Kiln Process Modeling to Achieve Energy Efficiency by Utilizing Agricultural Biomass as Alternative Fuels
- Chapter 10. Modeling and Simulation of Heat and Mass Flow by ASPEN HYSYS for Petroleum Refining Process in Field Application
- Chapter 11. Modeling of Solid and Bio-Fuel Combustion Technologies
- Chapter 12. Ambient Temperature Rise Consequences for Power Generation in Australia
- Index
