
- 500 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Dielectric Polymer Materials for High-Density Energy Storage
About this book
Dielectric Polymer Materials for High-Density Energy Storage begins by introducing the fundamentals and basic theories on the dielectric behavior of material. It then discusses key issues on the design and preparation of dielectric polymer materials with strong energy storage properties, including their characterization, properties and manipulation. The latest methods, techniques and applications are explained in detail regarding this rapidly developing area. The book will support the work of academic researchers and graduate students, as well as engineers and materials scientists working in industrial research and development.In addition, it will be highly valuable to those directly involved in the fabrication of capacitors in industry, and to researchers across the areas of materials science, polymer science, materials chemistry, and nanomaterials.- Focuses on how to design and prepare dielectric polymer materials with strong energy storage properties- Includes new techniques for adjusting the properties of dielectric polymer materials- Presents a thorough review of the state-of-the-art in the field of dielectric polymer materials, providing valuable insights into potential avenues of development
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Introduction
Abstract
Keywords
Acknowledgment
1.1 Film Dielectric Capacitors

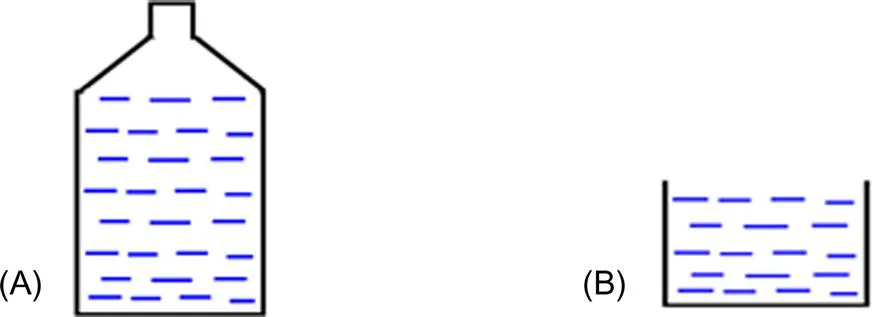
1.2 Key Science Issues
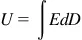
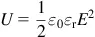
Table of contents
- Cover image
- Title page
- Table of Contents
- Copyright
- List of Contributors
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Fundamentals of Dielectric Theories
- 3. Preparation, Structure and Properties of Fluorine-containing Polymers
- 4. Manipulating Dielectric Properties by Modifying Molecular Structure of Polymers
- 5. High Energy Storage Dielectric Polymer Materials With Hierarchical Microstructures
- 6. Core-Shell Structural Fillers to High Energy Storage Dielectric Polymer Materials
- 7. Multiphase/Multicomponent Dielectric Polymer Materials With High Permittivity and High Breakdown Strength
- 8. Electrospinning Functional Fillers/Polymer Composites With High Energy Storage
- 9. Thermally Conductive Dielectric Polymer Materials for Energy Storage
- 10. Charging and Discharging Characteristics of Dielectric Polymer Materials
- 11. Dielectric Polymer Materials with High Thermal Stability
- 12. Processing of Polymeric Dielectrics for High Energy Density Capacitors
- 13. Future Perspectives
- Index