![]()
Chapter 1
BENJAMIN FRANKLIN
First, Know Thyself
OF ALL THE GIANTS IN THE PANTHEON of Founding Fathers, few continue to affect our lives as much as Benjamin Franklin. Many of his inventions are still in use, as are the famous sayings published in Poor Richard’s Almanac. What’s more, Franklin’s presence at key moments during the Revolution helped shape the institutions that govern our lives today. The man who snatched lightning from the sky with a key and a kite was a genuine renaissance man.
Born in Boston on January 17, 1706, Benjamin Franklin was the tenth of seventeen children born to Josiah and Abiah Franklin. His father, a soap and candle maker, taught him the value of industry and hard work, but dipping candles didn’t interest young Benjamin. His dreams were made of grander stuff.
At 12, Franklin was apprenticed to his brother’s print shop, where he learned the ways of publishing. Because his brother refused to publish Franklin’s writing, Franklin adopted the pseudonym “Mrs. Silence Dogood,” writing witty letters for the newspapers about the issues and people of the day. As he grew older, Franklin became ever more astute in his observations of how people behaved, thought, and lived.
After moving to Philadelphia, Franklin became a prominent citizen, publishing his own newspaper, The Pennsylvania Gazette. His most famous publication, however, was Poor Richard’s Almanac, which featured colorful sayings still quoted in contemporary conversations:
- 1.Little strokes fell great oaks. (1751)
- 2.After crosses and losses, men grow humbler and wiser. (1737)
- 3.Hunger never saw bad bread. (1733)
- 4.Three may keep a secret if two of them are dead. (1735)
- 5.Fish and visitors smell in three days. (1736)
- 6.God helps those who help themselves. (1736)
- 7.A good example is the best sermon. (1742)
Franklin’s achievements—from lightning rods to swim flippers to bifocals—astonished the 18th century world. To say that he was creative and innovative is an understatement. In addition to his accomplishments as an inventor, Franklin served as a printer and publisher, authoring many public letters that fueled the Revolutionary flame. He was a member of the Continental Congress, elected to the Committee of Five to draft the Declaration of Independence. He served as minister to France, Britain, and Sweden; as Postmaster General; as President of Pennsylvania (analogous to the modern position of Governor), and he negotiated the Treaty of Paris in 1783, ending the American Revolution. Franklin also organized the first volunteer fire department, charted and named the Atlantic Gulf Stream, founded the American Philosophical Society, obtained a charter for the first hospital in the United States, formed the first public lending library, and founded what is now the University of Pennsylvania.
Franklin accomplished more in one lifetime than most people can conceive of accomplishing in ten. Walter Isaacson called him “the most accomplished American of his age and the most influential in inventing the type of society America would become.” There’s no question that Franklin’s brilliance, determination, and perseverance enabled him to accomplish much in his 84 years. However, great accomplishments are typically not attained in a vacuum. It was his understanding of people, and his lifetime of relationship building, that allowed Franklin to achieve everything he did for the American people.
Historians often wonder how great historical figures would fare today. Few doubt that Franklin would be a renowned innovator and “thought leader,” no matter when he lived.
What Personal Identity Means For Leadership
Given all of the above, Franklin hardly seems the sort of man to experience an identity crisis. But that’s precisely what Franklin endured at a pivotal moment in his life and the life of the new nation. In fact, had it not been for this “dark night of the soul,” Franklin might not have cast his lot with the band of rebellious malcontents we now call the Founding Fathers.
Before we address Franklin’s defining moment—an event that compelled the celebrity inventor, newspaper mogul, and statesmen to risk his reputation, his fortune, and his life on a seemingly hopeless rebellion against the world’s greatest superpower, let’s examine the nature of personal identity and what it means for leadership.
What Is Personal Identity?
The basic answer to that question is that personal identity is the tales we tell ourselves to define (1) who we are and (2) our role in the world. We create identity by organizing our experiences (actually, the memories of our experiences) into one or more narratives. In turn, these narratives are condensed into role titles and/or role descriptions such as father and husband, president and CEO, team player, morally upright person, stamp collector, or fantasy-football enthusiast. These labels are the quick self-definitions we use to distinguish ourselves from others. They help us make sense of who we are and where we belong. They can also provide a sense of self-worth, mission, and purpose.
Obviously, leaders must know who they are to understand where they’re going, but the issue goes deeper than that. There are two types of identity that we all deal with: positional identity and personal identity.
“I’m the governor. I’m the mayor. I’m the boss. I’m the dad.”
Positional identity addresses activities and roles. It describes your position relative to others by pinpointing your roles, functions, and activities, as well as the organizations to which you belong and the causes you champion. “I’m a Baptist. I’m a weekend fisherman. I’m a community volunteer.” Positional identity describes what you do, not who you really are.
Personal identity is about deeper self-knowledge. It describes who you are vis-à-vis abstract ideas that include values, purposes, and missions. It’s often difficult to communicate your personal identity in a single word or pithy phrase.
Many people confuse positional and personal identity because they don’t have a firm grasp on who they are at the deepest levels. For this reason, most of us think in terms of positional identity if we think about the issue at all. “I’m an administrative assistant. I’m a golf caddy. I’m an animal rights advocate. That’s who I am.”
Positional identity describes what you do, and not who you really are.
Many organizations confuse positional identity and personal identity, if they even bother to address this issue (and many don’t). They think in terms of what they produce, not why they produce it. “We make milk products. We make computers. We disseminate our clients’ messages through public relations strategies and tactics.” These positional identities don’t define what the organizations really are and why they produce these particular products or services.
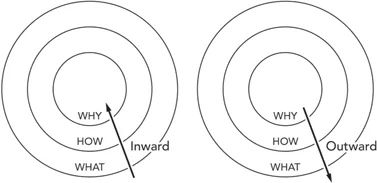
Not long ago, I watched a TED Talk featuring Simon Sinek, who spoke about the “Golden Circles.” At the center of three concentric circles he drew was the word why. Outside this inner circle was another circle featuring the word how, and the outermost circle was labeled what.
According to Sinek, most companies tackle the issue of identity from the outside inward.
They ask:
- 1.What are we going to do? (We’ll make computers.)
- 2.How are we going to make them? (We’ll make them this way.)
- 3.Why are we going to do this? (This question is rarely answered.)
What separates companies such as Apple (which recently surpassed Coke as the #1 brand worldwide) from businesses and organizations that work the “inward” process on the concentric circles is that Steve Jobs began his quest for organizational identity with the inner ring of the circles.
The first question Jobs sought to answer was the most important anyone can ask: why.
- 1.Why are we doing this? (We want to make life better for people.)
- 2.How are we going to do it? (We’ll make well-designed, easy-to-use computers.)
- 3.What are we making? (Mac, iPad, iPhone, etc.)
Too many leaders define their lives and purposes in the same way as the first organization: “This is what I do, and this is how I do it.” Why never enters the picture.
Creating a personal identity must begin with why. It must begin with understanding why you exist before moving to what to do next and how.
Leading others requires that you first understand yourself—that you first develop baseline self-awareness. Self-awareness allows you to honestly assess your strengths and weaknesses, and honestly assess those of the people and organizations you work with. There’s no such thing as effective leadership without people skills, and mastering people skills begins with self-awareness—understanding the identity of the person that is you.
Although Ben Franklin had a gift for self-awareness, he didn’t settle on a strong, fixed identity until surprisingly late in his life. Once he made that choice, however, he became—almost overnight—one of the most radical and influential champions of the American independence movement.
Franklin’s “Dark Night Of The Soul”
By the time of the Boston Tea Party in December 1774, Franklin had acquired a positional identity that would be the envy of every wannabe celebrity on American Idol, X Factor, or Keeping Up with the Kardashians. By today’s standards, Ben Franklin was bigger than the Beatles. As fate would have it, though, his personal identity was resting on quicksand.
It’s important to note that, hitherto, Franklin was thoroughly invested in the success of the British Empire. He identified as a British citizen first and an American second.
With the exception of George III, Franklin was the most famous man in the Empire—a household name across the Western Hemisphere. He was also a British official (though not formally). For almost eighteen years, he’d represented America’s interests to the British government as the London agent of Pennsylvania and Massachusetts—i.e., he was a lobbyist. Moreover, Franklin’s son William was then the Royal Governor of New Jersey.
Two decades earlier, Franklin had proposed the “Albany Plan,” which envisioned a central government for the thirteen colonies, headed by a crown-appointed president. As late as 1774, he sought to make America an equal political partner of Great Britain. If he had seen his dearest wish realized, a new symbol would have graced the Union Jack—one representing the thirteen united American colonies. His dream was a United Kingdom composed of England, Scotland, Ireland, and the American colonies. He didn’t envision or want a politically independent America. His hope was that America would grow, expand, and evolve within the British Empire.
As the agent for Massachusetts and Pennsylvania, and because of his fame and renowned intellect, Franklin’s advice on all things American was frequently sought in London’s highest circles. So when riots and boycotts broke out across the colonies in response to the Stamp Act (1765), it was to Franklin that London’s power elite turned for explanations and solutions. As crisis followed crisis from 1765 to 1775, the best and brightest in British government repeatedly turned to Franklin for advice and counsel. During these years, however, Franklin gradually lost touch with the worldviews and wishes of his New World brethren—a trend that eventually proved disastrous to his career in British politics. With his fingers off the pulse of colonial opinion, Franklin’s pronouncements proved wrong more often than right.
Matters finally came to a head after the Boston Tea Party in December 1773.
When this news arrived in London in January 1774, Franklin confronted the biggest crisis of his career. Having been called upon again and again to explain the actions of the colonists, as tensions and violence escalated, Franklin was running out of rational explanations for why Americans thought and behaved as they did. He was also running out of ways to explain the actions of the British government to his constituents back home. In short, Franklin found himself between a rock and a hard place.
His solution to this predicament was a clever one—far too clever for his own good.
He decided to leak a number of letters that had been passed to him by a third party whose identity remains unknown to this day. The letters, written by Governor Thomas Hutchinson of Massachusetts and Peter Oliver, Hutchinson’s lieutenant governor, essentially said that, because of the increasing violence in America, the liberties of the American people should be suppressed—at least temporarily. Franklin believed that if these letters were made public, Americans and the British government would blame the rising discontent on misguided officials such as Hutchinson, who were conspiring to deprive Americans of their rights as Englishmen.
Franklin guessed correctly that if the letters went public, there would be rioting in the colo...