
Innovative and Intelligent Technology-Based Services For Smart Environments - Smart Sensing and Artificial Intelligence
Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Smart Innovation, Ergonomics and Applied Human Factors (SEAHF'20), held online, 14-15 November 2020
- 264 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Innovative and Intelligent Technology-Based Services For Smart Environments - Smart Sensing and Artificial Intelligence
Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Smart Innovation, Ergonomics and Applied Human Factors (SEAHF'20), held online, 14-15 November 2020
About this book
This book contains a collection of high-quality papers describing the results of relevant investigations and cutting-edge technologies, aimed at improving key aspects of real life, including major challenges such as the development of smart cities, smart buildings, smart grids, and the reduction of the impact of human activities on the environment. Sustainability requires the use of green technologies and techniques and good practices. Artificial intelligence seems to be an appropriate approach to optimize the use of resources. The main focus of this book is the dissemination of novel and innovative technologies, techniques and applications of artificial intelligence, computing and information and communications technologies, and new digital services such as digital marketing, smart tourism, smart agriculture, green and renewable energy sources. Besides, this book focuses on nurturing energy trends including renewable energies, smart grids, human activity impact, communication, behaviour, and social development, and quality of life improvement fields based on the innovative use of sensors, big data and the Internet of things (IoT), telecommunications and machine learning.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Section I: Telecommunications and computing technologies
Compact and multiband CPW printed monopole antenna based on CLL elements for wireless applications
1 Introduction
2 Proposed Antennas Design
2.1 Basic structure: Monopole alone

2.2 Monopole with one CLL element

2.3 Monopole with two CLL elements

3 Simulation Results
3.1 Single-band antenna
3.1.1 Return loss
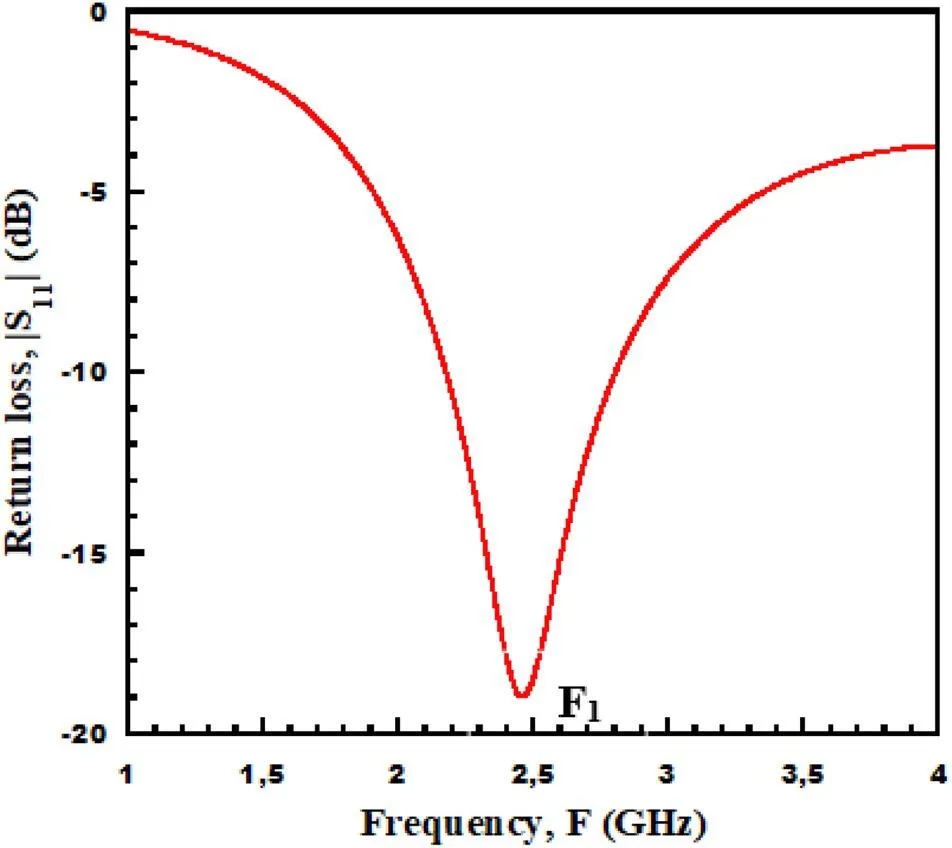
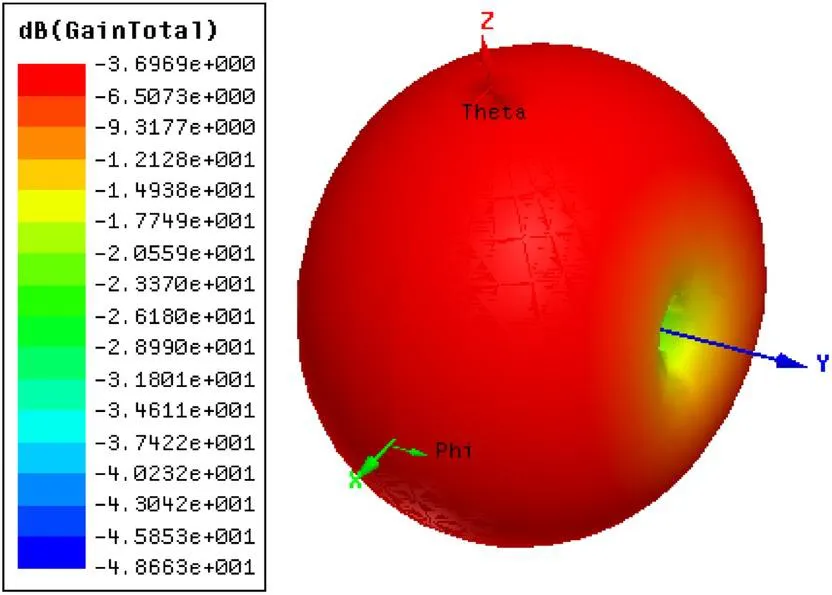
3.1.2 Radiation patterns
3.2 Dual-band antenna
3.2.1 Return loss
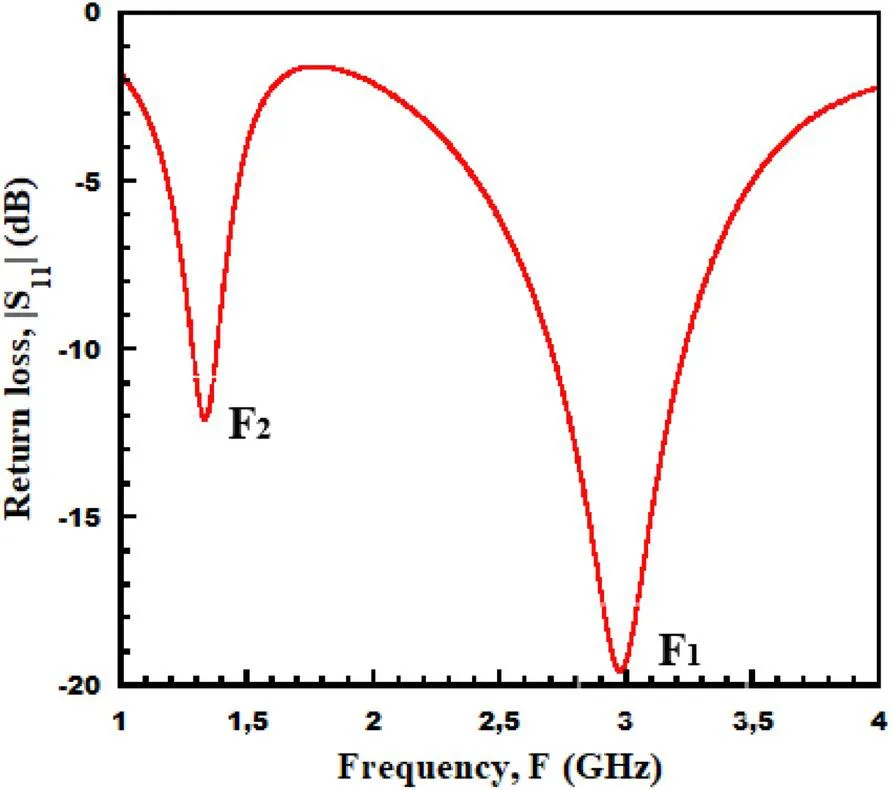
- The operating frequency F1 of the basic antenna is slightly shifted from 2.45 to 2.99GHz and remains unchanged. This shift of frequency can be explained by the coupling effect between the monopole and CLL element.
- The additional frequency F2 is shifted to a lower frequency.
3.2.2 Radiation patterns

Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- Section I: Telecommunications and computing technologies
- Section II: Smart sensing and artificial intelligence
- Section III: Green energy production and transfer systems
- Section IV: Digital marketing, smart tourism
- Author Index