![]()
Formulation of Strategy
After completing an internal and external analysis, organizations begin formulating their strategies. During this step they are answering questions such as:
a) Knowing what we now know, how do we want to move forward?
b) How can we best succeed in meeting our goals and objectives?
During this formulation phase, organizations develop strategies on various levels in the organization.
Strategy Levels
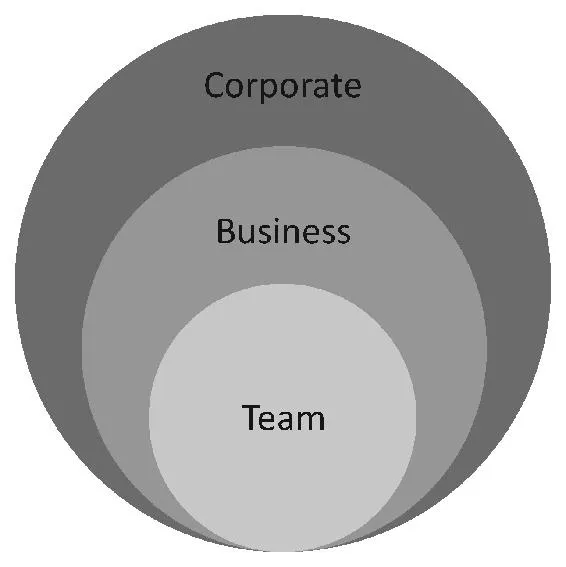
As mentioned earlier, the goal of developing strategies is to determine how an organization can plan to triumph in a time period in the future. This is done by focusing on three strategies; corporate, business and team. Each strategy becomes more focuses on a specific portion of the organization. The corporate strategy focuses on the entire organization, the business strategy is based on each SBU, and the team strategy is the most specific strategy, evaluating each individual group function within an SBU. In order to disseminate organizational strategies, we need to analyze the three levels of strategy shown below:
a) Business – the department’s strategic plan for helping to meet the corporate level strategy
b) Corporate – organizational level strategy setting the big picture for where the organization is going
c) Team – the individual team’s strategy for how it will add value to corporate and business strategies
The focus of any strategy is to gain a competitive edge and increase potential profitability. A good strategic plan is backed by the organization’s vision and mission statement. You can look at the strategic plan and understand, based on the vision and mission, why these actions make sense for this organization. Effective strategies detail how the organization’s resources, capabilities and competencies will be utilized. Decisions outlined as part of the strategy seek to decrease ambiguity in outcomes.
Business Level Strategy
Business level strategy focuses on the departmental or unit level within a particular product market. This strategy reflects the decisions that have been made regarding competing in discrete product markets. The business level strategy states who your consumers are, what their needs are, and how the unit will meet those needs. Defining these things can prove to be challenging considering increased participation in the global market.
Business level strategies have a direct relationship with the consumer. If you consider that the consumer is the life force behind your organization, it is in the organization’s best interest to meet those consumer needs in order to increase the organization’s returns. If you cannot keep the consumer satisfied, you cannot stay in business.
Managing Customer Relationships
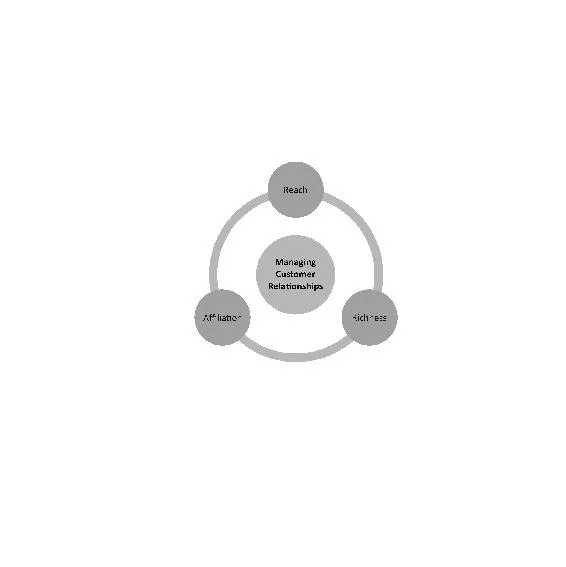
A common strategy of many successful organizations is to focus on innovative methods to please current consumers and, hopefully at the same time, satisfy new consumers. To achieve the goal of satisfying customers, organizations spend a good amount of time managing these relationships, so they have a better handle on current and future requirements. Customer relationships should be managed through three dimensional standpoints; Reach, Richness, and Affiliation.
Reach refers to the organization’s access and association with consumers. A great example of reach is with Amazon. Amazon gives consumers access to millions of different products and they reach the consumer through tens of millions of computers across the world. Although Amazon is not a brick and mortar store, its reach is more extensive than most other stores such as Barnes and Noble.
Richness is related to the bidirectional flow of information between the consumer and organization, specifically focusing on the complexity and detail of the flow. Improving the richness dimension helps organizations institute a competitive advantage which is the reason increasingly more organizations are utilizing the internet and online services to help better manage the flow of information. They are also using it to supply the consumer with a knowledge base about their products and solutions, so they can be better informed on how the organization can meet their needs. Use of these online methods has considerably reduced information interchange costs for consumers and organizations.
The final dimension, affiliation, refers to assisting productive exchanges with the consumer. An example of this would be Autotrader.com who offers an online service, as well as an app, which allows consumers to find information on cars and compare their features and cost. Consumers are given the flexibility to sort the information and filter the information to suit their needs. It even connects the consumer with suppliers in their area and assists with potential financing scenarios. This process creates a tremendous value for the consumer because they can go one place to get all the information they need instead of several different places and it is no cost to them.
Who Do We Need to Satisfy?
In order to have an effective business level strategy, we must understand who our target consumer is. Organizations use market segmentation to divide consumers into groups according to similarity in needs. This exercise is useful in several different situations. For example, the needs for catering services for individuals is different than the needs for catering services for companies. Groups can be formed off of just about any identifiable characteristic but there are ones that are commonly used by organizations in market segmentation.
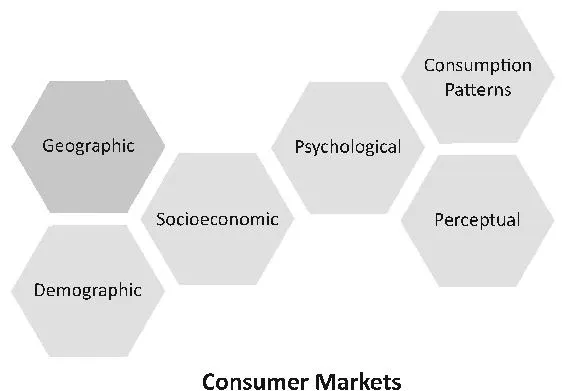
For consumer markets, there are several factors that are commonly used to segment the market. Demographic factors can be used to segment groups by age, income, sex, etc. It can also be used to divide consumers into generational groups with particular interests or desires. Socioeconomic factors can include the social class, stage in the life cycle of a family, etc. Geographic factors are cultural, regional, national differences, etc. Psychological factors can include lifestyle, personality traits, etc. Consumption patterns refer to consumers that utilize the product heavily, moderately, and lightly. Perceptual factors are things like benefit segmentation and perceptual mapping.
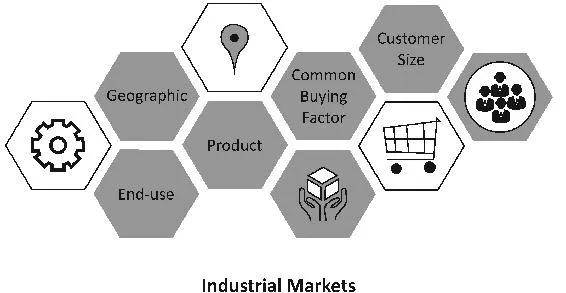
There are also several common segments used to divide an industrial market. End-use segments are segmented by Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) codes which classifies industry areas. These SIC codes help to reflect the end use of the product. Product segments are centered on technological differences or manufacturing economies. Geographic segments look at boundaries between countries or by regional discrepancies between them. Common buying factor segments consider groups of people who may think that the same buy factors are significant. Customer size segments divides things into groups by account size or geography.
What Consumer Needs Are We Satisfying?
After determining our target audience, we now look at what their specific needs are and how to satisfy these needs. Generally, customer needs are focused on benefits, features, or performance of the product. Organizations that are most effective are able to give consumers what they request, when they request it. The best way to understand the consumer’s needs are through frequent interactions. At a high level, consumers are looking for a product that adds value for them. In terms of defining value, consumers are either looking for low cost with adequate features or high quality with tolerable cost. Most organizations strive to get ahead of the consumer demands because failure to do this can result in a loss of consumers and ultimately lead to the loss of market shares.
How Will We Satisfy the Consumer’s Needs?
If you remember from earlier, core competencies give organizations a competitive advantage. Organizations utilize these core competencies to develop value adding strategies and meet consumer needs. Continuous improvement, innovation, and promotion of an organization’s core competencies is key to meet consumer needs and, hopefully, go above and beyond in the future.
Business Strategy Purpose
Business level strategy seeks to create dissimilarities between the organization and its competitors. Organizations want to set themselves apart from competitors and in order to do this, they must determine if they want to complete activities in a different way or complete dissimilar activities. Making this decision really determines the organization’s business level strategy which is a choice made by the organization about how they will utilize the organization’s value chain actions to establish a value that makes them stand out. Business level strategy, in essence, seeks to create a competitive advantage. Typical sources for creating this competitive advantage are:
a) Having lower costs than competitors
b) Performing actions differently
c) Delivering a product that costs less and is consider acceptable by the consumer
d) Obtaining the capability to make the organization’s product stand out so much that it commands a top price
e) Carrying out higher valued activities
Five Levels of Business Strategy
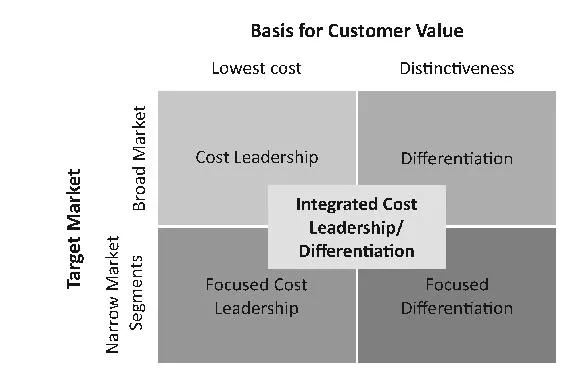
Common strategies used at the business level to set apart organizations from their competitors are cost leadership, differentiation, focused cost leadership, focused differentiation, and integrated cost leadership/differentiation. Each strategy develops a competitive advantage by varying its scope. Although the strategies are generally the same at any organization, the variance occurs with how each organization integrates their strategic actions. The graphic below illustrates the overall blueprint of where an organization’s business strategy may fall depending on the culture and condition of the organization. Most organizations are classified as cost leaders, differentiators, focused cost leaders, and focused differentiators. If the organization believes they identify in multiple areas, they become and integrated cost leader/differentiator.
Cost Leadership
In the cost leadership strategy, the goal is to have the price be the competing factor. The organization works on lowering their costs, so they shift that value to a wide customer base. In order for this strategy to be sustainable, you must have internal efficiencies that result in above average margins. Organizations using this strategy typically have top of the line facilities and low costs. Overhead and production costs are closely managed and controlled. This strategy works well for generic products or standardized products. Keeping a low cost is a continuous effort with this strategy so you can beat the competition. To obtain an edge over the competition, organizations must determine and control cost. They also should examine what reconfigurations can be done in the value chain to lower costs. Risks associated with this strategy are that technology could become obsolete, competitors able to imitate successfully, and tunnel vision on cost leadership resulting in loss of consumer perception of product differentiation. The graphic below further explains the relationship between cost leadership and Porter’s Five Forces.
Differentiation
This strategy focuses on delivering a product that is very unique, so unique that the price of the product is not an issue. In differentiation, high quality, speedy innovation, and superior customer service are characteristics. In this strategy, value is created by lowering the buyer’s costs for repairs, incr...