![]() Section 1. Introduction
Section 1. Introduction![]()
Chapter 1
Analytical Applications of Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles (Introduction)
Hamid Rashidi Nodeha and Binta Hadi Jume,b
a Food Technology and Agricultural Products Research Centre, Standard Research Institute Karaj 31745-139 Iran;
1.1 Introduction
Over the last decade, researchers in the applied sciences have shown great interest in the synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) and their application in environmental, food and biological approaches.1–3 Different types of these MNPs based on iron oxide II and III were prepared and investigated, such as magnetite, gamma iron oxide, platinum–iron oxide, nickel–iron oxide, titanium–magnetite, cobalt–magnetite, zinc–iron oxide, copper–iron oxide, manganese–magnetite, gold–magnetite, and magnetite–silica. Magnetic metal-oxide based nanoparticles possess high saturation magnetization properties and are a suitable material to use in drug/gene delivery or clinical use.4,5 Various methods have been used to synthesize MNPs including alkaline co-precipitation, microwave, hydrolysis, hydrothermal and flame spray methods.6 Recently, other methods have also been reported, including high thermal, sol–gel, oxidation, sonochemistry, and electrochemistry.4 Among the various types of magnetic nanoparticles, magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles are the most common because they have a relatively small particle size (< 100 nm), superior paramagnetic properties, appropriate surface area, good water dispersal, ease of functionalization, have greater permeability, less toxicity and are easy to synthesize via chemical co-precipitation.7–9 Magnetic nanoparticles were widely used in water treatment to extract or remove contaminates such as metal ions, pesticides, aromatic hydrocarbons, sulfonamides and phthalates in food and environmental water samples.10,11 Smart magnetic nanoparticles were also widely used as a sorbent in analytical sample preparation of biological samples and pharmaceutical analysis.11,12
However, pharmaceutical compounds, heavy metal ions, dyes and many other pollutants are hazardous for humans, animals and health,13,14 thus, development of rapid and sensitive techniques is important to analysis of hazardous species prior to discharge in the environmental cycle.13,14 Recently, MNPs and its derivatives are used as sorbents in sample preparation techniques to speed up the conventional techniques and overcome their drawbacks.15–17 Solid phase extraction (SPE) is the well-known sample preparation technique that is widely used in analytical chemistry toward various analytes and samples. Conventional SPE is a sensitive, simple, and flexible technique that has the ability to automate, but it suffers from the fact that it takes a long time for analysis (tedious and time consuming) and cartridges channeling/blocking. Hence, at the end of the 1990s, in order to overcome the limitation of liquid-based and solid-based extraction techniques, magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE) was introduced.18 In the MSPE technique, magnetic-based nanoparticles are used as sorbents and are dispersed into aqueous solution, followed by rapid collection using an external magnet.
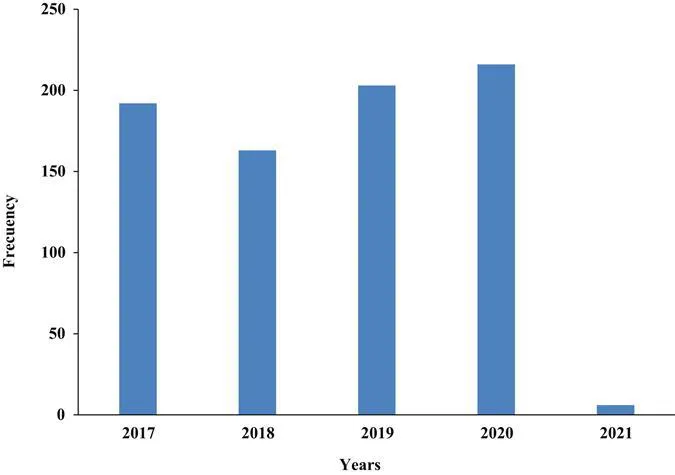
The utilization of magnetic nanoparticles in analytical applications has been gaining interest. Figure 1.1 illustrates the trend of the magnetic solid phase extraction, magnetic sample preparation, cleanup and determination in various sample matrices in the last 5 years. The trend has been increasing from 2018 to 2020.
Figure 1.1 Frequency of the use of magnetic materials for extraction and analytical determination of various analytes from various sample matrices from 2017–2021 as obtained from a Scopus search using the keywords “analytical application of the magnetic material” on 04 October 2020.
1.2 Sample Preparation Techniques
Sample preparation is a key factor in analytical chemistry since it directly affects the instrument's response, selectivity and analysis recoveries.19–21 Hence, quantitative analysis of analytes or pollutants in environmental water, drinking water, food, agricultural products, biological media of milk, urine, plasma and blood requires the removal of interferences to enhance the high extraction recovery with appropriate selectivity.22–26 Various sample preparation techniques are developed for food, dairy products, grocery, agricultural products, environmental samples and biological samples. The most common sample preparation techniques include liquid–liquid extraction (LLE), liquid–liquid microextraction (LLME), liquid–liquid microextraction (DLLME), QuEChERS (quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe), column chromatography extraction (CCE), solid phase extraction (SPE), solid phase microextraction (SPME), dispersive solid phase extraction (dSPE), stir bar sportive extraction (SBSE) and magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE). The proposed techniques owe their advantages and disadvantages e.g., LLE consumes a large volume of hazardous immiscible organic solvents, LLME/DLLME is not selective, QuEChERS is most effective for polar and mid-polar compounds and is highly suitable for food analysis.27 SPME and SBSE are solvent-less methods that enhance the enrichment of organic compounds from headspace and aqueous matrices, respectively. The SPME's fiber is relatively expensive and fragile.28 SPE is the most popular and standard technique that is widely used as an extraction and clean-up agent. The advantages of SPE techniques include high preconcentration factor, flexible, selective, easy to automate, regenerable and low organic solvent use.29,30 However, SPE is a tedious and time-consuming technique that also needs expensive cartridges, a vacuum manifold chamber, vacuum pump, back pressure and sorbent channeling.23,31 Hence, researchers are addressing these problems through the development of new dispersive SPE based on MNPs, that are known as magnetic solid phase extraction (MSPE). MSPE can enhance the extraction process by using an external magnet, which does not need filtration and centrifugation.
1.3 Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction (MSPE)
Magnetic separation technology (MST) was introduced first in 1909 to isolate iron from ore.32 Several decades later, magnetic separation was established as a powerful separation technique in bio-separation, environmental and material science. As discussed previously, the application of magnetic nanoparticles in extraction methodology can overcome the conventional SPE disadvantages.18 Incorporation of magnetic nanoparticles in sorbent can enhance the extraction process by using an external magnet without the need for a filtration and centrifugation process.33 Hence, using a magnetic-based material as the SPE sorbent provides advantages including low cost, easily extracted with an external magnet from liquid samples, quick, short extraction time, water dispersive, high adsorption capacity and sensitive to polar and nonpolar pesticides.23
Magnetic solid phase extraction procedures include several aspects;
- 1 Synthesis (preparation) of magnetic nanoparticles or magnetic-based materials.
- 2 Modifying or functionalizing magnetic nanoparticles with different materials in order to increase selectivity, increase adsorption capacity, increase stability and adapt to different environments.
- 3 Dispersing of the modified magnetic nanoparticles into the solution containing analytes.
- 4 Shaking or vortexing the solution in order to extract the analytes from the solution onto the solid phase adsorbent.
- 5 Collecting the magnetic sorbent from the solution by assistance of an external magnet.
- 6 Desorption of trapped analytes using a suitable solvent with stirring or ultrasound.
- 7 Separating or collecting the adsorbent again with a magnet for reuse.
- 8 Collecting solvent that contains analytes.
- 9 Instrument analysis in order to identify the analytes.
1.4 Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles
...