
- 480 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This textbook comprehensively presents different types of analog function circuits and outlines the function circuit types implemented with lowpass filters, peak detectors, and sample and hold circuits. The text analyzes the complete architecture of a function circuit, identifies the applications of op-amps for performing a function circuit, and explores new ways of deriving function circuits using a sawtooth wave generator and a triangular wave generator. It covers important topics including waveform generators, analog dividers, time division multipliers-cum-dividers (MCDs), peak responding MCDs, vector magnitude circuits, multifunction converters, and phase sensitive detector circuits. The textbook will serve as an ideal study material for senior undergraduate and graduate students in the fields of electrical, electronics, and communications engineering. The textbook is accompanied by teaching resources, including a solutions manual for instructors.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Part C Design of Function Circuits
11 Design of Analog Multipliers – Multiplexing
11.1 Triangular Wave–Based Time Division Multipliers
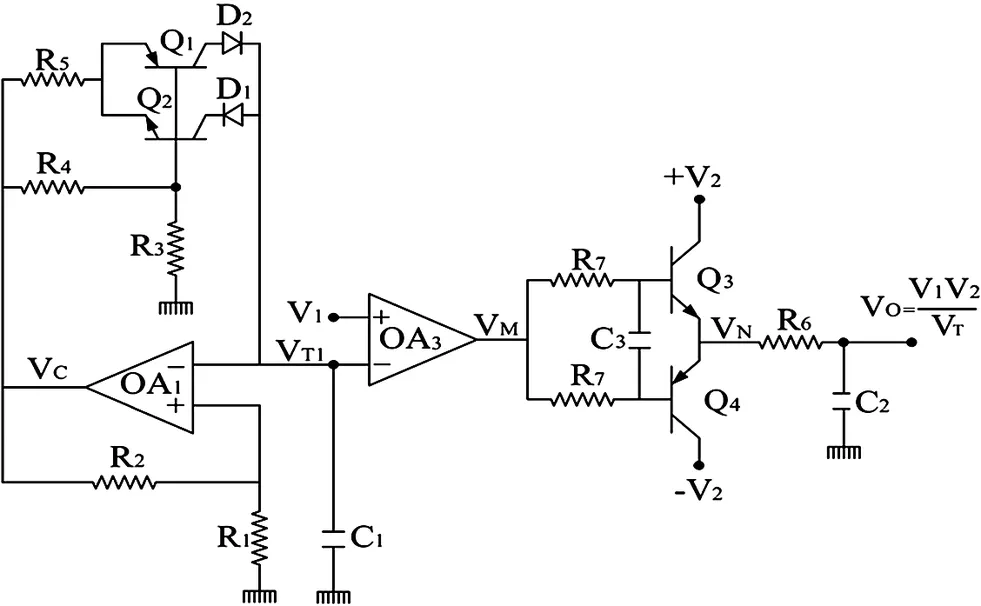

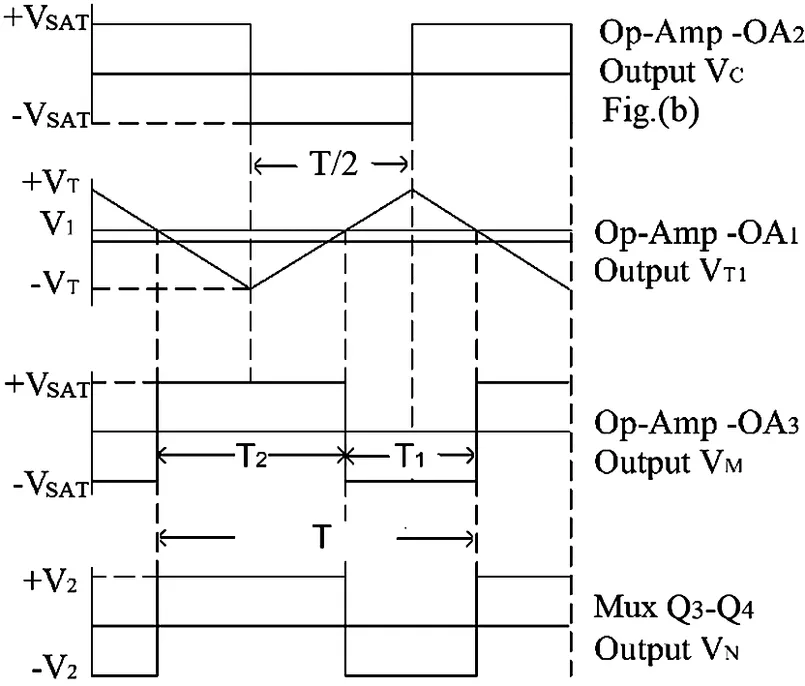
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Preface
- Useful Notations
- Abbreviations
- Introduction
- Part A Fundamentals of Function Circuits
- Part B Principles of Function Circuits
- Part C Design of Function Circuits
- Part D General on Function Circuits
- Part E Miscellaneous Function Circuits
- Part F Applications of Function Circuits
- Appendix A Analog Function Circuits Tutorial Kit
- Index