
Blockchain From Concept to Execution
With 10 Blockchains, 3 DLTs, 182 MCQs, 70 Diagrams & Many Sample Codes
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Blockchain From Concept to Execution
With 10 Blockchains, 3 DLTs, 182 MCQs, 70 Diagrams & Many Sample Codes
About this book
Encyclopedia on Blockchain for beginners and experts alike
Key Features
? Includes the basics of Blockchain
? Comparative study of public Blockchains (Ethereum, Hashgraph, Cardano, Algorand, Solana etc.)
? Comparison of interoperable Blockchains (Polkadot vs. Cosmos vs. Polygon).
? Comparison of private permissioned DLTs (Fabric vs. R3 Corda vs. Quorum).
? Comparison of R3 Corda opensource and Enterprise
? Comparison of Hyperledger Besu and GoQuorum
? Use Cases as Decentralized Identity, CBDC, NFT, Smart Cities etc.
Description
Today, the Blockchain comes with many variations, including shared ledger, distributed ledger, mutable ledger, etc. In addition to that, there are adjoining technologies as the layer-2 setup and low code environments for smart contracts. Knowing them all and matching the individual's requirements is a must for the future IT industry. "Blockchain From Concept to Execution" is thoughtfully designed to match the need of the students and experts alike. Phase I covers the most widely adopted Blockchains of today. The first chapter starts with the very basic concepts of Blockchain that everyone should learn. The remaining chapters of this phase discuss some of the most popular Blockchains of today. Phase II further looks over the popular public inter-operable Blockchains in the market. It also explores the competitive study between the different public Blockchains and inter-operable Blockchains. Phase III illustrates the private permissioned DLTs that are adopted by the organizations. The final chapter in this phase also comes with a comparative study to help the reader choose one over the other. Phase IV describes some of the most popular industry use cases as of today. Phase V gives a guideline on how an industry can fast-track the Blockchain adoption and some research area of tomorrow.
What you will learn
? Freshers can learn different Blockchains and DLTs through 20 Chapters with 182 MCQs, 70 diagrams and, sample codes.
? Experts can explore the comparative study of Blockchains and DLTs
? Browse most popular use cases of "Decentralized Identity", "Tokenization, DeFi, NFT and CBDC" and "Smart Cities".
Who this book is for
This book would be most suitable for business leaders, decision-makers, solution architects, business analysts, trainers, developers, and all Blockchain enthusiasts to understand the capabilities and application of different Blockchain and DLT frameworks and help them to choose the right one for their business needs.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Blockchain
2. Ethereum
3. Hedera Hashgraph
4. Tezos
5. Cardano
6. Algorand
7. Solana
8. Avalanche
9. Polygon
10. Polkadot
11. Cosmos
12. Comparison of Blockchains
13. Hyperledger Fabric
14. R3 Corda
15. Consensys Quorum
16. Comparison of Hyperledger Fabric, R3 Corda and Consensys Quorum
17. Decentralized Identity
18. Tokenization, DeFi, NFT and CBDC
19. Blockchain and 5G for IoT
20. Production and Beyond
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
CHAPTER 1
Introduction to Blockchain
1.1 The Blockchain Market
1.2 Evolution of Blockchain Technology and Hype
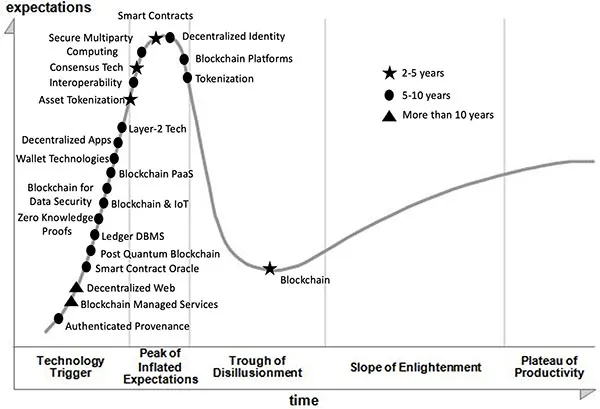
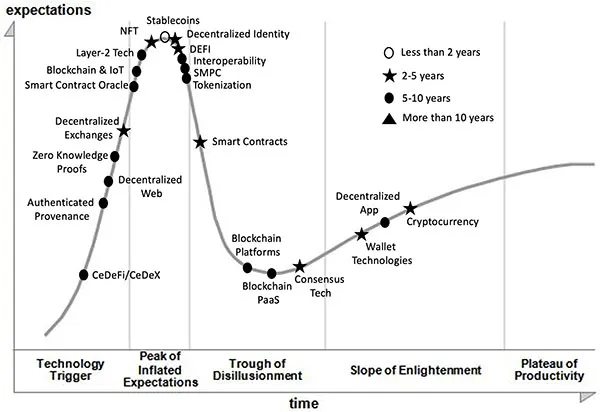
1.3 Birth of Bitcoin
1.4 Bitcoin vs. Previous Generation Electronic Money
- Possibility of mass hacking
- Single point of failure
- High transaction fees
- Immunity to Fraud
- No single point of failure
- Low transaction fees
- Universally acceptable
- Instantaneous Settlements
- Prevents Identity Theft
1.5 Key Concepts
1.5.1 Cryptography, Encryption, and Decryption
- Encryption or transforming the original data to a cryptic or uninterpretable format.
- Decryption or converting the encrypted data back to its original form.
- Symmetric cryptography
- Asymmetric cryptography
1.5.1.1 Symmetric Cryptography
1.5.1.2 Asymmetric Cryptography
- Public key, that can be visible to others
- Private key, that stays only with the owner
- Alice wishes to send a secret message to Bob. Alice would encrypt the transaction with Bob’s public key and only Bob can decrypt it using his own private key.
- Alice signs a document using her private key, also known as “Digital Signature”. The others who know Alice’s public key can validate that the document is actually signed by Alice.
1.5.1.2.1 RSA
1.5.1.2.2 DSA
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- About the Author
- Acknowledgements
- Preface
- Errata
- Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Blockchain
- PHASE I – PUBLIC BLOCKCHAINS
- PHASE II – INTEROPERABLE BLOCKCHAINS
- PHASE III – PRIVATE PERMISSIONED DLT
- PHASE IV – USE CASES
- PHASE V – Blockchain Adoption and Future
- Glossary
- Index