
Silver Nanoparticles
Synthesis, Functionalization and Applications
Parteek Prasher, Mousmee Sharma
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Silver Nanoparticles
Synthesis, Functionalization and Applications
Parteek Prasher, Mousmee Sharma
About This Book
Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Functionalization and Applications [Provided by Editors] The book "SILVER NANOPARTICLES: Synthesis, functionalization and Applications" presents a detailed investigation of the various methods of synthesizing AgNPs via chemical and green methods. The surface engineered silver nanoparticles present immense applications in the contemporary era starting from theranostics, biosensors, next generation antimicrobials, fabrication of solar cells, to the effective soil management leading to a sustainable agriculture. The widespread utility of AgNPs necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the operational strategies revolving around their surface modification and conjugation. This book epigrammatically discusses the candidature of engineered AgNPs as the material of future [Edited by Taimur] Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Functionalization and Applications presents detailed information about the range of methods of synthesizing silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). The book systematically delves into the subject with an introductory chapter before moving to chemical synthesis of AGnPs and fabrication methods which help in assigning functional properties for useful nanomaterials. Basic and advanced synthetic methods like surface functionalization and bioconjugation are covered. Additionally, the book informs about impactful applications of AGNPs across a range of industries. Through this book, readers will be able to understand the importance of silver nanoparticles as a futuristic material in scientific investigations and gain a comprehensive understanding of the operational strategies revolving around their surface modification and conjugation. Key Features: -Covers the basics of silver nanoparticle (AGNP) synthesis -Focuses on green methods of AGNPs - Covers information about surface modification and functionalization of AGNPs with different molecules (including biomolecules) -Covers a range of applications of AGNPs -Includes advanced applications of AGNPs in next-generation antibiotics Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Functionalization and Applications a handy reference for scholars in advanced chemical engineering, materials science and pharmacology programs as well as anyone who wants to know all about silver nanoparticles.
Frequently asked questions
Information
Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles
Parteek Prasher, Mousmee Sharma
Abstract
1. Chemical Synthesis
1.1. Green Synthesis
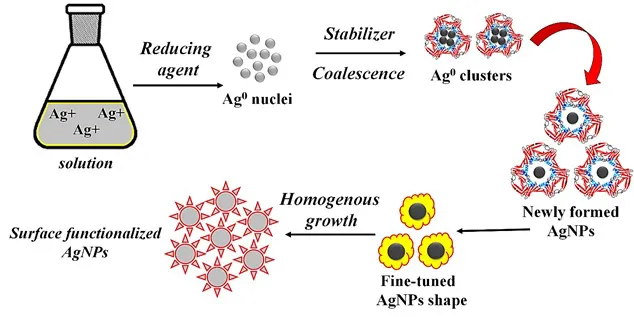
Sequence of steps for the synthesis of surface functionalized AgNPs.

Sources for the green synthesis of AgNPs.
| Bacteria | AgNPs Characteristics | Reducing Agent | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extracellular synthesis by Pseudomonas antarctica, Pseudomonas proteolytica, Pseudomonas meridiana, Arthrobacter kerguelensis and Arthrobacter gangotriensis and two mesophilic bacteria Bacillus indicus and Bacillus cecembensis | Spherical shape, average diameter in the range 6-13 nm | Cell free culture supernatant | [1] |
| Endophytic bacterium was isolated from the plant red fountain grass (Pennisetum setaceum) | Monodispersed spherical shape, average diameter in the range 83-176 nm | Bacterial wet biomass | [2] |
| Acidophilic actinobacterial SH11 strain isolated from pine forest soil | Polydispersed spherical shape, mean diameter 13.2 nm | Cell free culture supernatant | [3] |
| Endophytic Bacterium Pantoea ananatis | Spherical shape, average diameter in the range 8.06-91.32 nm | Cell free culture supernatant | [4] |
| Bacillus brevis (NCIM 2533) | Spherical shape, average diameter in the range 41-68 nm | Bacterial cell filtrate | [5] |
| Extracellular biosynthesis with Bacillus methylotrophicus DC3 strain | Spherical shape, average diameter in the range 10-30 nm | Bacterial dry biomass | [6] |
| Extracellular synthesis by Soil bacteria Cupriavidus sp | Spherical, crystalline shape, average diameter in the range 10-50 nm | Cell free supernatant | [7] |
| Bacterial exopolysacch... |