5G and Beyond
The Future of IoT
Parag Chatterjee, Robin Singh Bhadoria, Yadunath Pathak, Parag Chatterjee, Robin Singh Bhadoria, Yadunath Pathak
- 230 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
5G and Beyond
The Future of IoT
Parag Chatterjee, Robin Singh Bhadoria, Yadunath Pathak, Parag Chatterjee, Robin Singh Bhadoria, Yadunath Pathak
About This Book
The Internet of Things (IoT) has seen the eventual shift to the "Internet of Everything" in the recent years, unveiling its ubiquitous presence spanning from smart transports to smart healthcare, from smart education to smart shopping. With the 5G rollouts across the different countries of the world, it raises newer perspectives toward the integration of 5G in IoT. For IoT-based smart devices, 5G not only means speed, but also better stability, efficiency, and more secure connectivity. The reach of 5G in IoT is extending in multifarious areas like self-driving vehicles, smart grids for renewable energy, AI-enabled robots on factory floors, intelligent healthcare services... The endless list is the real future of 5G in IoT.
Features:
- Fundamental and applied perspectives to 5G integration in IoT
-
- Transdisciplinary vision with aspects of Artificial Intelligence, Industry 4.0, and hands-on practice tools
-
- Discussion of trending research issues in 5G and IoT
-
As 5G technologies catalyze a paradigm shift in the domain of IoT, this book serves as a reference for the researchers in the field of IoT and 5G, proffering the landscape to the trending aspects as well as the key topics of discussion in the years to come.
Frequently asked questions
Information
Part I Fundamental Architectural Concepts for 5G and IoT
1 The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on 5G-Enabled IoT Networks
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.1.1 Artificial Intelligence: State of the Art and Prospects
- 1.1.2 Important Subsets of AI
- 1.1.3 Background of AI
- 1.1.4 Current Research in 5G
- 1.2 Role of AI and 5G in Digital Transformation across Industries
- 1.3 Impact of Machine Learning for a 5G Future
- 1.3.1 Categorization of Machine Learning Models for 5G Deployment
- 1.4 Potential and Limitations of AI and Machine Learning for 5G
- 1.4.1 Potential of AI
- 1.4.2 Limitations of Using AI and ML
- 1.5 Requirements and Key Enabling Technology in 5G IoT
- 1.6 Artificial Intelligence Driven Cases for Real-Time Business and 5G IoT
- 1.6.1 COVID-19, Digital Healthcare and the Role of 5G
- 1.6.2 Real-World Business Use Cases for AI
- 1.7 Conclusions
- References
1.1 Introduction
1.1.1 Artificial Intelligence: State of the Art and Prospects
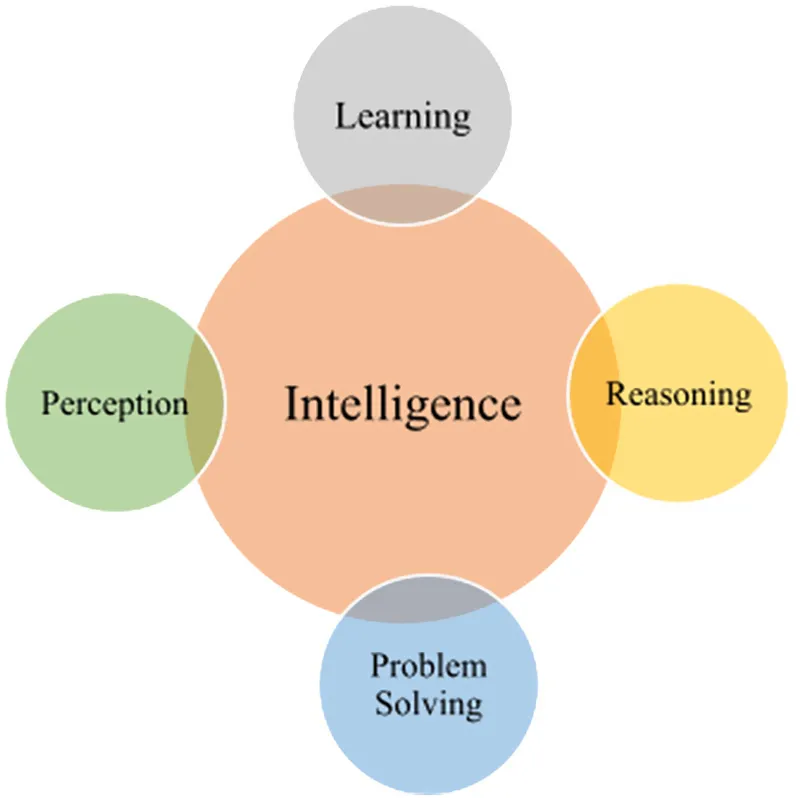
- To correlate perception and action smartly with huge knowledge of the world
- To know how to solve a real-world problem accurately and using cognitive functions
- To apply high-level logic to solution finding,
- To solve knowledge-based tasks and learn from mistakes
- To mimic human intelligence.
- Perception: The process of inferencing, acquiring, selecting, and organizing valuable information from unprocessed input. Humans use their experience, sense organs and the environment for perception. Intelligent machines undertake perception in a logical manner [3].
- Learning: The process by which new understanding can be acquired from different sources, such as books, life experience, teaching by experts, knowledge and skills gained through study. Learning increases a persons knowledge in new fields and areas.
- Reasoning: The act of thinking in a logical way to predict something, to judge or make decisions on real-world cases [1].
- Problem solving: The method of discovering a problem, analyzing it, then finding the best solution in the minimum time using generic or ad hoc methods [20].
1.1.2 Important Subsets of AI