
- 300 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Mastering AWS Lambda
About this book
Build cost-effective and highly scalable Serverless applications using AWS Lambda.About This Book• Leverage AWS Lambda to significantly lower your infrastructure costs and deploy out massively scalable, event-driven systems and applications• Learn how to design and build Lambda functions using real-world examples and implementation scenarios• Explore the Serverless ecosystem with a variety of toolsets and AWS services including DynamoDB, API Gateway, and much more!Who This Book Is ForIf you are a Cloud administrator and/or developer who wishes to explore, learn, and leverage AWS Lambda to design, build, and deploy Serverless applications in the cloud, then this is the book for you! The book assumes you have some prior knowledge and hands-on experience with AWS core services such as EC2, IAM, S3, along with the knowledge to work with any popular programming language such as Node.Js, Java, C#, and so on.What You Will Learn• Understand the hype, significance, and business benefits of Serverless computing and applications• Plunge into the Serverless world of AWS Lambda and master its core components and how it works• Find out how to effectively and efficiently design, develop, and test Lambda functions using Node.js, along with some keen coding insights and best practices• Explore best practices to effectively monitor and troubleshoot Serverless applications using AWS CloudWatch and other third-party services in the form of Datadog and Loggly• Quickly design and develop Serverless applications by leveraging AWS Lambda, DynamoDB, and API Gateway using the Serverless Application Framework (SAF) and other AWS services such as Step Functions• Explore a rich variety of real-world Serverless use cases with Lambda and see how you can apply it to your environmentsIn DetailAWS is recognized as one of the biggest market leaders for cloud computing and why not? It has evolved a lot since the time it started out by providing just basic services such as EC2 and S3 and today; they go all the way from IoT to Machine Learning, Image recognition, Chatbot Frameworks, and much more! One of those recent services that is also gaining a lot of traction is AWS Lambda! Although seemingly simple and easy to use, Lambda is a highly effective and scalable compute service that provides developers with a powerful platform to design and develop Serverless event-driven systems and applications.The book begins with a high-level introduction into the world of Serverless computing and its advantages and use cases, followed by a deep dive into AWS Lambda! You'll learn what services AWS Lambda provides to developers; how to design, write, and test Lambda functions; as well as monitor and troubleshoot them. The book is designed and accompanied with a vast variety of real-world examples, use cases, and code samples that will enable you to get started on your Serverless applications quickly.By the end of the book, you will have gained all the skills required to work with AWS Lambda services!Style and approachThis step-by-step guide will help you build Serverless applications and run Serverless workloads using the AWS Lambda service. You'll be able to get started with it in a matter of minutes with easy-to-follow code snippets and examples.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Event-Driven Model
- What event-driven model is all about
- Understanding the event-driven model of Lambda along with a few simple event-driven architectures for better understanding
- Getting started with simple event-driven use cases of Lambda that range from basic data manipulations to automated infrastructure management and so on
Introducing event-driven architectures

Understanding events and AWS Lambda
- AWS services: Lambda supports a few of AWS's services as preconfigured event sources that you can use to develop easy event-driven systems with. Few of the services namely S3, SNS, SES, Cognito, CloudFromation, CloudWatch fall under a branch relatively termed as regular AWS services; whereas DynamoDB and Kinesis fall under something called as stream based services as in both these cases, Lambda polls the streams for any updates and when it does find one, it triggers the corresponding function to run. In this chapter, we will be looking at few of the commonly used AWS services used as event mappings and how you can leverage them to perform simple tasks for your cloud environment.
- Custom applications: Custom applications are your own home grown applications or external world entities that can generate their own events. This can be anything from a simple web based application or even mobile device.
Lambda architecture patterns
- Serverless microservices: Microservices are designed and developed to be independent and self-sufficient, which is exactly why they are an amazing candidate for running with the help of Lambda. A Lambda function too, in its own is an independent code that can execute for a finite time when triggered by an external source. The only downside here is that, because of the deep granularity, the sheer number of microservices and the corresponding Lambda functions that you will end up with will be really high. Managing that many functions can be a challenge especially when you need to do changes, new deployments and so on.
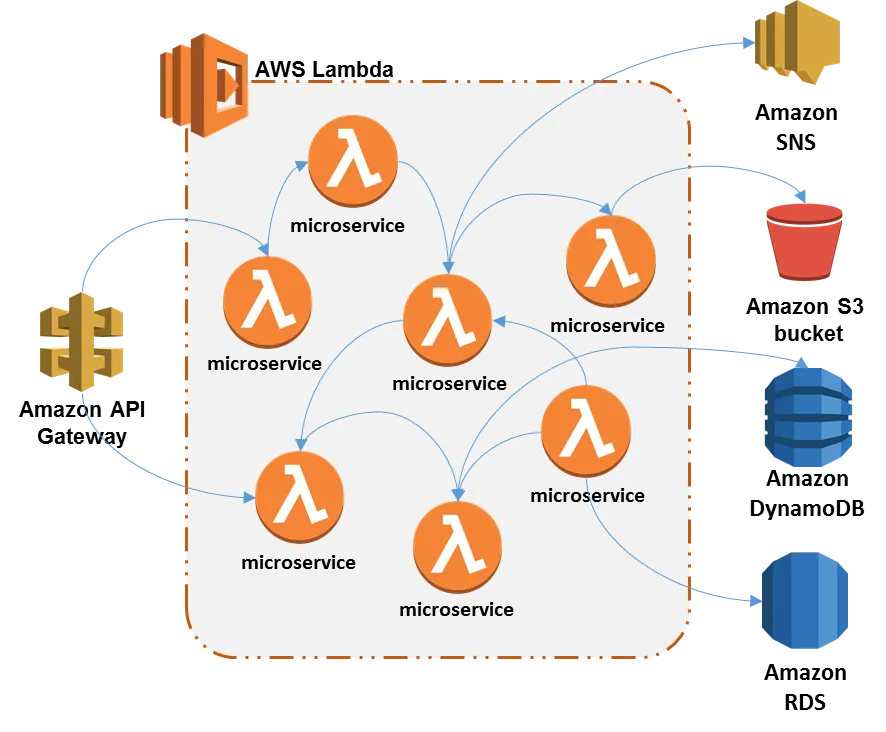
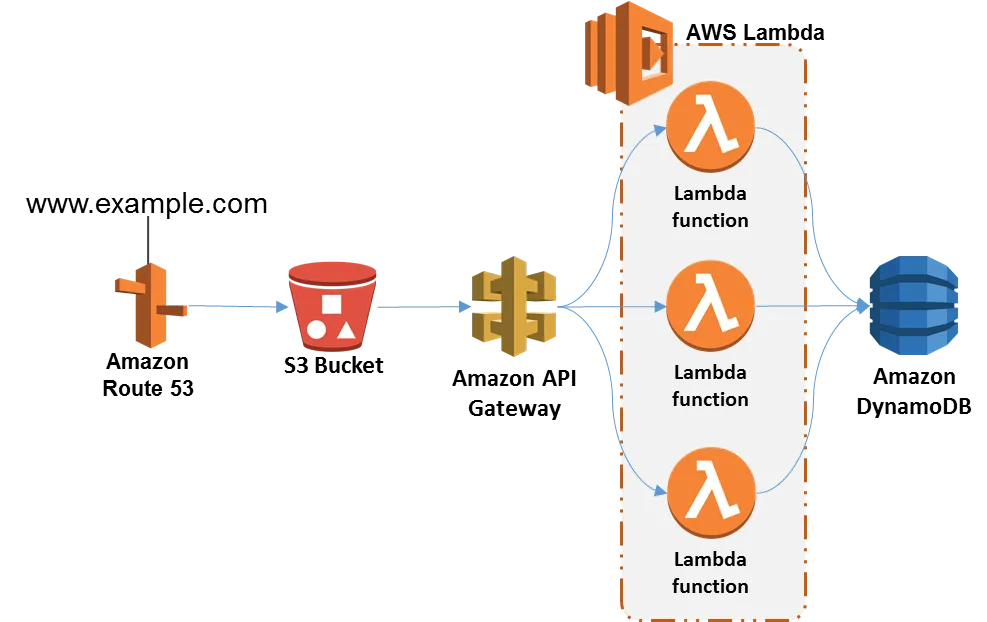
- Serverless multi-tier applications: Perhaps one of the most commonly used architecture patterns, Lambda is an ideal platform to host the business logic of your applications. With the presentation logic handled in S3 in the form of static website hosting, and the backend taken care of by a variety of database services ranging from DynamoDB, RDS to ElastiCache; Lambda is the perfect service to run the logic of your applications as shown in the image below:
- Real-time stream processing: When we talk about streams and AWS, only one word comes to our mind and that is Kinesis. AWS Kinesis is a powerful and scalable solution that enables you to design and develop applications that can process as well as analyze large quantities of streaming data. Mix that with Lambda and you have yourselves a variety of use cases where this design becomes applicable such as transactions processing, log analysis, social media analytics, and much more!

- Backend services for mobile or IoT: AWS Lambda can also be used to develop and support complete backend services for your IoT as well as mobile applications. You can use this pattern in conjunction with AWS API Gateway to ...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Credits
- About the Authors
- About the Reviewer
- www.PacktPub.com
- Customer Feedback
- Preface
- Introducing AWS Lambda
- Writing Lambda Functions
- Testing Lambda Functions
- Event-Driven Model
- Extending AWS Lambda with External Services
- Build and Deploy Serverless Applications with AWS Lambda
- Monitoring and Troubleshooting AWS Lambda
- Introducing the Serverless Application Framework
- AWS Lambda - Use Cases
- Next Steps with AWS Lambda