
- 185 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Getting Started with Terraform - Second Edition
About this book
Build, Manage and Improve your infrastructure effortlessly.About This Book• An up-to-date and comprehensive resource on Terraform that lets you quickly and efficiently launch your infrastructure• Learn how to implement your infrastructure as code and make secure, effective changes to your infrastructure• Learn to build multi-cloud fault-tolerant systems and simplify the management and orchestration of even the largest scale and most complex cloud infrastructuresWho This Book Is ForThis book is for developers and operators who already have some exposure to working with infrastructure but want to improve their workflow and introduce infrastructure as a code practice. Knowledge of essential Amazon Web Services components (EC2, VPC, IAM) would help contextualize the examples provided. Basic understanding of Jenkins and Shell scripts will be helpful for the chapters on the production usage of Terraform.What You Will Learn• Understand what Infrastructure as Code (IaC) means and why it matters• Install, configure, and deploy Terraform• Take full control of your infrastructure in the form of code• Manage complete infrastructure, starting with a single server and scaling beyond any limits• Discover a great set of production-ready practices to manage infrastructure• Set up CI/CD pipelines to test and deliver Terraform stacks• Construct templates to simplify more complex provisioning tasksIn DetailTerraform is a tool used to efficiently build, configure, and improve the production infrastructure. It can manage the existing infrastructure as well as create custom in-house solutions.This book shows you when and how to implement infrastructure as a code practices with Terraform. It covers everything necessary to set up the complete management of infrastructure with Terraform, starting with the basics of using providers and resources. It is a comprehensive guide that begins with very small infrastructure templates and takes you all the way to managing complex systems, all using concrete examples that evolve over the course of the book. The book ends with the complete workflow of managing a production infrastructure as code—this is achieved with the help of version control and continuous integration. The readers will also learn how to combine multiple providers in a single template and manage different code bases with many complex modules. It focuses on how to set up continuous integration for the infrastructure code.The readers will be able to use Terraform to build, change, and combine infrastructure safely and efficiently.Style and approachThis book will help and guide you to implement Terraform in your infrastructure. The readers will start by working on very small infrastructure templates and then slowly move on to manage complex systems, all by using concrete examples that will evolve during the course of the book.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Collaborative Infrastructure
Version control with Git 101
- You have access to all versions of all files in the Git repository at any time; it's almost impossible to lose any part of a piece of code or a previous state of the code.
- Multiple developers can work on one project at the same time without interfering with each other's code and without fear of losing any changes made by colleagues. In Git, the possibilities of collaborative work are unlimited.
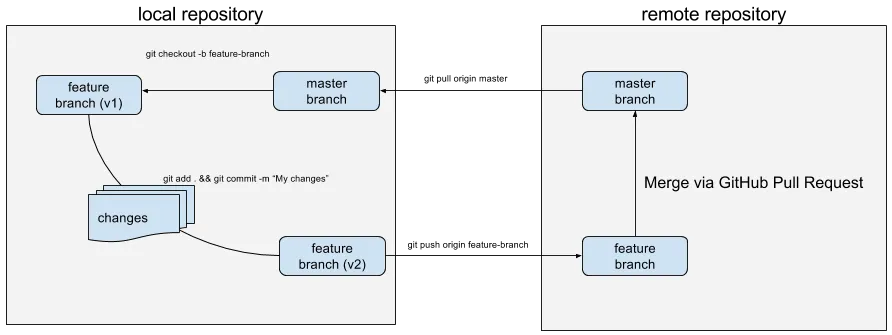
- The developer creates a new branch from a master branch.
- Commits changes to a new feature branch.
- Pushes this branch to the remote repository.
- After code review, this branch is merged into the master branch in the remote repository.
- Finally, changes to the master branch are pulled to the local repository's master branch, and the cycle starts again.
Moving templates to Git
$> git status On branch master Initial commit Untracked files: (use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed) .terraform/ base.json development.tfvars custom_data_source.rb graph.png id_rsa.pub modules/ playbook.yml rolling_update.rb specs/ template.tf terraform.tfstate terraform.tfstate.backup variables.tf nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
.terraform/
- .gitignore
- base.json
- development.tfvars
- id_rsa.pub
- modules/
- template.tf
- terraform.tfstate
- terraform.tfstate.backup
- variables.tf
$> git add . $> git commit -m "Initial commit"
$> git remote add origin [email protected]:Fodoj/packt-terraform-book.git $> git push origin master
Protecting secrets in a Git repository
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Credits
- About the Author
- About the Reviewer
- www.PacktPub.com
- Customer Feedback
- Preface
- Infrastructure Automation
- Deploying First Server
- Resource Dependencies and Modules
- Storing and Supplying Configuration
- Connecting with Other Tools
- Scaling and Updating Infrastructure
- Collaborative Infrastructure
- Future of Terraform
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app