
SAS for Finance
Forecasting and data analysis techniques with real-world examples to build powerful financial models
- 306 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
SAS for Finance
Forecasting and data analysis techniques with real-world examples to build powerful financial models
About this book
Leverage the analytical power of SAS to perform financial analysis efficiently
Key Features
- Leverage the power of SAS to analyze financial data with ease
- Find hidden patterns in your data, predict future trends, and optimize risk management
- Learn why leading banks and financial institutions rely on SAS for financial analysis
Book Description
SAS is a groundbreaking tool for advanced predictive and statistical analytics used by top banks and financial corporations to establish insights from their financial data.
SAS for Finance offers you the opportunity to leverage the power of SAS analytics in redefining your data. Packed with real-world examples from leading financial institutions, the author discusses statistical models using time series data to resolve business issues.
This book shows you how to exploit the capabilities of this high-powered package to create clean, accurate financial models. You can easily assess the pros and cons of models to suit your unique business needs.
By the end of this book, you will be able to leverage the true power of SAS to design and develop accurate analytical models to gain deeper insights into your financial data.
What you will learn
- Understand time series data and its relevance in the financial industry
- Build a time series forecasting model in SAS using advanced modeling theories
- Develop models in SAS and infer using regression and Markov chains
- Forecast inflation by building an econometric model in SAS for your financial planning
- Manage customer loyalty by creating a survival model in SAS using various groupings
- Understand similarity analysis and clustering in SAS using time series data
Who this book is for
Financial data analysts and data scientists who want to use SAS to process and analyze financial data and find hidden patterns and trends from it will find this book useful. Prior exposure to SAS will be helpful but is not mandatory. Some basic understanding of the financial concepts is required.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Budget and Demand Forecasting
- Understanding the Markov model and exploring its use
- Forecasting using a Markov model
- Comparing Markov model forecasts with ARIMA generated forecasts
- Showcasing the use of the Markov model Monte Carlo method for data imputation
The need for the Markov model
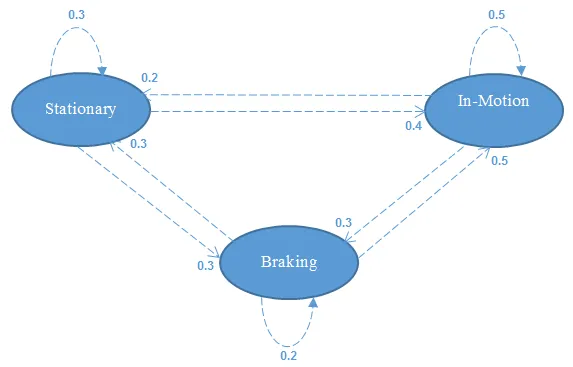
| Original state | Transitioned state |
| Stationary | Stationary |
| Stationary | In motion |
| Stationary | Braking |
| In motion | In motion |
| In motion | Stationary |
| In motion | Braking |
| Braking | Braking |
| Braking | Stationary |
| Braking | In motion |
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- Packt Upsell
- Contributors
- Preface
- Time Series Modeling in the Financial Industry
- Forecasting Stock Prices and Portfolio Decisions using Time Series
- Credit Risk Management
- Budget and Demand Forecasting
- Inflation Forecasting for Financial Planning
- Managing Customer Loyalty Using Time Series Data
- Transforming Time Series – Market Basket and Clustering
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app