
eBook - ePub
Ionic Liquids
Synthesis, Properties, Technologies and Applications
- 175 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Ionic Liquids
Synthesis, Properties, Technologies and Applications
About this book
The current book brings together the latest developments in the area of ionic liquids, including synthesis, purity control, toxicity, and scaling-up technologies. In addition, the authors explore the applications of ionic liquids in organic synthesis and catalysis, separation techniques and nanomaterials engineering. Written by key experts in the field, this book is an invaluable material for organic and green chemists in academia and industry.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
J.J. Parajó, M. Villanueva and J. Salgado
1 Thermal stability of ionic liquids
J.J. Parajó, M. Villanueva and J. Salgado Departamento de Física Aplicada, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Spain
Abstract: Thermal stability of 50 ionic liquids (ILs) has been analyzed using a Perkin Elmer thermogravimetric device. Several families with fixed anions and different cations and vice versa were chosen to provide a comprehensive knowledge of thermal properties of ILs against structure. For all the selected ILs, dynamic scans were performed under air atmosphere and a heating rate of 10 K · min−1 to estimate the short-term thermal stability. Isothermal studies were also carried out for some of the above compounds, at temperatures lower than onset temperature (Tonset), in order to evaluate the long-term thermal stability.
One of the most used parameters to characterise the long-term thermal stability of an IL is Maximum Operation Temperature (MOT). Because the estimation of this parameter involves the calculation of the activation energy of the degradation process, the kinetics of some of the ILs was analyzed by using different dynamic kinetic methods (Kissinger, Kissinger–Akahira–Sunose (KAS), Flynn–Wall–Ozawa (FWO) and Friedman), and the obtained energy values were compared to those obtained through isothermal methods. There was relatively good concordance in the values of MOT using different criteria.
Keywords: thermogravimetry, onset temperature, long-thermal stability, maximum operation temperature, activation energy
1.1 Introduction
Ionic liquids (ILs) have been considered “designer-solvents” [1] and proposed for medical, industrial, cosmetic and food applications [2] due to their intrinsic properties. These include nonvolatility, nonflammability, high thermal stability, high polarity, large electrochemical window and high thermal conductivity, among others.
The thermal stability of a compound, which should be determined from the maximum temperature of operation, can change depending on the use and conditions that this compound is submitted to. For example, a system with low oxidation stability and relative evaporation capacity, which was firstly classified as slightly stable, might be used without problems in application under an inert atmosphere and in a closed system. Due to these dependences and possibilities, the definition of thermal stability and maximum operation temperature for ILs is nowadays an open question [3, 4].
Additionally, thermal stability of ILs is currently being evaluated using thermogravimetric (TG) analysis at a single linear heating rate in controlled atmosphere. The onset and peak decomposition temperatures obtained from these experiments often overestimate the long-term thermal stabilities of ILs due to the scanning nature of this test, and isothermal studies [5, 6] at temperatures significantly lower than those exhibit appreciable decomposition [7, 8].
Thus, in order to establish a more realistic thermal degradation temperature, some parameters have been defined in the literature; for instance the temperature T0.01/10h, (temperature at which the decomposition of ILs reaches 1% in 10 h) [4, 9, 10].
This work summarizes the main analysis and conclusions with regard to the thermal stability of ILs obtained from previous works by our group. The comparison presented here is especially important since all the results are obtained in similar experimental conditions, using the same technique and apparatus, providing a large database of thermal stability results for ILs.
1.2 Materials and methodology
The selected ILs have different origin; some were kindly provided by Merck KGaA, others were purchased from different companies as Sigma Aldrich and Iolitec and some of them were synthetized by co-workers; the specified fraction purity was higher than 0.95 in all the cases. The 50 ILs analyzed in this work are listed in Table 1.1, and the cations and anions moieties structures of these ILs are shown in Figure 1.1.

Table 1.1: Selected ILs, short name, CAS number, mass fraction purity and provenance.
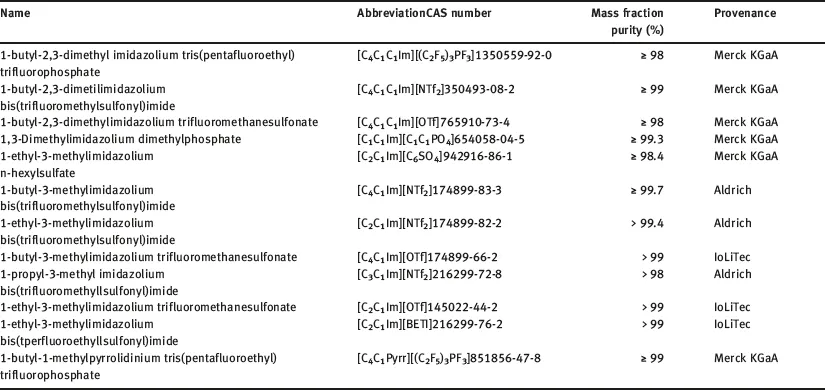
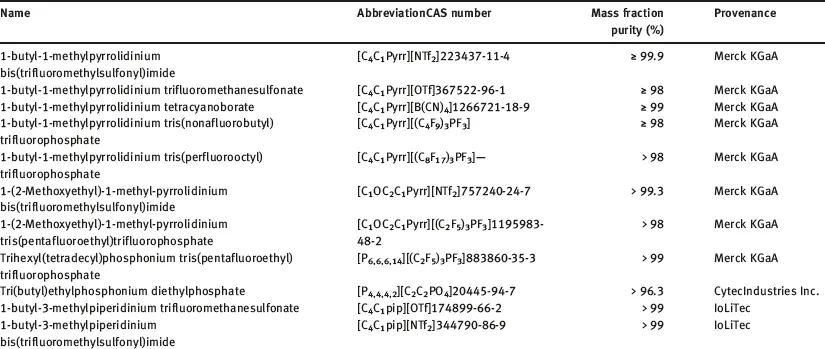

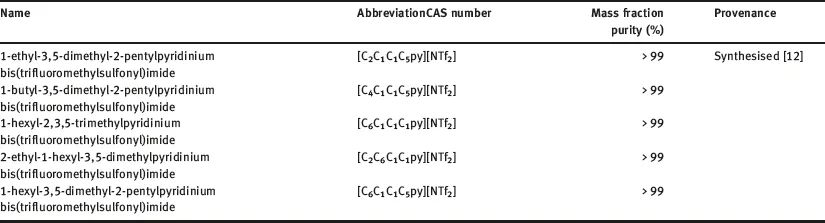
ILs were used, in the main part of this work, without further purification, because, in many potential industrial applications, contact with air does not allow to avoid the residual water content, which is the main impurity. Nevertheless, and taking into account that the influence of water content on thermal stability has not been deeply studied, thermal stability of some ILs purified and saturated of water has also been analyzed.
Thermogravimetry is the most commonly used technique to analyze the thermal stability of fluids operating in dynamic and isothermal modes. Dynamic experiments were performed at temperatures from 373 to 1,073 K with a heating rate of 10 K · min−1 and a purge gas flow of 20 cm3 · min−1. From the experimental curve, TG, and the corresponding derivative, DTG, onset and endset temperatures were determined as it is shown in Figure 1.2. Additionally, temperature at which the 1%, 2%, 5% and 10% of mass loss appears T1%, T2%, T5% and T10%, respectively, the remaining ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- Preface
- List of contributors
- 1 Thermal stability of ionic liquids
- 2 Liquid–liquid equilibria in systems of ionic liquids: A guide to experiments and data analysis
- 3 Aqueous biphasic systems formed by cholinium-based ionic liquids and mixtures of polymers
- 4 Multigranular modeling of ionic liquids
- 5 Ionic liquids at electrified interfaces for advanced energy/charge storage applications
- 6 Static and dynamical properties of colloidal silver nanoparticles in [EMim][PF6] ionic liquid
- 7 Industrialisation of surface treatment with electrodeposition processes from deep eutectic solvents
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Ionic Liquids by Rasmus Fehrmann, Catherine Santini, Rasmus Fehrmann,Catherine Santini in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Physical Sciences & Environmental Science. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.