
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
OLED Display Fundamentals and Applications
About this book
This new edition specifically addresses the most recent and relevant developments in the design and manufacture of OLED displays
- Provides knowledge of OLED fundamentals and related technologies for applications such as displays and solid state lighting along with processing and manufacturing technologies
- Serves as a reference for people engaged in OLED research, manufacturing, applications and marketing
- Includes coverage of white + color filter technology, which has become industry standard technology for large televisions
Information
Edition
2Chapter 1
Introduction
The basic structure of organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) was reported by Tang and Van Slyke at Eastman Kodak in 1987 [1]. This was a groundbreaking study and was later referred to as the “first OLED paper.” Now, almost 30 years later, there is a large market for OLED devices. The first OLED product was developed by Pioneer for car audio. Then the first mass production of AMOLED by SK display (a joint manufacturing venture by Eastman Kodak and Sanyo Electric) for Kodak's LS633 digital camera (Figure 1.1) accelerated the use of OLED for display applications.
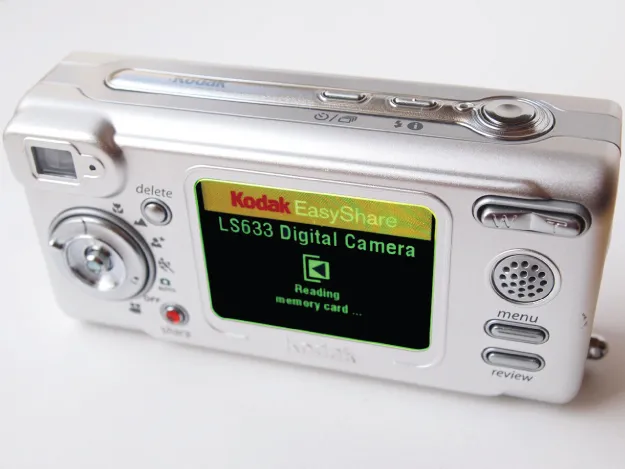

Figure 1.1 The first active-matrix OLED display product on the market
(Kodak LS633 digital camera).
This was followed by the widescale development of many other OLED-based products, including cellular phones (Figure 1.2), smart watches (Figure 1.3), audio players (Figure 1.4), and portable global positioning satellite (GPS) devices, which now provide high-resolution displays in brilliant, multitone colors.
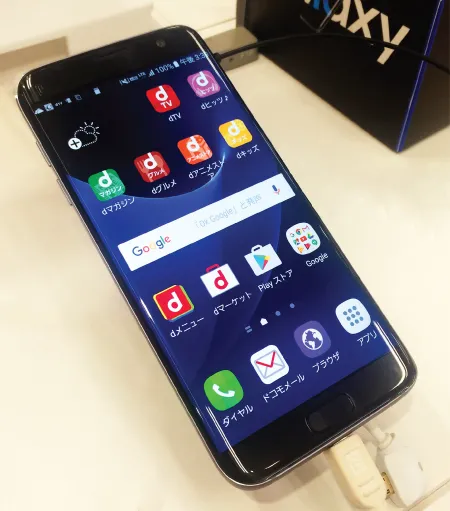
Figure 1.2 Example of a cellular phone using active-matrix OLED (AMOLED)
(Galaxy S7 smartphone by Samsung).
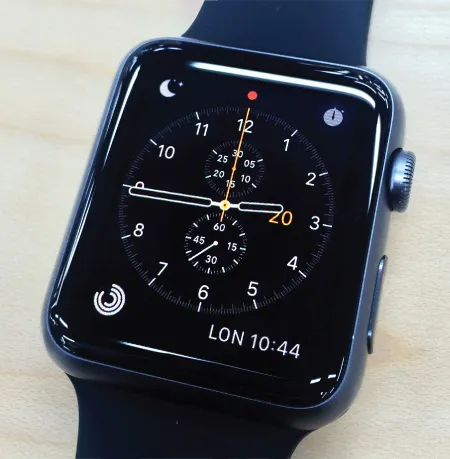

Figure 1.3 Example of a smart watch using active-matrix OLED (AMOLED)
(Apple Watch Series 2 by Apple).
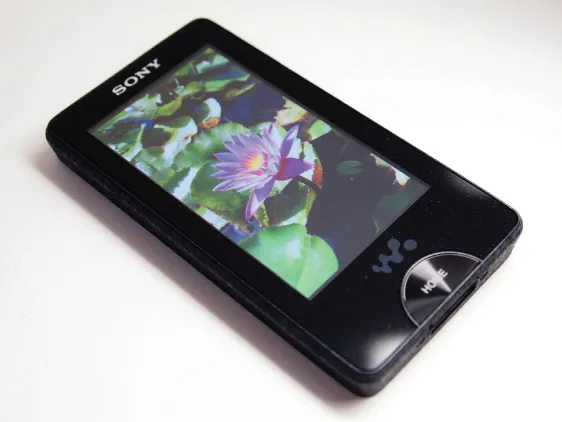

Figure 1.4 Example of an audio player using active-matrix OLED (AMOLED)
(Sony Walkman NW-X-1050).
Larger-display products have also been introduced on the market, such as those shown in Figure 1.5. Much larger prototypes have also been developed (Figure 1.6). Because of their superior features such as slim flat-screen design and aesthetically pleasing screen image, and due to high-contrast image signal emission and very good response time, the current state of the art of OLED television technology that has debuted in the marketplace is indeed groundbreaking [2].
The main objective of this book is to explain the basics and application of this promising technology from various perspectives.
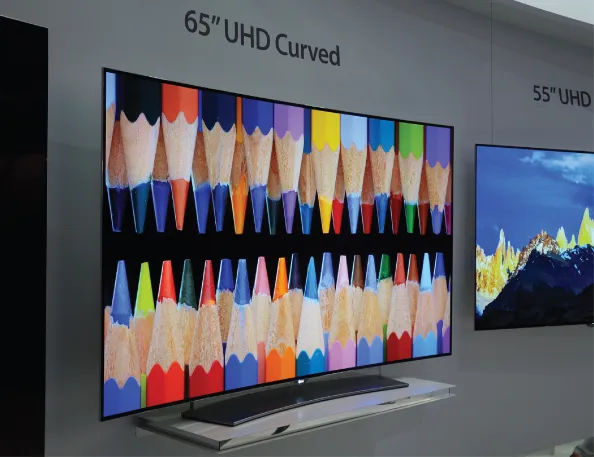

Figure 1.5 Example of a large television using active-matrix OLED (AMOLED)
(65-in. curved OLED TV demonstrated in SID2015 by LG display).
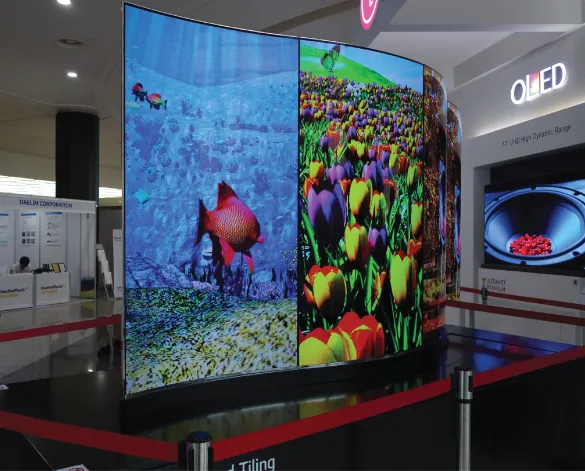

Figure 1.6 111-in. dual-sided flexible OLED television prototype
(LG Display at IMID2016).
References
- 1 C. W. Tang and S. A. Van Slyke, Organic electroluminescent diodes, Appl. Phys. Lett. 51(12):913–915 (1987).
- 2 T. Tsujimura, W. Zhu, S. Mizukoshi, N. Mori, M. Yamaguchi, K. Miwa, S. Ono, Y. Maekawa, K. Kawabe, M. Kohno, and K. Onomura, Advancements and outlook of high performance active-matrix OLED displays, SID 2007 Digest, 2007, p. 84.
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Table of Contents
- About the Author
- Preface
- Series Editor's Foreword to the Second Edition
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: OLED Devices
- Chapter 3: OLED Manufacturing Process
- Chapter 4: OLED Display Module
- Chapter 5: OLED Color Patterning Technologies
- Chapter 6: TFT and Driving for Active-Matrix Display
- Chapter 7: OLED Television Applications
- Chapter 8: New OLED Applications
- Chapter 9: OLED Lighting
- Appendix
- Index
- Wiley-SID Series in Display Technology
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access OLED Display Fundamentals and Applications by Takatoshi Tsujimura in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Electrical Engineering & Telecommunications. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.