
eBook - ePub
Mathematics: The Man-Made Universe
Sherman K. Stein
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 592 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
Mathematics: The Man-Made Universe
Sherman K. Stein
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
Anyone can appreciate the beauty, depth, and vitality of mathematics with the help of this highly readable text, specially developed from a college course designed to appeal to students in a variety of fields. Readers with little mathematical background are exposed to a broad range of subjects chosen from number theory, topology, set theory, geometry, algebra, and analysis.
Starting with a survey of questions on weight, the text discusses the primes, the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, rationals and irrationals, tiling, tiling and electricity, probability, infinite sets, and many other topics. Each subject illustrates a significant idea and lends itself easily to experiments and problems. Useful appendices offer an overview of the basic ideas of arithmetic, the rudiments of algebra, suggestions on teaching mathematics, and much more, including answers and comments for selected exercises.
Starting with a survey of questions on weight, the text discusses the primes, the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, rationals and irrationals, tiling, tiling and electricity, probability, infinite sets, and many other topics. Each subject illustrates a significant idea and lends itself easily to experiments and problems. Useful appendices offer an overview of the basic ideas of arithmetic, the rudiments of algebra, suggestions on teaching mathematics, and much more, including answers and comments for selected exercises.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es Mathematics: The Man-Made Universe un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a Mathematics: The Man-Made Universe de Sherman K. Stein en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Mathematics y Number Theory. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
Categoría
MathematicsCategoría
Number Theory1
Questions on Weighing
This chapter will raise some important questions about numbers. While they may seem to be mere recreational puzzles that could be understood and investigated by anyone who can do simple arithmetic, in fact they concern a fundamental property in number theory. Not until Chapter 3 will the “why” behind the answers be considered. The goal of this chapter is to offer an opportunity to experiment with an open-ended problem and to see how a single mathematical idea can appear in a variety of disguises.
The questions, which concern weighing, will be introduced by a few examples. Say that we have a two-pan scale of the type seen in chemistry labs and statues of “Justice”:
Furthermore, we have an unlimited supply of 5- and 7-ounce measures. Now, supposing that potatoes weigh only whole numbers of ounces, rather than any amount as they actually do, let us ask which potatoes we would be able to weigh with our balance and our two types of measures.
For instance, using only the 5-ounce measures, we can weigh 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, . . . ounces. Or using only the 7-ounce measures, we can weigh 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, . . . ounces. Moreover, we could place one of each type together on a pan:
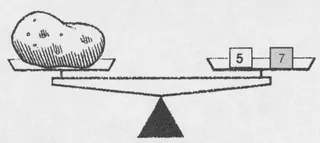
Thus we can weigh 12 ounces, 12 = 5 + 7. Or we could put one of each type of weight alone on a pan:
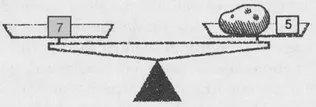
In this way we can weigh 2 ounces, since a potato of this weight, together with the 5-ounce measure, balances the 7-ounce measure.
Can we weigh a 3-ounce potato? Yes, by placing two 5-ounce measures on one pan and a 7-ounce measure with the potato:
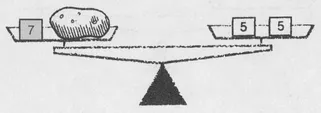
The balancing records the equation 3 + 7 = 2 ⋅ 5.
Can we weigh a 4-ounce potato? Yes. For instance, by placing two 5-ounce measures with the potato and two 7-ounce measures on the other pan:
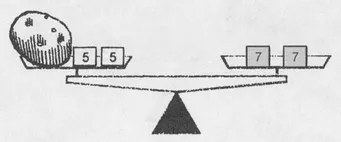
The corresponding equation is
4 + 2 ⋅ 5=2 ⋅ 7.
Or we could place three 7-ounce measures with the potato, which then balance five 5-ounce measures. The equation in this case is 4 + 3 ⋅ 7 = 5 ⋅ 5.
Can we weigh a 1-ounce potato? Even this can be done, as the reader may prefer to work out for himself before reading the next sentence. Two 7-ounce measures and the potato on one pan balance three 5-ounce measures on the other pan. The reader may wish to pause and devise still other ways of measuring this 1-ounce potato with 5- and 7-ounce measures.
Once we know that we can weigh a 1-ounce potato, then we know that we can weigh any number of ounces. For instance, we can weigh a 6-ounce potato as follows. First recall that two 7-ounce measures and a 1-ounce potato balance three 5-ounce measures:
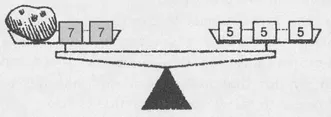
Repeating this arrangement of measures six-fold weighs a six-ounce potato. That is, from the relation 1 + 2 ⋅ 7 = 3 ⋅ 5 5 it follows that 6(1 + 2 ⋅ 7) = 6(3 ⋅ 5) or
6 + 12 ⋅ 7 = 18 ⋅ 5.
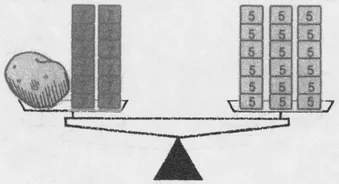
Of course, this may not be the simplest method for weighing a 6-ounce potato. Indeed, 6 + 3 ⋅ 5 5 = 3 ⋅ 7, so we could have managed by placing three 5-ounce measures with the potato and three 7-ounce measures on the other pan. But the reasoning at least assures us that if we can weigh a 1-ounce potato with a supply of two types of measures, then we can weigh any whole number of ounces with those measures.
So much for the combination 5 and 7. Suppose we turn to another combination, 8 and 21. Even if we have only 8-ounce and 21-ounce measures available, we can measure a 1-ounce potato, since
1 + 3 ⋅ 21 = 8 ⋅ 8.
Eight 8-ounce measures on one pan will balance the potato and three 21-ounce measures on the other pan.
The reader may now suspect that perhaps any pair of measures can weigh a 1-ounce potato. But this is not so. If, for example, we have only 6-ounce and 8-ounce measures, then we could never hope to measure a 1-ounce potato, or, for that matter, any odd number of ounces. (The reader should pause to think about why this is so.)
We are now in a position to ask some basic questions. Suppose we have at our disposal an unlimited supply of measures of two types. How can we decide whether we can weigh a 1-ounce potato with them? For instance, can we use 539-ounce and 1619-ounce measures to weigh a 1-ounce potato? More generally we can ask: What potatoes can we weigh with an unlimited supply of two given types of measures? Keep in mind that all potatoes and measures weigh a whole number of ounces (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, . . .). The whole numbers will usually be referred to as the natural numbers.
The questions really concern numbers, not potatoes. Let us gradually translate the second question into the language of numbers: Denote the weights of the two measures by A and B ounces respectively. In our first combination we had A = 5 and B = 7. The weight of the potato will be denoted by W ounces.
There are various methods of weighing the potato. One consists in putting several A-ounce measures on the pan with the potato and several B-ounce measures on the other pan. How many of each we use will depend on W, A, B, and our arithmetic. Say that we use X of the A-ounce measures and Y of the B-ounce measures:
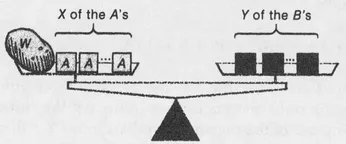
The corresponding equation is
W + XA = YB,
an equation that asserts merely that the scale in the figure balances. (We omit the multiplication sign between letters.)
For A = 5 and B = 7, let us see what X and Y are for various W. When W = 1, for instance, we have 1 + 4 ⋅ 5 = 3 ⋅ 7. Here X = 4 and Y = 3. Also 1 + 11 ⋅ 5 = 8 ⋅ 7, so that X = 11 and Y = 8 also perform the weighing when W=1.
Another method of weighing consists in placing only B-ounce measures with the potato and only A-ounce measures on the other pan. For A = 5, B = 7, the equation 1 + 2 ⋅ 7 = 3 ⋅ 5 illustrates this. We have W + XB = YA, where W = 1, X = 2, Y = 3.
A third method consists in placing the potato on one pan and the measuring weights on the other pan. For example, if W = 12 we have 12 = 5 + 7; if W = 27 we have 27 = 4 ⋅ 5 + 1 ⋅ 7. This method corresponds to an equation of the type W = XA + YB.
No other practical method exists, for there would be no point in placing measures of equal weight on both pans, since they could be removed without affecting the balance. Thus we need to consider only three types of equations:
W + XA = YB, W + XB = YA, W = XA + YB.
In all of these, X and Y are to be natural numbers, possibly including zero. The question about potatoes now becomes one about natural numbers: Let A and B be natural numbers. For which natural numbers W can we find natural numbers X and Y such that at least one of these equations holds:
W + XA = YB, W + XB = YA, W = XA + YB?
The potatoes are gone, but we are left with t...