
eBook - ePub
A Manual of Neonatal Intensive Care
Janet M Rennie
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 424 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
A Manual of Neonatal Intensive Care
Janet M Rennie
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
Highly Commended, BMA Medical Book Awards 2014The fifth edition of this highly successful and well-regarded book continues to provide those working in neonatal intensive care units with precise instructions on the diagnosis and management of common neonatal problems. This edition has been extensively updated and revised, while retaining the backgro
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es A Manual of Neonatal Intensive Care un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a A Manual of Neonatal Intensive Care de Janet M Rennie en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Medicine y Medical Theory, Practice & Reference. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
PART 1
Organization and delivery of care
1 Epidemiology and neonatal outcomes
2 Organization of neonatal care
3 Clinical governance, risk management and legal aspects of neonatal practice
1
Epidemiology and neonatal outcomes
Key points
▪ Around 7% of all births are of low birth weight (<2500 g) or preterm (<37 completed weeks of pregnancy).
▪ About 15 per 1000 pregnancies are twin pregnancies, but 25% of all babies with very low birth weight (<1500 g) are twins or higher multiples.
▪ The outcome for babies born at 25 weeks of gestation or less has improved, but there is still a high risk of death, with motor and/or learning difficulty in a high percentage of the survivors.
■ Epidemiology: definitions in perinatal medicine
Neonatologists need knowledge and understanding of current international, national and local statistics in order to provide adequate information during the counselling of parents when there is the expectation of a preterm or complicated birth. To make sense of the published statistics it is first essential to define the terms that are commonly used in perinatal medicine (Fig. 1.1).
▪ Preterm: any baby born below 37 weeks’ completed gestation, i.e. less than 259 completed days of gestation, measured from the first day of the last normal menstrual period. Extreme preterm is often used to describe delivery below 26 weeks’ completed gestation.
▪ Low birth weight: a baby with a birth weight of less than 2500 g (up to and including 2499 g).
▪ Very low birth weight: birth weight of less than 1500 g.
▪ Extremely low birth weight (ELBW): birth weight of less than 1000 g.
▪ Stillbirth: a stillborn baby is defined as a baby born after the 24th week of pregnancy who did not show any signs of life at any time after being born. If there are no signs of life at birth, a baby born before 24 weeks’ gestation is classed as a miscarriage. The stillbirth rate (see below) is the number of stillbirths expressed per 1000 live births and stillbirths.
▪ Live birth: a birth at any gestation (including below 24 weeks) where the baby shows signs of life after delivery.
▪ Neonatal death: the death of a neonate born with signs of life (see above) within the first 28 days after delivery. It is often subdivided into early neonatal death within the first 7 days of life and late neonatal death occurring after the 7th day but before the completed 28th day of life.
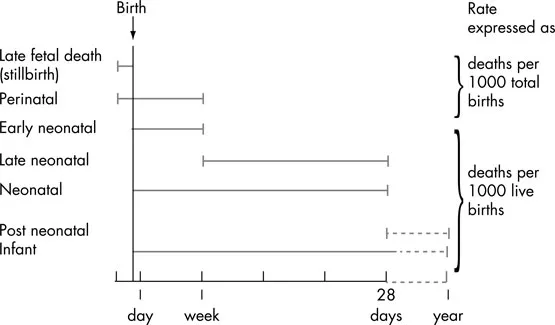
Fig. 1.1 Definition of stillbirth and infant mortality rates
▪ Infant mortality rate: the number of infants dying within the first year of life per 1000 live births.
▪ Perinatal mortality rate: the number of stillbirths and neonatal deaths in the first week of life per 1000 total births (live and stillborn).
The Millennium Development Goal is to achieve a two-thirds reduction in mortality in children younger than 5 years by 2015; there was a worldwide reduction of 3.1 million neonatal deaths between 1990 and 2010. Most of the deaths still occur in sub-Saharan Africa or south Asia, with less than 1% of the deaths in high-income countries.
The value of understanding the outcomes of babies born prematurely extends beyond the counselling of parents and families. Such studies allow the guidance of health and social care provision, both in the perinatal period and extending into childhood.
Around 7% of all births in the UK are of babies with birth weight <2500 g, and about 1.2% of all births are of babies <1500 g. The percentage of ELBW babies has risen considerably from 0.27% in 1983 to around 0.5% in 2009. Unfortunately national data in England and Wales did not record gestational age until 2005, when the linkage with the NHS numbers for babies was established. Data are available for Scotland from the early 1970s and show a steadily rising trend with an increase in the number of multiple preterm births.
The availability of gestational age-specific mortality data for England and Wales shows that there is, as expected, a steadily declining mortality as gestational age increases, with the exception of post-dates babies of 42 weeks (Fig. 1.2). Note the logarithmic scale on the y-axis.
Within the UK, the mortality figures vary considerably by the ethnic origin of the mother, and international comparisons of perinatal mortality data are often performed. The World Health Organization has recommended that babies of gestational age below 22 weeks and birth weight below 500 g should be excluded from comparisons between countries because of differences in incidence and reporting of births of such babies.
Valuable information about the outcome of extremely preterm babies born in England and Wales is available from the two EPICure studies. These were prospective, geographical studies which included all deliveries below 26 weeks, for 1995 and 2006. The survival figures for babies admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) born below 26 weeks are shown in Fig. 1.3; improvement in survival is seen between the 1995 and 2006 cohort, which is significant at 24 and 25 weeks’ gestation.
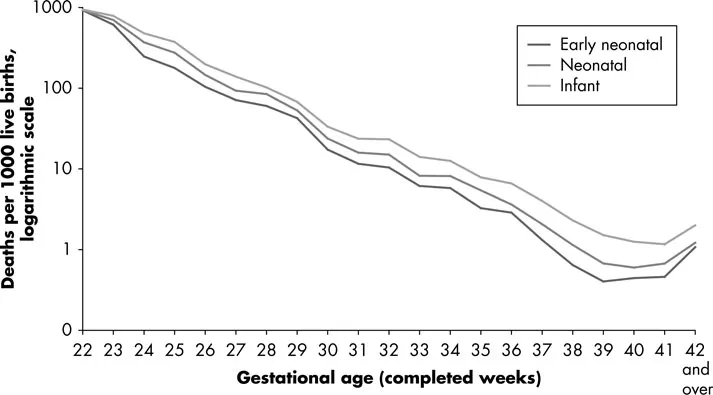
Fig. 1.2 Infant mortality by gestational age, babies born in 2008, England and Wales.
Source: ONS childhood mortality statistics, unpublished data. Data from Office of National Statistics, compiled by Allison Mc Farlane; from Rennie and Robertson (2012) with permission
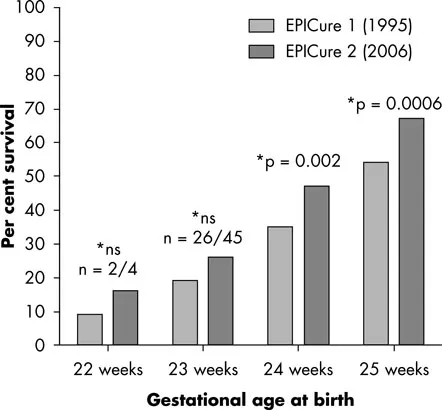
Fig. 1.3 Outcome of babies born below 26 weeks’ gestation
There are, however, limitations in the applicability of national geographical outcomes due to small numbers of the most extreme preterm infants and changing patterns of neonatal care with time (use of surfactant, antenatal steroids, temperature control, increased use of non-invasive ventilation, centralization of care, minimal handling, etc.).
■ Neonatal outcomes
In surviving infants born extremely preterm, a number of significant medical morbidities are seen which appear largely unchanged across the 10 years between EPICure 1 and 2 (Fig. 1.4). Although cerebral palsy (CP) has long been monitored as an adverse outcome of preterm birth, and there is no doubt that there is an increased risk of CP in extremely preterm babies, far more survivors of preterm birth are disabled by their learning problems.
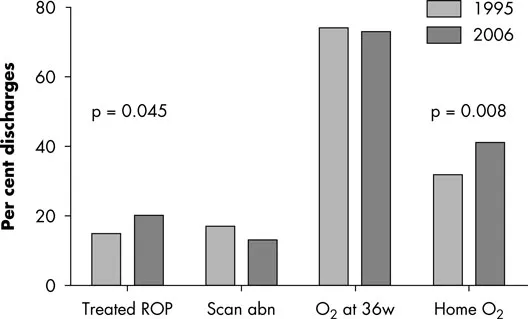
Fig. 1.4 Major neonatal morbidities at discharge in infants born <26 weeks. abn, abnormal; ROP, retinopathy of prematurity; w, weeks
Severe motor outcomes such as CP are relatively rare, affecting approximately 10% of very low birth weight babies. In EPICure 1, in infants born at less than 26 weeks, 14% of surviving babies showed moderate motor disability and 4% severe motor disability. Cognitive outcomes appear to be a continuum of disability, with a very significant fall away in cognitive outcomes in babies born at less than 32 weeks of gestation (Fig. 1.5). However, when assessed by the requirement for special educational needs provision in school, the effects of even mild degrees of prematurity can be detected (Fig. 1.6).
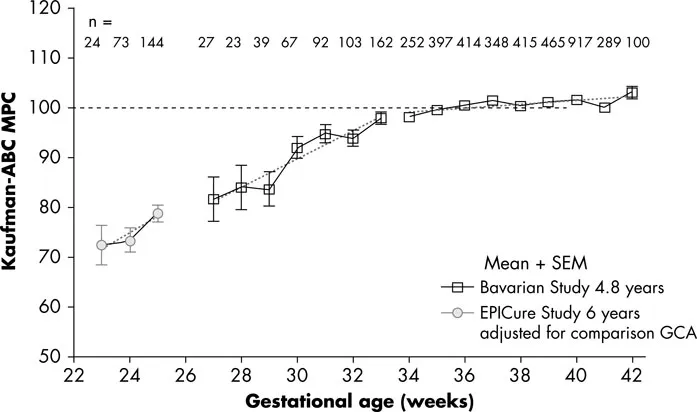
Fig. 1.5 Cognitive outcomes following preterm birth. ABC MPC, Assessment Battery for Children Mental Processing Composite; GCA, general conceptual ability; SEM, standard error of the mean. With permission from Marlow et al. (2005)
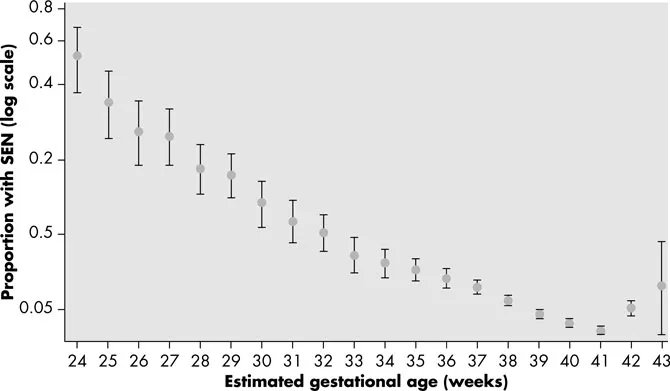
Fig. 1.6 Percentage of children with special educational needs (SEN) by gestation at delivery (note the logarithmic scale). Redrawn from Mackay et al. (2010). From Rennie and Robertson (2012) with permission
It should also be recognized that the assessment of neurodisability following extreme preterm birth varies dependent on the age of assessment. Although severe disability is readily detectable early, some of the milder forms of disability are not detectable until later childhood. In addition to adverse motor and cognitive outcomes, more detailed follow-up has demonstrated significantly increased behavioural symptoms (especially social, thought and attention difficulties), emotional disorders such as anxiety and depression, and autistic-like disorders. Our understanding of how prematurity affects individuals into adult life is curre...