
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
David Jiles
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 626 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials
David Jiles
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
A long overdue update, this edition of Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials is a complete revision of its predecessor. While it provides relatively minor updates to the first two sections, the third section contains vast updates to reflect the enormous progress made in applications in the past 15 years, particularly in magnetic recordin
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a Introduction to Magnetism and Magnetic Materials de David Jiles en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Sciences physiques y Matière condensée. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
Section II
Magnetism in Materials
Magnetic Phenomena on the Microscopic Scale
5 Magnetic Properties
We will now look at the causes of hysteresis in ferromagnets and how the variation of magnetization with magnetic field can be quantified in restricted cases such as at low field and in the approach to saturation. High-resolution measurements of the variation of M with H indicate that there are discontinuities. This is known as the Barkhausen effect. We will also consider the change in length of a ferromagnet as it is magnetized, that is, the magnetostriction, and discuss anisotropy in relation to magnetostriction.
We have shown in the previous chapter that most of the important macroscopic magnetic properties of ferromagnets can be represented on a B-H plot or hysteresis loop. From this, the magnetization can be calculated at every point on the hysteresis curve using the general formula B = μ0(H + M). As the magnetization curve is traversed, there are discontinuous, irreversible changes in the magnetization known as the Barkhausen effect after its discoverer. In recent years, the Barkhausen effect has become an important tool for investigating the microstructural properties of ferromagnetic materials.
One important bulk property of interest, which is not contained in the hysteresis plot, is the magnetostriction. This is the change in length of a material either as a result of a magnetic order (spontaneous magnetostriction) or under the action of a magnetic field (field-induced magnetostriction). This will also be discussed in this chapter.
5.1 HYSTERESIS AND RELATED PROPERTIES
5.1.1 INFORMATION FROM THE HYSTERESIS CURVE
Which are the most important macroscopic magnetic properties of ferromagnets?
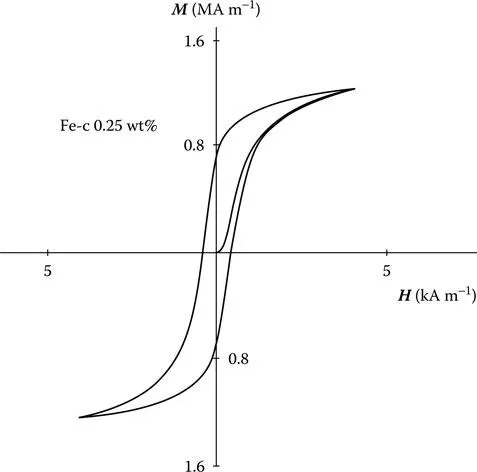
From the hysteresis curve such as the one shown in Figure 5.1, we can define a number of magnetic properties of the material, which can be used to characterize the hysteresis loop. A question immediately arises: How many degrees of freedom are there in a hysteresis loop? Or to put the question another way: How many parameters are needed to characterize a hysteresis loop? Clearly, there is no general answer to this, but for the commonly encountered sigmoid-shaped hysteresis loop such as the one in Figure 5.1, we can start to enumerate the important properties and thereby make an estimate.
5.1.2 PARAMETRIC CHARACTERIZATION OF HYSTERESIS
Which are the parameters that can be used to define hysteresis?
First of all, the saturation magnetization M0 will give us an upper limit to the magnetization that can be achieved. At temperatures well below the Curie point, the technical saturation Ms can be used instead. The width of the loop across the H axis, which is twice the coercivity Hc, is also an independent parameter since this can be altered by heat treatment and hence is not dependent on Ms. The height of the curve along the B-axis, that is, the remanence is also an independent parameter since it is not wholly dependent on Ms and Hc. The orientation of the hysteresis curve on the B-H plane, which can be represented by , the slope of the curve at the coercive point, is also independent of the other parameters.
The hysteresis loss WH may also be an independent parameter as may the initial permeability . Finally, the curvature of the sides of the hysteresis loop, which although not immediately obvious as an independent parameter, is clearly not dependent on factors such ...