
eBook - ePub
Stand-alone Solar Electric Systems
The Earthscan Expert Handbook for Planning, Design and Installation
Mark Hankins
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 248 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
Stand-alone Solar Electric Systems
The Earthscan Expert Handbook for Planning, Design and Installation
Mark Hankins
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
One of the best ways to get power to remote, off-grid locations, whether in developed or developing countries, is through the use of solar electric systems. This practical guide describes how to plan, design and install solar electric systems in a manner that is hands-on, graphic and technically complete. Highly illustrated chapters cover:
- solar energy basics
- components of solar electric systems (modules, batteries, regulators, inverters and appliances)
- installation practice
- on planning and servicing systems
- water pumping
- refrigeration
- village electrification.
This is the must-have guide for electric technicians and designers, development workers, and anyone who wants to install their own off-grid system.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es Stand-alone Solar Electric Systems un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a Stand-alone Solar Electric Systems de Mark Hankins en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Biowissenschaften y Ökologie. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
1
How to Use this Book: An Overview of Solar Electric Technology
Off-grid solar electricity is a convenient form of electricity for people far from the electric grid or for people who want electric power without having to ‘hook up’. Whether the requirement is a cabin in the woods, a rural house in a developing country, a cruising sailboat or a garden shed, this book can help you to plan and install a solar system so that it robustly meets the required needs. Moreover, with this book you will also be able to understand the electricity flows in the system you use – a critical concept in a world increasingly short on energy. Most of all, you will be able to proudly say that you harvest your own power – and you did it yourself!
This chapter gives readers a basic understanding of the common components of off-grid solar electric systems. It also provides a brief background of solar electric technology, summarizing the applications, parts, advantages and disadvantages of solar electric systems including solar modules, batteries, charge controllers, inverters and appliances. The end of the chapter has a basic introduction to common electric terminology.
Common Uses of Solar Electricity
Solar electricity is electric power generated from sunlight using devices called solar cell modules. Solar electricity can replace, cost-effectively, small applications of petroleum-fuelled generators, grid power and even dry cell batteries. The technology has spread rapidly throughout the world for both on-grid and off-grid application. Millions of rural off-grid homes are using solar photovoltaic (PV) systems throughout the developed and developing world.
Small off-grid solar electric systems differ from grid or generator electricity in a number of ways:
• Small off-grid PV systems are based on extra-low-voltage direct current electricity, not low-voltage 230 or 110 volts (V) alternating current (see the Glossary for a definition of ‘extra-low’ and ‘low’ voltage).
• Off-grid PV systems usually store energy in batteries.
• Electricity is generated on-site by photovoltaic modules.
• For systems to be economical, all electricity produced must be used efficiently.
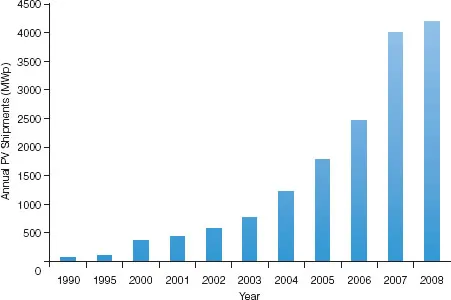
Figure 1.1 World shipments of PV modules, 1990–2008
Solar electric technology is developing very quickly; its worldwide use is increasing rapidly as prices of other electric energy sources rise. Before the 1990s, solar electricity was a new technology, used mostly for off-grid telecommunications systems, signalling, water pumping and remote clinic power.
Since the mid-1990s, world production of solar modules increased rapidly, largely because of demand for grid-connected systems in Europe, the US and Japan. Meanwhile, the price of solar cell modules fell from about US$100 per peak watt in 1974 to less than US$4 per peak watt in 2008. Decreased prices caused a rapid expansion of solar PV into rural markets in the early 1990s. Today, solar electricity is often the most viable power source for many off-grid applications in rural areas that have not been electrified.
Off-grid and grid-connected solar PV systems are very different, both in their component make-up and in the principles used to design them. Off-grid solar (also called ‘stand-alone’) systems usually require battery banks to store energy and they must be carefully designed to meet expected loads during cloudy periods. Meanwhile, grid-connected systems feed unused power directly into the grid and usually do not utilize battery storage systems.
This book is a general guide for installers of small off-grid systems below 1 kilowatt peak in size to be used in conjunction with system component installation manuals and national electrical codes and regulations, which should always be referred to and complied with. Chapter 11 deals specifically with installing systems of over 500Wp. Lists of literature on installing larger systems and grid-tied systems can be found in Chapter 12 (as well as from providers of training courses). Installation work should always be carried out by (or with) appropriately qualified technicians.

(a) Solar lighting system on a girls’ boarding school in Tanzania

(b) Pole-mounted panels at a health centre in Rwanda (Walt Ratterman is second from right)

(c) PV system in a Kenyan game park

(d) Ten year old solar water pumping system in Puntland, Somalia

(e) Small lighting system in Bangladesh
Figure 1.2 Common PV applications
Sources: (a) Frank Jackson; (b, c) Mark Hankins; (d) Mark Hankins; (e) MicroEnergy International
The list below describes some of the important applications for which off-grid solar electric power is utilized (see Chapter 11 for case studies on different types of systems).
Household lights, televisions, sound systems, radios and small appliances
Often known as ‘solar home systems’ (SHS), small PV systems provide electricity for lighting and entertainment appliances. Night-time lighting is crucial for education, commerce, craft work and all types of social activity. Off-grid rural people need information and entertainment, and they value televisions, stereo systems, computers and communication devices.
Small industries and institutions
Schools and small businesses in rural areas use solar electricity to power lights, small machines, calculators, light tools, computers, typewriters, communication devices and security systems.
Telecommunications
Because telecommunication systems are often installed in isolated places with no access to power, stand-alone photovoltaic systems are a common choice to power radios, remote repeaters, base stations for cell-phone networks and weather-monitoring equipment.
Health centre vaccine refrigeration and lighting
Solar electric systems are popular for vaccine refrigeration in rural health centres. Such solar refrigerators are also utilized to freeze ice packs and to keep blood plasma cool. The World Health Organization supports programmes that install solar electric refrigerators and lighting in health centres around the world.
Water pumping
Arrays of solar cell modules connected to electric pumps are used to pump water from wells or boreholes. This water is used for drinking, washing, other household purposes and for small irrigation projects. Solar electricity can also be used to help purify drinking water. It is relatively expensive to use solar PV for commercial-scale irrigation.
Electric fencing and other uses
Solar electric fences keep wild animals inside game parks (and out of farm land), while also keeping domestic animals within designated areas. Other common uses of solar electric systems include street-lighting, road-sign illumination, railway and marine signal lighting, security systems and protection of pipelines from corrosion.
Table 1.1 Solar electricity advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of solar electric power | Disadvantages of solar electric power |
• PV systems consume no fuel and convert freely available sunlight directly into electricity. • PV systems produce electricity quietly without giving off exhaust gases or pollutants. • PV systems require comparatively little maintenance. Solar modules have no moving parts and last over 20 years. • PV systems are particularly economical for small applications. Applications where power demand is below 3–5kWh/day are particularly cost effective using solar PV. • PV systems can be tailored to the size of the application needed, be it lighting, pumping or audio visual, and they can be easily expanded as demand increases. • PV systems are safe when properly installed. Risks of electric shock are low with 12 and 24 volt DC systems, and there is much less fire-risk than for kerosene or generator solutions. | • PV systems often have higher up-front costs than other solutions. Even if a solar PV system cost is more economical than generators or kerosene over its lifetime, it is often difficult for low-income people to access cash to buy the system up-front. • Most off-grid PV systems require batteries to store electric power. Batteries require maintenance and must be replaced at the end of their lives. The performance of PV systems is dependent on the quality of batteries available on the local market or the availability of imported batteries. • Small PV systems often require efficient or direct current (DC) appliances. These often cost more than commonly available alternating current (AC) appliances. • PV systems must be designed and installed by qualified technicians. Poorly designed or installed PV systems perform less effectively than other solutions. • Large stand-alone PV systems often need to be backed up by petroleum-fuelled generators (or wind-power systems) to supply power during peak-use or cloudy periods. • Solar electric systems are not economical for thermal loads such as cooking, water heating or ironing clothes. |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Electric (PV) Off-Grid Systems
When deciding on a system, always consider the advantages and disadvantages of the technology for your particular requirements. The table above summarizes some of these for solar PV systems.
Using this Book to Design and Install Solar Electric Systems
The following sec...