
eBook - ePub
Manufacturing in Digital Industries
Prospects for Industry 4.0
J. Paulo Davim, J. Paulo Davim
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 125 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
Manufacturing in Digital Industries
Prospects for Industry 4.0
J. Paulo Davim, J. Paulo Davim
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
Digital Industry can provide the framework for examining the challenges of future production technology.
This book describes some of the various aspects that can, and may, influence future manufacturing. Computational intelligence techniques, cyber-physical systems, virtual and cloud-based manufacturing and man-machine interaction are studied and some of the most recent research completed by international experts in industry and academia is considered. Case studies provide practical solutions.
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es Manufacturing in Digital Industries un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a Manufacturing in Digital Industries de J. Paulo Davim, J. Paulo Davim en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Technology & Engineering y Mechanical Engineering. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
1 Supply chain 4.0 in shipbuilding industry
Magdalena Ramirez-Peña
School of Engineering, Universidad de Cádiz, Avda. Universidad de Cádiz, Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain
Alejandro J. Sánchez Sotano
School of Engineering, Universidad de Cádiz, Avda. Universidad de Cádiz, Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain
Víctor Pérez-Fernandez
School of Engineering, Universidad de Cádiz, Avda. Universidad de Cádiz, Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain
Jorge Salguero
School of Engineering, Universidad de Cádiz, Avda. Universidad de Cádiz, Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain
Francisco J. Abad
Navantia S.A., SME Astillero Bahía de Cádiz, Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain
Alvaro Gomez-Parra
School of Engineering, Universidad de Cádiz, Avda. Universidad de Cádiz, Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain
Moises Batista
School of Engineering, Universidad de Cádiz, Avda. Universidad de Cádiz, Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain
Abstract
Industry 4.0 (I4.0) brings with it a series of changes in the companies; among them we find those that affect the business models to get the concept of smart factory. This change in business models implies a complete communication network between different companies, factories, suppliers, resources and others optimized in real time, so that maximum efficiency is achieved for all parties involved. The objective is in identifying a methodology that allows to define the supply chain (SC) that improves the performance and sustainability of the shipbuilding industry. Therefore, this chapter aims at connecting each of the key I4.0 technologies with the most significant SC paradigms: lean, agile, resilience and green to define what the shipbuilding SC should be. This study shows how each of the enabling technologies affects the SC, what paradigms to achieve and what steps to follow through the simulation of discrete events to end up implementing the shipbuilding supply chain in a 4.0 environment.
Keywords: shipbuilding, supply chain, LARG, lean, agile, resilient, green, Industry 4.0, Shipyard 4.0,
1.1 Introduction
Going back to the origins of supply chain (SC) definition, it is possible to say that SC involves the set of flows of materials and information that take place within a company from the suppliers of raw materials to the consumer of the final product [1]. The term supply chain dates back to the early 1980s [2] and is usually used to relate the company to its suppliers [3], to analyze purchases[4], for the control of logistic activities [5] among other activities.
It is said that SC has evolved a great deal in recent years until it was considered as a strategic concept in the business model of successful companies, representing one of the areas with the today’s greatest investment [6].
Figure 1.1 shows how this strategic tool has a transversal and multidisciplinary character, thus affecting the three levels of strategy that exist in the company, and the corporate strategy in the first place being the one that frames the company in the sector and market that is going to compete.
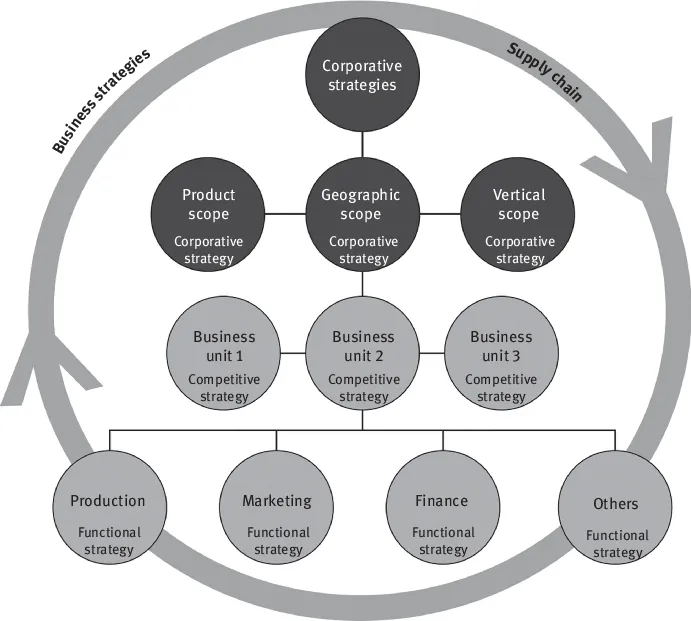
Figure 1.1: Supply chain and strategic business levels.
In the second level, the competitive strategy will define how it will compete in those sectors and markets previously delimited. The functional strategy, the last one, will be implemented within each area that comprises the company.
In this regard, within the areas that constitute the company dedicated to shipbuilding, our object of study defines what certain authors consider within the new business models as distributed manufacturing [7]. A shipyard concentrates on a number of heterogeneous manufacturing units organized based on information technology to obtain a product, the ship. This type of distributed manufacturing based on information technology is adjusted within what is considered to be a smart factory [8].
Smart manufacturing is, on the other hand, the basis of Industry 4.0 (I4.0), which translated the objective of this case to Shipyard 4.0. Approaching from the objective of the SC, throughout the chapter we will see which of the paradigms that exist on it will be the most appropriate for its adaptation and which enabling technologies will be necessary. Evaluate the current situation to arrive at a definition of SC 4.0 in the shipbuilding sector.
1.2 Industry 4.0
The first industrial revolutions are associated with changes related to technologies that affect production systems in various ways. Therefore, the steam power is introduced from the first industrial revolution. The second industrial revolution is followed with mass production and electrical energy. The third revolution is led by automation and information technologies to what is considered the fourth revolution focused on cyber-physical systems (Figure 1.2).
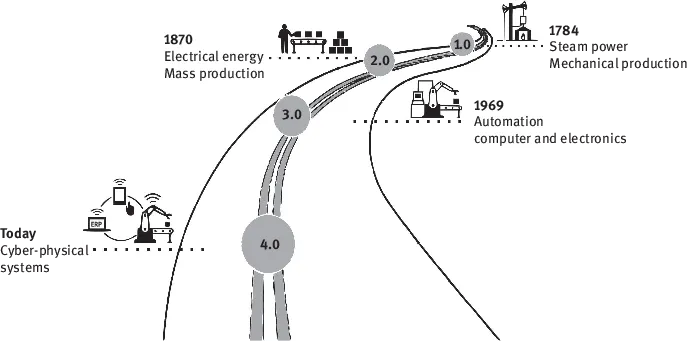
Figure 1.2: Industrial revolutions.
The phenomenon I4.0 (originated in Germany through the proposal to establish strategies based on high technologies made by Kagermann, Lukas and Wahlster [9]) is considered in a first publication to be on the road toward the fourth industrial revolution. Subsequently, Kagermann, Wahlster and Heibig [10] made recommendations on how to implement the I4.0 strategy as a new type of industrialization based on the leadership maintained over the years by German industry, due both to its specialization in the sector and to its dedication to R&D&I in manufacturing technologies.
In Europe, the European Commission “Factories of the Future” is created as a growth strategy, posing manufacturing as a key enabler of enrichment not only economically but also sustainably and inclusively through a public–private partnership, which in turn guarantees R&D and industrial competitiveness. To this end, its objectives include increasing competitiveness and sustainability through R&D activities and promoting the purposes for an intelligent, green and inclusive economy, among others. Figure 1.3 shows the roadmap structure [11].
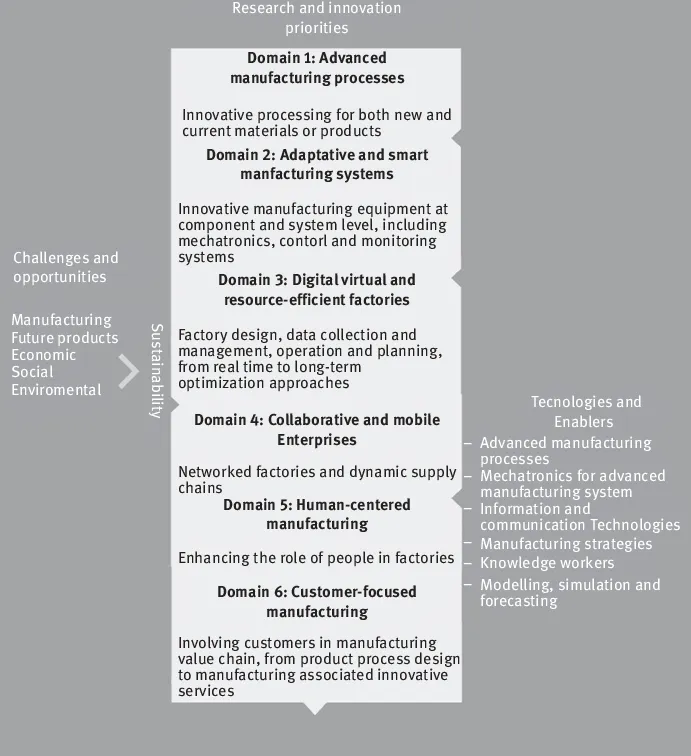
Figure 1.3: Roadmap structure for factories of the future (adapted from [11]).
In the United States, the US president’s science and technology advisory committee begins work in 2011 on what is known as the Advanced Manufacturing Partnership (AMP), whose goal is to chart the path that will lead to the revitalization of the manufacturing sector. The organization is made up of various universities and technology institutes, technology companies and institutions, and federal agencies such as defense and energy. Its work plan has five distinct workflows. Technology development that enables technologies and areas of cutting-edge technology will be identified as follows: shared infrastructure, where the network of manufacturing innovation institutes will be created for technology transfer; public policy defines the macroagreement and facilitates collaboration among all participants; education and workforce development empowering academic communities, facilitating practices in the sector [12].
In 2014, Molnar and Houtman published the second version of AMP 2.0 in which they established the recommendations focused on three pillars, enabling innovation prioritizing three technological areas: advanced detection, control and platforms for manufacturing within area 1; visualization, computing...