
Comprehensive Organic Chemistry Experiments for the Laboratory Classroom
Carlos A M Afonso, Nuno R Candeias, Dulce Pereira Simão, Alexandre F Trindade, Jaime A S Coelho, Bin Tan, Robert Franzén, Carlos A M Afonso, Nuno R Candeias, Dulce Pereira Simão, Alexandre F Trindade, Jaime A S Coelho, Bin Tan, Robert Franzén
- 951 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Comprehensive Organic Chemistry Experiments for the Laboratory Classroom
Carlos A M Afonso, Nuno R Candeias, Dulce Pereira Simão, Alexandre F Trindade, Jaime A S Coelho, Bin Tan, Robert Franzén, Carlos A M Afonso, Nuno R Candeias, Dulce Pereira Simão, Alexandre F Trindade, Jaime A S Coelho, Bin Tan, Robert Franzén
Información del libro
This expansive and practical textbook contains organic chemistry experiments for teaching in the laboratory at the undergraduate level covering a range of functional group transformations and key organic reactions.The editorial team have collected contributions from around the world and standardized them for publication. Each experiment will explore a modern chemistry scenario, such as: sustainable chemistry; application in the pharmaceutical industry; catalysis and material sciences, to name a few. All the experiments will be complemented with a set of questions to challenge the students and a section for the instructors, concerning the results obtained and advice on getting the best outcome from the experiment. A section covering practical aspects with tips and advice for the instructors, together with the results obtained in the laboratory by students, has been compiled for each experiment.
Targeted at professors and lecturers in chemistry, this useful text will provide up to date experiments putting the science into context for the students.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
 | |||
| Number of sessions (Duration of each session) | Hazard level | Difficulty level | Level of study |
| 2 or 3 (3 h each) | Low | Low | Introductory |
| Class names Aromatic compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, hydrocarbons | |||
| Concepts involved Acid–base reactions. Fundamental experimental techniques of unitary operations: Extraction, distillation, filtration and thin-layer chromatography. Purification of compounds by recrystallization and characterization through their physical properties and IR spectra | |||
| Chemicals neededp-Toluidine, benzoic acid, naphthalene, methylene chloride, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, sodium sulfate, ethanol, petroleum ether (40–60 °C) (also known as light petroleum (40–60 °C)) | |||
| Equipment and experimental techniques involved Usual laboratory glassware; extraction, filtration, distillation and recrystallization apparatus; TLC plates | |||
| Keywords Acid–base reactions, distillation, extraction, filtration, IR spectroscopy, physical properties, thin-layer chromatography | |||
Background
Additional Safety
Experimental Procedure
Laboratory Session 1 (3 h)
Separation (ref. 4)
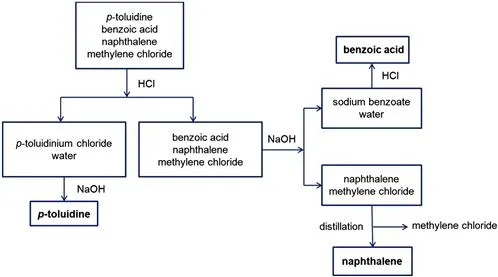
- In a separatory funnel introduce 150 mL of the mixture to be separated (this volume of solution contains 3 g of p-toluidine, 3 g of benzoic acid and 3 g of naphthalene, in methylene chloride).
- Extract the mixture with 25 mL of an aqueous HCl (3N) solution and shake thoroughly. Allow to stand and separate the aqueous layer. Repeat this procedure twice. Finally, extract the organic layer with 25 mL of water. Collect the aqueous extracts in an Erlenmeyer flask (solution A).
- Recover the organic phase from the previous extraction and extract it with 25 mL of an aqueous NaOH (3N) solution and shake thoroughly. Allow to stand and separate the aqueous layer. Repeat this procedure twice. Finally, extract the organic layer with 25 mL of water. Collect the aqueous extracts in an Erlenmeyer flask (solution B).
- Keep the organic phase left after the two previous extractions in an Erlenmeyer flask (solution C) and dry it with anhydrous sodium sulfate.
Recovery
- To the solution A add a concentrated NaOH solution until no more precipitate formation is observed. Assure that the medium is basic by testing with indicator paper. Cool the mixture in ice, filter with suction at the water vacuum pump and collect the crystals in a Büchner funnel. Wash them with a small amount of ice cold water. Let them dry at the air over filter paper.
- To the solution B add a concentrated HCl solution until no more precipitate formation is observed. Ensure that the medium is acidic by testing with indicator paper. After this point proceed as described in step 5 for solution A.
- Filter the solution C through a fluted filter paper and collect the filtrate in a 250 mL round-bottomed flask. Distil the methylene chloride in a rotary evapora...