![]()
Part
I
Methodology of Policy Analysis
![]()
Chapter
1
The Process of Policy Analysis
- Learning Objectives
- Introduction
- Methodology of Policy Inquiry
- Multidisciplinary Policy Analysis
- Forms of Policy Analysis
- The Practice of Policy Analysis
- Critical Thinking and Public Policy
- Chapter Summary
- Review Questions
- Demonstration Exercises
- Bibliography
- Case 1.1 The Goeller Scorecard and Technological Change
- Case 1.2 Using Influence Diagrams and Decision Trees to Structure Problems of Energy and Highway Safety Policy
- Case 1.3 Mapping International Security and Energy Crises
Learning Objectives
By studying this chapter, you should be able to:
- Define and illustrate phases of policy analysis
- Distinguish four strategies of policy analysis
- Contrast reconstructed logic and logic-in-use
- Distinguish prospective and retrospective policy analysis
- Distinguish problem structuring and problem solving
- Describe the structure of a policy argument and its elements
- Understand the role of argument mapping in critical thinking
- Interpret scorecards, spreadsheets, influence diagrams, decision trees, and argument maps
Introduction
Policy analysis is a process of multidisciplinary inquiry aiming at the creation, critical assessment, and communication of policy-relevant knowledge. As a problem-solving discipline, it draws on social science methods, theories, and substantive findings to solve practical problems.1
Methodology of Policy Inquiry
The methodology of policy inquiry refers to the critical investigation of potential solutions to practical problems. Abraham Kaplan, one of the founders of the policy sciences, observed that the aim of methodology is to help understand and question, not only the products of policy inquiry, but the processes employed to create these products. The methodology of policy inquiry contributes to the reflective understanding of theories, methods, and practices of specialized fields such as benefit–cost analysis in economics, implementation analysis in political science, and program budgeting in public administration. These and other specialized fields hold an important place in the process of policy inquiry because they help provide its multidisciplinary foundations.
The methodology of policy inquiry is not the same as methods such as regression analysis, ethnographic interviewing, or benefit-cost analysis, because methodology is concerned with the philosophical assumptions that justify the use of these methods. Nor is the methodology of policy inquiry equivalent to one or another philosophy of science, for example, logical positivism, hermeneutics, or pragmatism.2 On the contrary, the methodology of policy inquiry is productively eclectic; its practitioners are free to choose among a range of scientific methods, qualitative as well as quantitative, and philosophies of science, so long as these yield reliable knowledge.3 In this context, policy analysis includes art and craft, which may be regarded as scientific to the extent that they succeed in producing knowledge that is reliable because it can be trusted. Ordinary commonsense knowing and well-winnowed practical wisdom, both products of evolutionary learning across generations of problem solvers, often produce conclusions that are at least as reliable, and sometimes more so, than those produced by specialized social science methods.4
The rationale for policy analysis is pragmatic. For this reason, policy analysis is unmistakably different from social science disciplines that prize knowledge for its own sake. The policy-relevance of these disciplines depends, not only on their status as sciences, but on the extent to which they are successful in illuminating and alleviating practical problems. Practical problems, however, do not arrive in separate disciplinary packages addressed, as it were, to social science departments. In today’s world, multidisciplinary policy analysis seems to provide the best fit with the manifold complexity of public policymaking.
Multidisciplinary Policy Analysis
Policy analysis is partly descriptive. It relies on traditional social science disciplines to describe and explain the causes and consequences of policies. But it is also normative, a term that refers to value judgments about what ought to be, in contrast to descriptive statements about what is.5 To investigate problems of efficiency and fairness, policy analysis draws on normative economics and decision analysis, as well as ethics and other branches of social and political philosophy, all of which are about what ought to be. This normative commitment stems from the fact that analyzing policies demands that we choose among desired consequences (ends) and preferred courses of action (means). The choice of ends and means requires continuing tradeoffs among competing values of efficiency, equity, security, liberty, democracy, and enlightenment.6 The importance of normative reasoning in policy analysis was well stated by a former undersecretary in the Department of Housing and Urban Development: “Our problem is not to do what is right. Our problem is to know what is right.”7
Policy-Relevant Knowledge
Policy analysis is designed to provide policy-relevant knowledge about five types of questions:
- Policy problems. What is the problem for which a potential solution is sought? Is global warming a man-made consequence of vehicle emissions, or a consequence of periodic fluctuations in the temperature of the atmosphere? What alternatives are available to mitigate global warming? What are the potential outcomes of these alternatives and what is their value or utility?
- Expected policy outcomes. What are the expected outcomes of policies designed to reduce future harmful emissions? Because periodic natural fluctuations are difficult if not impossible to control, what is the likelihood that emissions can be reduced by raising the price of gasoline and diesel fuel or requiring that aircraft use biofuels?
- Preferred policies. Which policies should be chosen, considering not only their expected outcomes in reducing harmful emissions, but the value of reduced emissions in terms of monetary costs and benefits? Should environmental justice be valued along with economic efficiency?
- Observed policy outcomes. What policy outcomes are observed, as distinguished from the outcomes expected before the adoption of a preferred policy? Did a preferred policy actually result in reduced emissions, or did decreases in world petroleum production and consequent increases in gasoline prices and reduced driving also reduce emissions?
- Policy performance. To what extent has policy performance been achieved, as defined by valued policy outcomes signaling the reduction of global warming through emissions controls? To what extent has the policy achieved other measures of policy performance, for example the reduction of costs of carbon emissions and global warming to future generations?
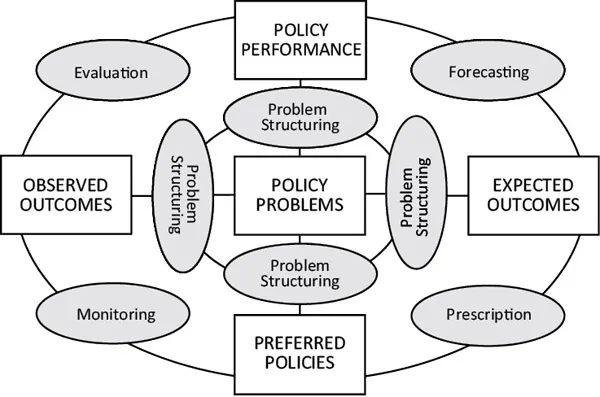
Answers to these questions yield these five types of policy-relevant knowledge, which are shown as rectangles in Figure 1.1.8
Policy problems are representations of problem situations, which are diffuse sets of worries, inchoate signs of stress, or surprises for which there is no apparent solution. Knowledge of what problem to solve requires knowledge about the antecedent conditions of a problem situation (e.g., school dropouts as an antecedent of unemployment), as well as knowledge about values (e.g., safe schools or a living wage) whose achievement may lead to the definition of the problem and its potential solutions. Knowledge about policy problems also includes at least two potential solutions to the problem and, if available, the probabilities that each alternative is likely to achieve a solution. Knowledge about policy problems plays a critical role in policy analysis, because the way a problem is defined shapes the identification of available solutions. Inadequate or faulty knowledge may result in serious or even fatal errors: defining the wrong problem.9
Figure 1.1
Multidisciplinary Policy Analysis
Expected policy outcomes are likely consequences of adopting one or more policy alternatives designed to solve a problem. Knowledge about the circumstances that gave rise to a problem is important for producing knowledge about expected policy outcomes. Such knowledge is often insufficient, however, because the past does not repeat itself, and the values that shape behavior may change in future. For this reason, knowledge about expected policy outcomes is not “given” by the existing situation. To produce such knowledge may require creativity, insight, and the use of tacit knowledge.10
A preferred policy is a potential solution to a problem. To select a preferred policy, it is necessary to have knowledge about expected policy outcomes as well as knowledge about the value or utility of the expected outcomes. Another way to say this is that factual as well as value premises are required for a policy prescription. The fact that one policy is more effective or efficient than another does not alone justify the choice of a preferred policy. Factual premises must be joined with value premises involving equality, efficiency, security, democracy, enlightenment, or some other value.
An observed policy outcome is a present or past consequence of implementing a preferred policy. It is sometimes unclear whether an outcome is actually an effect of a policy. Some effects are not policy outcomes, because many outcomes are the result of other, extra-policy factors. It is important to recognize that the consequences of action cannot be fully stated or known in advance, which means that many consequences are neither anticipated nor intended. Fortunately, knowledge about observed policy outcomes can be produced after policies have been implemented.
Policy performance is the degree to wh...