
Freight Derivatives and Risk Management in Shipping
Manolis G. Kavussanos, Dimitris A. Tsouknidis, Ilias D. Visvikis
- 520 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Freight Derivatives and Risk Management in Shipping
Manolis G. Kavussanos, Dimitris A. Tsouknidis, Ilias D. Visvikis
Información del libro
This advanced practical textbook deals with the issue of risk analysis, measurement and management in the shipping industry. It identifies and analyses the sources of risk in the shipping business and explores in detail the "traditional" and "modern" strategies for risk management at both the investment and operational levels of the business.
The special features and characteristics of all available freight derivative products are compared and contrasted between them. Practical applications of derivatives are showcased through realistic practical examples, while a number of concepts across the contents of this book appear for the first time in the literature. The book also serves as "the reference" point for researchers in the area, helping them to enhance their knowledge of risk management and derivatives in the shipping industry, but also to students at both undergraduate and postgraduate levels. Finally, it provides a comprehensive manual for practitioners wishing to engage in the financial risk management of maritime business. This second edition has been fully updated in order to incorporate the numerous developments in the industry since its first edition in 2006. New chapters have been introduced on topics such as Market Risk Measurement, Credit Risk and Credit Derivatives, and Statistical Methods to Quantify Risk. Furthermore, the second edition of this book builds upon the successful first edition which has been extensively (i) taught in a number of Universities around the world and (ii) used by professionals in the industry.
Shipowners, professionals in the shipping industry, risk management officers, credit officers, traders, investors, students and researchers will find the book indispensable in order to understand how risk management and hedging tools can make the difference for companies to remain competitive and stay ahead of the rest.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
1
Introduction to the shipping markets and their empirical regularities
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Market segmentation of the shipping industry
1.2.1 General cargo and bulk cargo movements
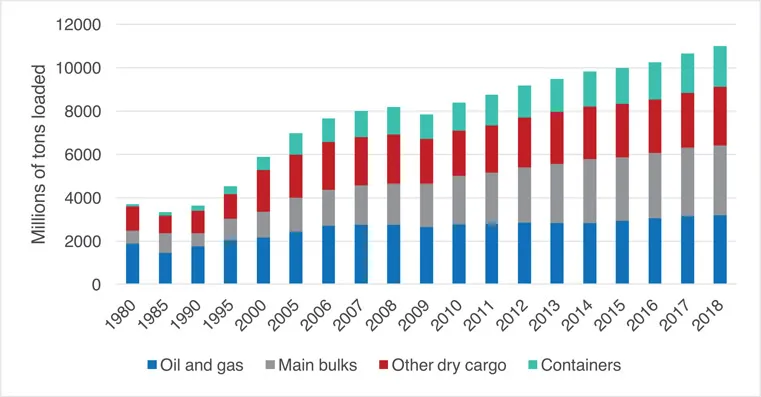
- For the period 1980 to 2005 figures for main bulks include iron ore, grain, coal, bauxite/alumina and phosphate.
- From 2006 onwards, main bulks include iron ore, coal and grain only; while bauxite/alumina and phosphate are included under “Other dry cargo”.
- Commodity demand and shipping supply forces. For instance, low value goods move in large consignments as economies of scale make the freight cost per unit very low. Such examples include the shipping transportation of crude oil, coal, iron ore, etc. The economics of the industrial processes generating the demand for raw materials and finished products of these commodities are also important. Physical characteristics of the commodities transported have a role to play, as agricultural goods, for instance, are perishable and require specialised and more expensive storage facilities – often refrigerated – in comparison to commodities such as coal and iron ore. In general, storage, insurance and financial costs must be weighed against transportation costs in the decision of charterers over what consignment size to transport.
- Cargo consignments. These are proportional to transport distances, as economies of scale are important for the long-haul transportation of commodities. It is more economical than to use larger vessels to transport commodities over long distances.
- Transport system restrictions, such as limitations in ports (i.e. maximum draught, berth size and cargo handling facilities). These may be particularly important in developing countries with limited infrastructure, and regulations dictating a certain PSD in certain regions of the world. For instance, it is not possible for large gearless vessels with deep draughts to approach certain relatively shallow ports in developing countries, and as a consequence consignment sizes and vessels used in these trades are smaller.
- Vessel availability. Consignments of over 2,000–3,000 tons can fill a whole vessel (or hold of a vessel) rather than part of a vessel and are transported in bulk. Smaller consignments, which fill only part of the vessel (or hold), move as general cargo.