
eBook - ePub
The Manual of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Abeer Feteih, Michael Fein, Natacha Tardio, Abeer Feteih, Michael Fein, Natacha Tardio
This is a test
Compartir libro
- 212 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
eBook - ePub
The Manual of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Abeer Feteih, Michael Fein, Natacha Tardio, Abeer Feteih, Michael Fein, Natacha Tardio
Detalles del libro
Vista previa del libro
Índice
Citas
Información del libro
The Manual of Allergy and Clinical Immunology provides brief clinical summaries of complex and emerging topics encountered in the field of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. As knowledge in the specialty is rapidly evolving, this book condenses this material while maintaining an evidence-based approach to the practice. It addresses recent developments in allergy and clinical immunology, as there is an increased awareness and interest in these topics due to their impact on a large cohort of the population. It is a quick 'go-to' practical and informative guide for students and residents studying for their exams as well as for clinicians in practice.
Key Features
- Serves as a handy, practical reference guide to immunologic and allergic diseases for healthcare professionals in both primary and specialty medicine, as well as a study resource for medical students and trainees
-
- Summarizes high-yield clinical information in the field to make it easily accessible and user friendly for clinicians and students
-
- Several chapters include a unique section on the management of allergic/immunologic disorders in pregnant women
-
Preguntas frecuentes
¿Cómo cancelo mi suscripción?
¿Cómo descargo los libros?
Por el momento, todos nuestros libros ePub adaptables a dispositivos móviles se pueden descargar a través de la aplicación. La mayor parte de nuestros PDF también se puede descargar y ya estamos trabajando para que el resto también sea descargable. Obtén más información aquí.
¿En qué se diferencian los planes de precios?
Ambos planes te permiten acceder por completo a la biblioteca y a todas las funciones de Perlego. Las únicas diferencias son el precio y el período de suscripción: con el plan anual ahorrarás en torno a un 30 % en comparación con 12 meses de un plan mensual.
¿Qué es Perlego?
Somos un servicio de suscripción de libros de texto en línea que te permite acceder a toda una biblioteca en línea por menos de lo que cuesta un libro al mes. Con más de un millón de libros sobre más de 1000 categorías, ¡tenemos todo lo que necesitas! Obtén más información aquí.
¿Perlego ofrece la función de texto a voz?
Busca el símbolo de lectura en voz alta en tu próximo libro para ver si puedes escucharlo. La herramienta de lectura en voz alta lee el texto en voz alta por ti, resaltando el texto a medida que se lee. Puedes pausarla, acelerarla y ralentizarla. Obtén más información aquí.
¿Es The Manual of Allergy and Clinical Immunology un PDF/ePUB en línea?
Sí, puedes acceder a The Manual of Allergy and Clinical Immunology de Abeer Feteih, Michael Fein, Natacha Tardio, Abeer Feteih, Michael Fein, Natacha Tardio en formato PDF o ePUB, así como a otros libros populares de Medicina y Medicina clinica. Tenemos más de un millón de libros disponibles en nuestro catálogo para que explores.
Información
PART 1RHINOCONJUNCTIVITIS
1 Allergic Rhinitis
Abeer Feteih, Hoang Pham, Michael Fein, Geneviève Genest, and Jaime Del Carpio
2 Rhinosinusitis
Abeer Feteih, Hoang Pham, Michael Fein, Geneviève Genest, and Jaime Del Carpio
3 Ocular Allergy
Fatemah Al-Yaqout and Abeer Feteih
4 Allergen Immunotherapy
Abeer Feteih, Walaa Almasri, Geneviève Genest, Hoang Pham, and Phil Gold
1Allergic Rhinitis
ABEER FETEIH, HOANG PHAM, MICHAEL FEIN, GENEVIÈVE GENEST, AND JAIME DEL CARPIO
DOI: 10.1201/9781003174202-2
This chapter will describe the different types of rhinitis and will mainly focus on allergic rhinitis.
GENERAL BACKGROUND
- Allergic rhinitis is an IgE-mediated inflammatory disease of the nasal mucosal membranes (1).
- It is estimated to affect around 20%–25% of Canadians (2).
- Rhinitis (atopic or non-atopic) is a risk factor for developing asthma. It is more likely that the person will develop asthma when the rhinitis is more persistent and severe (2).
- Allergic rhinitis in childhood is more frequent in boys, but in adults, it is more frequent in women (3).
- Symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) usually do not develop until 2–7 years of age (3).
- Despite the high prevalence and negative impact on quality of life and productivity, rhinitis is often overlooked and remains undertreated (1, 3–5).
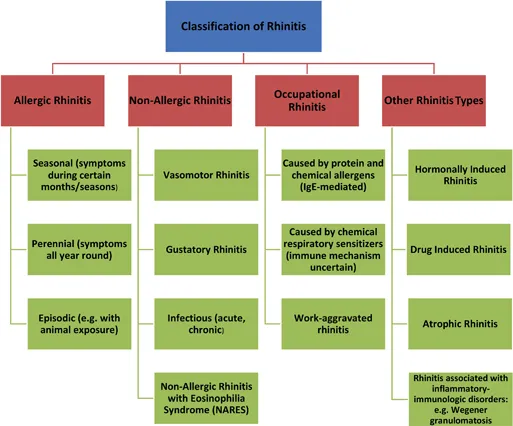
Figure 1.1Classification of rhinitis. (Figure created with BioRender.com.) [Adapted from (3).]
OTHER COMMON CAUSES OF RHINITIS
Rhinitis is a very common presentation with many potential etiologies. A focused history will guide diagnosis; aeroallergen skin testing, or specific IgE testing is required to evaluate for an allergic component (see Table 1.1).
Table 1.1 Other Causes of Rhinitis
Condition | Key suggestive features |
|---|---|
Vasomotor Rhinitis^ | Predominant rhinorrhea and nasal obstruction Triggered by temperature/humidity changes (e.g. cold air), irritants/strong odors (e.g. perfumes, smoke), exercise |
Drug-Induced Rhinitis* | Rhinitis Medicamentosa—overuses topical nasal decongestants (alpha-adrenergic agonists) for more than 3 days Patient may be taking antihypertensive medication that disrupts sympathetic/parasympathetic vascular tone leading to nasal congestion & rhinorrhea NSAIDs and alcohol can cause acute rhinitis symptoms in patients with NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease |
Hormonal Rhinitis | Associated with pregnancy, menstrual cycles, menopause, and puberty, hypothyroidism and acromegaly |
Non-Allergic Rhinitis with Eosinophilia Syndrome (NARES) | Prominent symptoms of perennial rhinorrhea and sneezing without other features of facial pain, nasal obstruction, nasal polyps, sinus mucosal thickening Marked response to intranasal steroids Eosinophilia in nasal tissues (research centers only) |
Gustatory Rhinitis^ | Clear rhinorrhea after consumption of hot and/or spicy foods |
Occupational Rhinitis | Question the patient about workplace exposures such as cold dry air, dust particulate matter, vapors, smoke, chemicals, strong odors |
Atrophic Rhinitis | Observed in young to middle-aged adults from dry climates; associated with nasal dryness, foul-smelling nasal crusts |
Infectious Rhinitis | Acute onset of fever, nasal congestion, mucopurulent nasal discharge, headache, smell disturbance, post-nasal drip, cough Lacks recurrent seasonal pattern Lacks nasal or ocular pruritus |
Local Allergic Rhinitis | Difficult to diagnose outside specialized research centres that are able to do nasal provocation tests to aeroallergens Frequently report watery rhinorrhea, sneezing, and itching despite negative conventional aeroallergen testing |
* Other causes of drug-induced rhinitis include ACE-inhibitors (e.g. perindopril), alpha-receptor antagonists (e.g tamsulosin), and phosphodiesterase 5-selective inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil). ^Vasomotor & Gustatory rhinitis may respond to intranasal anticholinergics (e.g. ipratropium). Adapted from (3–5). | |
Classification of Allergic Rhinitis [According to “Allergic Rhinitis and Its Impact on Asthma (ARIA)” (1)]
- “Intermittent”: Presence of symptoms <4 times a week or for <4 weeks
- “Persistent”: Presence of symptoms >4 days a week and for >4 weeks
- “Mild”: When none of the following are present:
- Sleep disturbance
- Impairment of daily activities, leisure, and/or sport
- Impairment of school or work
- Troublesome symptoms
- “Moderate-severe”: In the presence of ≥1 of these symptoms:
- Sleep disturbance
- Impairment of daily activities, leisure, and/or sport
- Impairm...