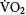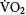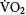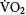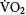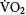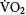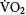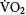![]()
Chapter 4
Armstrong N, McManus AM (eds): The Elite Young Athlete.
Med Sport Sci. Basel, Karger, 2011, vol 56, pp 59-83
______________________
Endurance Training and Elite Young Athletes
Neil Armstrong · Alan R. Barker
Children's Health and Exercise Research Centre, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK
______________________
Abstract
Endurance training consists of a structured exercise programme that is sustained for a sufficient length of time with sufficient intensity and frequency to induce an improvement in aerobic fitness. Elite young athletes generally have higher peak oxygen uptakes (peak
) than their untrained peers largely due to their greater maximal stroke volumes. Trained young athletes have faster
kinetic responses to step changes in exercise intensity but whether this is due to enhanced oxygen delivery or increased oxygen utilization by the muscles remains to be explored. Blood lactate accumulation in young athletes during submaximal exercise is lower than in untrained youth and this appears to be due to enhanced oxidative function in the active muscles. No well-designed, longitudinal endurance training studies of elite young athletes have been published. Even in the general paediatric population peak
is the only component of aerobic fitness on which there are sufficient data to examine dose-response effects of endurance training. The existence of a maturational threshold below which children are not trainable remains to be proven. The magnitude of training responses is independent of sex. Pre-training peak
has a moderate but significant inverse relationship with post-training peak
which suggests that elite young athletes are likely to experience smaller increases in peak
with further endurance training than untrained youth. Empirical evidence strongly indicates that both trained and untrained young people can benefit from endurance training but the relative intensity of exercise required for optimum benefits is higher than that recommended for adults.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel
Endurance training consists of a structured exercise programme that is sustained for a sufficient length of time and at sufficient intensity and frequency to induce an improvement in aerobic fitness. Aerobic fitness may be defined as the ability to deliver oxygen to the muscles and to utilize it to generate energy through aerobic metabolism to support muscle activity during exercise.
Peak oxygen uptake (peak
), the highest rate at which a child or adolescent can consume oxygen during exercise, is widely recognized as the best single indicator of young people’s aerobic fitness [
1]. Peak
limits the rate at which oxygen can be provided during exercise and is therefore a key component of high level performance in many sports (e.g. aspects of cycling and track athletics) but it does not describe fully all aspects of sport-related aerobic fitness [
2]. In several sports (e.g. football, hockey, basketball), intermittent exercise and the ability to engage in rapid changes of pace is at least as important as achieving and maintaining maximal aerobic performance. Under these conditions, it is the transient kinetics of
which describe the relevant component of aerobic fitness [
3]. During sustained exercise lactate accumulates within the muscle and, although output does not match production, some lactate diffuses into the blood where, during sub-maximal exercise, it accumulates and can be sampled and analysed to provide an estimate of the relative anaerobic and aerobic contribution to the exercise. Blood lactate accumulation is therefore a useful indicator of aerobic fitness with reference to the ability to sustain submaximal exercise as in long distance running [
4].
Numerous cross-sectional studies have demonstrated that elite young athletes show higher aerobic fitness than their non-athletic or untrained peers but, although interesting, these data are limited by the inability to establish cause and effect from endurance training. To determine the endurance trainability of children and adolescents (i.e. the extent to which the physiological markers of aerobic fitness change as a result of regular participation in appropriate exercise) requires longitudinal endurance training studies but understanding has been clouded by the paucity of well-designed investigations.
This chapter briefly describes the principal components of aerobic fitness, outlines studies comparing and contrasting the aerobic fitness of trained and untrained youth, and explores the mechanisms underpinning changes in aerobic fitness with endurance training. There are insufficient data to rigorously analyse the effects of endurance training on the aerobic fitness of elite young athletes. Even in the general paediatric popula...