
Learning Jupyter 5
Explore interactive computing using Python, Java, JavaScript, R, Julia, and JupyterLab, 2nd Edition
Dan Toomey
- 282 páginas
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Learning Jupyter 5
Explore interactive computing using Python, Java, JavaScript, R, Julia, and JupyterLab, 2nd Edition
Dan Toomey
Información del libro
Create and share livecode, equations, visualizations, and explanatory text, in both a single document and a web browser with Jupyter
Key Features
- Learn how to use Jupyter 5.x features such as cell tagging and attractive table styles
- Leverage big data tools and datasets with different Python packages
- Explore multiple-user Jupyter Notebook servers
Book Description
The Jupyter Notebook allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations, and explanatory text. The Jupyter Notebook system is extensively used in domains such as data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, and machine learning. Learning Jupyter 5 will help you get to grips with interactive computing using real-world examples.
The book starts with a detailed overview of the Jupyter Notebook system and its installation in different environments. Next, you will learn to integrate the Jupyter system with different programming languages such as R, Python, Java, JavaScript, and Julia, and explore various versions and packages that are compatible with the Notebook system. Moving ahead, you will master interactive widgets and namespaces and work with Jupyter in a multi-user mode.
By the end of this book, you will have used Jupyter with a big dataset and be able to apply all the functionalities you've explored throughout the book. You will also have learned all about the Jupyter Notebook and be able to start performing data transformation, numerical simulation, and data visualization.
What you will learn
- Install and run the Jupyter Notebook system on your machine
- Implement programming languages such as R, Python, Julia, and JavaScript with the Jupyter Notebook
- Use interactive widgets to manipulate and visualize data in real time
- Start sharing your Notebook with colleagues
- Invite your colleagues to work with you on the same Notebook
- Organize your Notebook using Jupyter namespaces
- Access big data in Jupyter for dealing with large datasets using Spark
Who this book is for
Learning Jupyter 5 is for developers, data scientists, machine learning users, and anyone working on data analysis or data science projects across different teams. Data science professionals will also find this book useful for performing technical and scientific computing collaboratively.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
Introduction to Jupyter
- Cell tagging
- Customizing keyboard shortcuts
- Copying and pasting cells between Notebooks
- A more attractive default style for tables
- First look at Jupyter
- Installing Jupyter
- Notebook structure
- Notebook workflow
- Basic Notebook operations
- Security in Jupyter
- Configuration options for Jupyter
First look at Jupyter
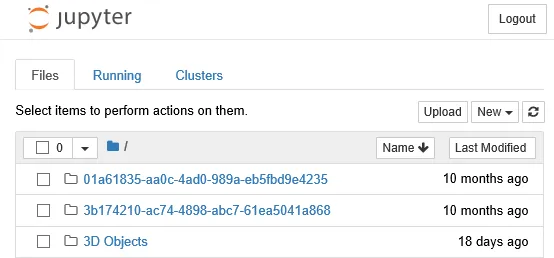
- The product title, Jupyter, in the top left (as expected). The logo and the title name are clickable and will return you to the Jupyter Notebook home page.
- There are three tabs which are displayed: Files, Running, and Clusters:
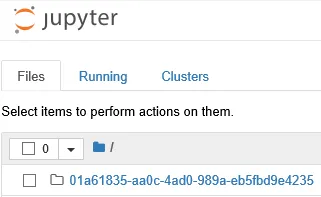
- The Files tab shows the list of files in the current directory of the page (described later on in this section).
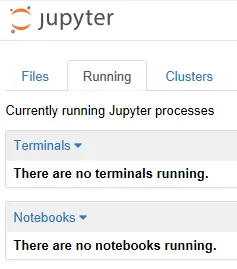
- The Running tab presents another screen, which shows the currently running processes and Notebooks. The drop-down lists for Terminals and Notebooks are populated with their running members:
- The Clusters tab presents another screen which displays a list of available clusters. This topic is covered in a later chapter:
- In the top right corner of the screen, are three buttons: Upload, New (menu), and a Refresh notebook list button.
- The Upload button is used to add files to the Notebook space. You may also just drag and drop as you would when handling files. Similarly, you can drag and drop Notebooks into specific folders as well.
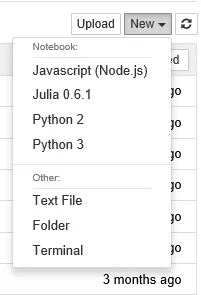
- The menu with New at the top presents a further menu of the Notebook for the different Notebook engines that have been installed (I had installed Jupyter earlier these are not default values) Javascript (Node.js), Julia 0.6.1, Python 2 (which will not be covered in this book), and Python 3. The additional Other menu items are Text File, Folder, and Terminal:
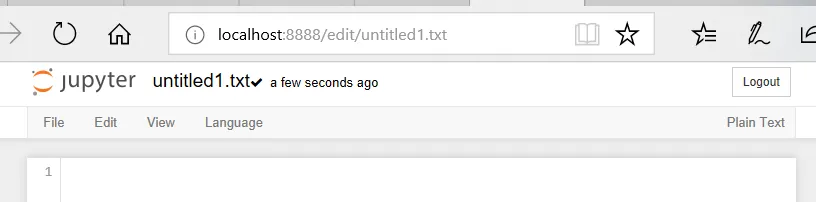
- The Text File option is used to add a text file to the current directory. Jupyter will open a new browser window for you, running a text editor. The text entered is automatically saved and will be displayed in your Notebook files and directory display:
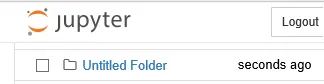
- The Folder option creates a new folder with the name Untitled Folder. Remember that all of the file and folder names are editable:
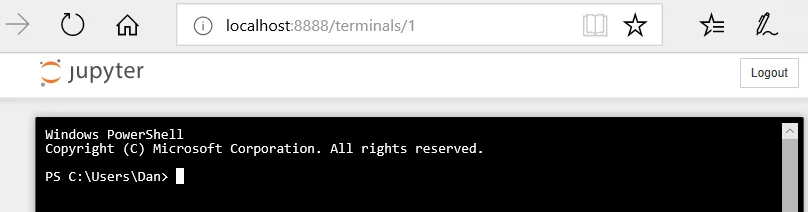
- The Terminals option is used to open a new Terminal (command) window. The resulting display on a Windows machine looks as follows:
- The Python 3 option is used to start a new Python 3 Notebook. The interface looks like it does in the following screenshot. You have full file editing capabilities for your script, including saving as a new file. You a...