![]()
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
What Is a Financial Model?
Let our advance worrying become advance thinking and planning.
— Winston Churchill
In times when the demand-supply equation may not really be conducive to business operations or may undergo erratic swings, corporate needs to have a dynamic mechanism to gauge the likely impact of the market turbulence on their fortunes and thus arises the need for financial modeling.
Among the various possible uses of the same, generating the revenue and expense forecasts is of paramount importance. In conjunction with the proposed capital expenditure plans and debt servicing obligations of the company, this could be a source of crucial insights for decision-making and foresee the possible scenarios of profitability and liquidity.
Often we build calculations depicting a real life situation, quantifying inputs/outputs of an operation or a process. We call it a calculation as long as quantum of variables and scenarios are limited. As you continue to add variables and scenarios, it takes the shape of model. In a nutshell, a model is nothing but a series of calculations (simple and/or complex) structured in a particular fashion so that it’s comprehensible.
The exercise would then act as a baseline for management’s adoption of contingency measures:
• Sprucing up their marketing efforts to streamline revenues or adopting cost-rationalization initiatives
• Scaling down of capex plans (or alternatively prioritizing between various projects) determine how much investment capital is required and thus scout for additional funding
(if required)
• Undertaking production cuts, as deemed to be appropriate, to prevent inventory build-up beyond tolerable limits
While the measures as outlined above could vary according to the unique business dynamics of the various segments of the company, it goes without saying that the exercise of creating a sound financial model would go a long way in helping management cope with uncertainty and focus on the value-creation process for stake-holders.
Companies require robust financial models to help them in analyzing the complexities of the geographies where they operate, consider multiple currencies in their projections, evaluate varying capacity as well as capacity utilizations combinations to find out the optimal capacity under varying industry demand-supply scenarios and a host of similar cases.
Part Science, Part Art
Building models is a fluid, creative activity, and there are as many ways to build a model as, say, to write a book. Most of them will result in working models, but not necessarily very good ones; there are, after all, bad books. But there are also excellent books with very different styles.
Financial modeling is an art form; to the purest MS Excel guru or financial theorist, the ability to model out a concept in your own unique style is the ultimate form of professional expression. You live and breathe a model from its inception, through multiple iterations, until its completion.
Financial modeling is part science and part art. Maybe the art part is just 10 percent but this 10 percent can change valuation from 1 Bn to 10 Bn (If not 100!). There are so many variables that impact valuation and assigning weightages to them is what the art is.
A modeler must be a good mathematician as well as someone who can think creatively and who possesses sound logic in order to pre-empt possible outcomes and make sound and reasonable assumptions about the business. Like a fortune teller, you need to be able to read the situation and ask the right questions, assess possible roadblocks and side-step potential pitfalls.
The process should always be a deliberate and thoughtful process. Spend enough time on it, step into the shoes of the user and play the Devil’s Advocate. It’s the absolute confidence and familiarity with your model that will let you take the investor’s questions head on and show that cool “Steve Jobs-esque” confidence in the face of difficult questions.
Plus no matter how complex be the underlying logic, your models should be SIMPLE TO UNDERSTAND. The intellect and interest lies in making a simple, scalable and robust model.
Concept
So let’s say, you have a power plant as follows:
You can build a working model of the power plant.
So, a model is a representation, generally in miniature, to show the construction or appearance of something.
Definition
The Oxford Dictionary defines the word model as a simplified mathematical description of a business/process. Model is a representation of reality.
What Is a Financial Model?
It is a simplified representation of company performance-both past and future performance.
In other words, financial modeling is the task of building an abstract representation of a financial decision making situation. A mathematical model is designed to represent the anticipated performance of a financial asset or a portfolio of a business, a project, or any other form of financial investment. A typical financial model would enable simulation of cost and revenue relations to support business decisions. It is prepared whenever any organization is considering project finance, bidding for a project, evaluating acquisition target, carrying out periodic financial planning, conducting capital structure studies, and so on.
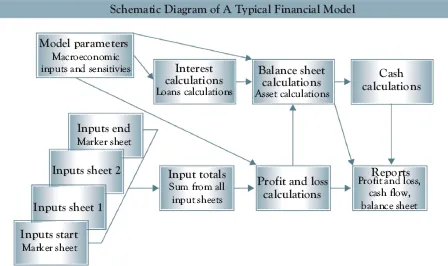
Schematic Diagram of a Typical Financial Model
A well-designed financial model has a clear purpose, flows intuitively from inputs to final outputs, is well documented, and is easy to use and read.
The core elements of a financial model are:
1. Revenue: The channels from which your business generates revenue and how much from each stream
2. Cost of Goods (COGS): The cost of selling your product or service
3. Operational Expenditures (OPEX): How much your business spends in order to sustain the scale of its day to day operations
4. Income Statement: How much net profits or losses your business will incur during a period of time
5. Cash Flow: How much cash your business generates and uses during a given time period
6. Capital Expenditures (CAPEX): Money spent acquiring or upgrading physical assets that is, property
7. Balance Sheet: Summary of a company’s assets, liabilities and share-holders equity at a given time period
8. Working Capital: How well a company manages its current assets vs. current liabilities?
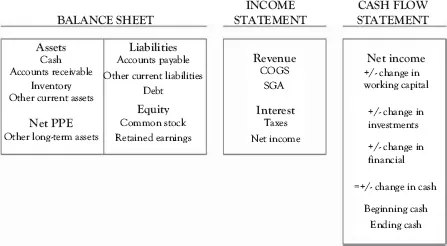
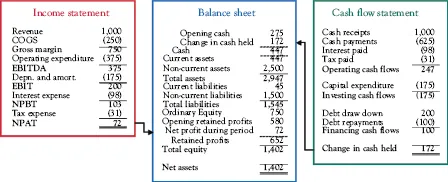
The Three Financial Statements
Flowchart of Interlinks Among the Three Financial Statements
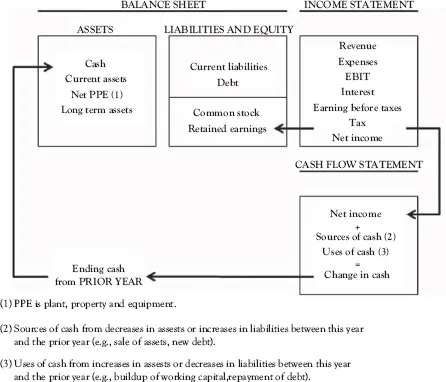
Another representation is as follows:
![]()
CHAPTER 2
Approach to Financial Modeling
Building reliable and thorough models needn’t be a ...