Pocket Guide to Teaching for Clinical Instructors
Ian Bullock, Mike Davis, Andrew Lockey, Kevin Mackway-Jones, Ian Bullock, Mike Davis, Andrew Lockey, Kevin Mackway-Jones
- English
- ePUB (apto para móviles)
- Disponible en iOS y Android
Pocket Guide to Teaching for Clinical Instructors
Ian Bullock, Mike Davis, Andrew Lockey, Kevin Mackway-Jones, Ian Bullock, Mike Davis, Andrew Lockey, Kevin Mackway-Jones
Información del libro
The Pocket Guide to Teaching for Clinical Instructors, 3rd edition, provides a concise introduction to teaching. Written by experienced medical educators from the Advanced Life Support Group and Resuscitation Council (UK), this best-selling guide gives comprehensive and practical advice on the most effective teaching methods.
Pocket Guide to Teaching for Clinical Instructors covers basic principles and practical aspects of teaching in a variety of modalities. This edition includes material which reflects current developments within instructor courses and includes new material on feedback, an awareness of non-technical skills, the teaching of teams and supporting learners.
This book is essential reading for anyone interested in teaching doctors and healthcare professionals in any context. It is aimed at the relative newcomer to the teaching role in all its variety and provides essential, practical advice as to how to get the best out of learners.
Preguntas frecuentes
Información
CHAPTER 1
Adult learning
Learning outcomes
- how adults learn
- the contribution of experiential learning
- motivation
Introduction
Knowles and the adult learner
Autonomy and self-determination
Life experience and knowledge
Unfreezing – change – refreezing
Goal orientated
Relevance orientated
Practical
… we are not machines and this course gives room for us to think and makes the whole teaching session and the teamwork alive and interesting. It opens up for discussions and that is where you really learn something – not only from the instructors but also from the other candidates.
Esteem
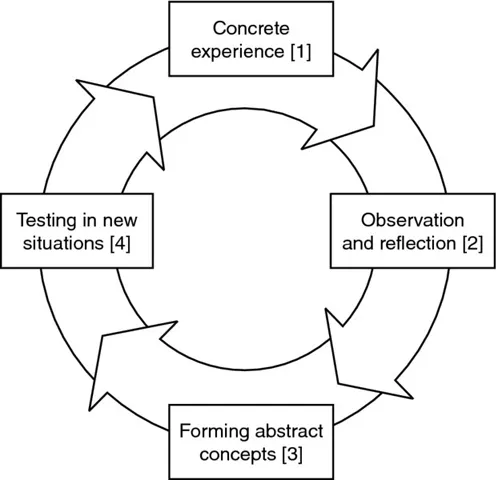
The experiential learning cycle