Business Model Generation
A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers
Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Business Model Generation
A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers
Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur
Informazioni sul libro
Business Model Generation is a handbook for visionaries, game changers, and challengers striving to defy outmoded business models and design tomorrow's enterprises. If your organization needs to adapt to harsh new realities, but you don't yet have a strategy that will get you out in front of your competitors, you need Business Model Generation.
Co-created by 470 "Business Model Canvas" practitioners from 45 countries, the book features a beautiful, highly visual, 4-color design that takes powerful strategic ideas and tools, and makes them easy to implement in your organization. It explains the most common Business Model patterns, based on concepts from leading business thinkers, and helps you reinterpret them for your own context. You will learn how to systematically understand, design, and implement a game-changing business model--or analyze and renovate an old one. Along the way, you'll understand at a much deeper level your customers, distribution channels, partners, revenue streams, costs, and your core value proposition.
Business Model Generation features practical innovation techniques used today by leading consultants and companies worldwide, including 3M, Ericsson, Capgemini, Deloitte, and others. Designed for doers, it is for those ready to abandon outmoded thinking and embrace new models of value creation: for executives, consultants, entrepreneurs, and leaders of all organizations. If you're ready to change the rules, you belong to "the business model generation!"
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Section 1
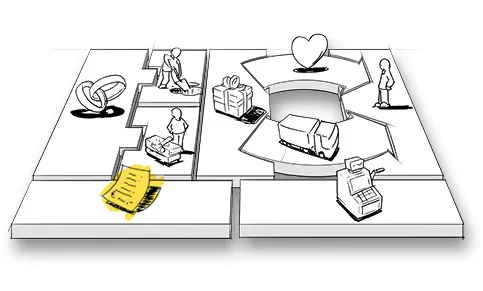
Canvas
The Business Model Canvas
Chapter Contents
- Definition of a Business Model
- The 9 Building Blocks
- The Business Model Canvas Template
Def_Business Model
The 9 Building Blocks





9
C$ Cost Structure