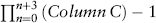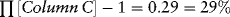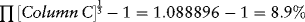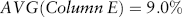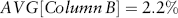Investment Theory and Risk Management
Steven Peterson
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Investment Theory and Risk Management
Steven Peterson
Informazioni sul libro
A unique perspective on applied investment theory and risk management from the Senior Risk Officer of a major pension fund
Investment Theory and Risk Management is a practical guide to today's investment environment. The book's sophisticated quantitative methods are examined by an author who uses these methods at the Virginia Retirement System and teaches them at the Virginia Commonwealth University. In addition to showing how investment performance can be evaluated, using Jensen's Alpha, Sharpe's Ratio, and DDM, he delves into four types of optimal portfolios (one that is fully invested, one with targeted returns, another with no short sales, and one with capped investment allocations).
In addition, the book provides valuable insights on risk, and topics such as anomalies, factor models, and active portfolio management. Other chapters focus on private equity, structured credit, optimal rebalancing, data problems, and Monte Carlo simulation.
- Contains investment theory and risk management spreadsheet models based on the author's own real-world experience with stock, bonds, and alternative assets
- Offers a down-to-earth guide that can be used on a daily basis for making common financial decisions with a new level of quantitative sophistication and rigor
- Written by the Director of Research and Senior Risk Officer for the Virginia Retirement System and an Associate Professor at Virginia Commonwealth University's School of Business
Investment Theory and Risk Management empowers both the technical and non-technical reader with the essential knowledge necessary to understand and manage risks in any corporate or economic environment.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
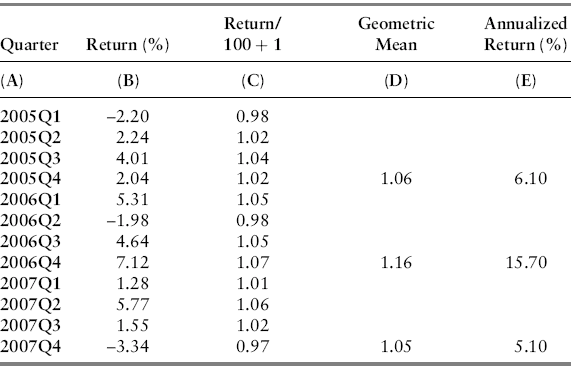
Estimating Returns
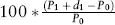
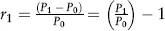
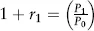
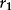
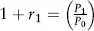
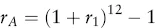
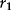
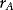
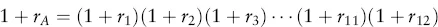
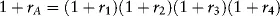
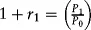
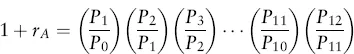
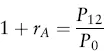
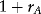
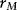
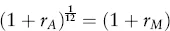
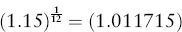
| Date | Return (%) |
| 2005Q1 | –2.20 |
| 2005Q2 | 2.24 |
| 2005Q3 | 4.01 |
| 2005Q4 | 2.04 |
| 2006Q1 | 5.31 |
| 2006Q2 | –1.98 |
| 2006Q3 | 4.64 |
| 2006Q4 | 7.12 |
| 2007Q1 | 1.28 |
| 2007Q2 | 5.77 |
| 2007Q3 | 1.55 |
| 2007Q4 | –3.34 |