
eBook - ePub
Liminal Thinking
Create the Change You Want by Changing the Way You Think
Dave Gray
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 184 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Liminal Thinking
Create the Change You Want by Changing the Way You Think
Dave Gray
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
"Why do some people succeed at change while others fail? It's the way they think! Liminal thinking is a way to create change by understanding, shaping, and reframing beliefs. What beliefs are stopping you right now? You have a choice. You can create the world you want to live in, or live in a world created by others. If you are ready to start making changes, read this book."
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Liminal Thinking è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Liminal Thinking di Dave Gray in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Personal Development e Conflict Resolution. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
PART 1
How Beliefs Shape Everything
The following six principles constitute a theory of beliefs: how they come into being, why they are necessary, how they are reinforced over time, and why people cling to their beliefs, even when they are incomplete, obsolete, or invalid. They are beliefs about beliefs.
PRINCIPLE
1
Beliefs Are Models
Reality leaves a lot to the imagination.
—John Lennon

There is an ancient story called The Blind Men and the Elephant. It’s told often, so it’s likely you have heard it, but it’s an important story to understand, so I will repeat it just in case.
A king calls for the blind men of the capital to be brought to his palace. He has an elephant brought in and asks the men to describe it. The king asks the blind men, “Can you tell me, what sort of thing is an elephant?” One man, who felt the elephant’s head, says it is like a large pot. Another, who felt the tail, says it is like a rope. Another, who felt the ear, says it is like a hand fan. Another, who felt the side, says it is like a wall. More blind men are called, and they say that it is like a pillar, a pipe, and so on. Each describes a different part of the elephant based on his personal experience. The blind men begin to argue and come to blows, each asserting that he is right and the others are wrong.
What is going on in this story? Each blind man has a grip on one aspect of reality, but none of them holds the whole truth. Each man’s picture of the elephant is constrained by the boundaries of his own experience.
Why can’t they just talk to each other? If they would only compare notes, they could get a better picture of the whole elephant. It probably wouldn’t be perfect, but it would be much, much better.
What is wrong with these men?
The problem is that they cannot separate their experiences from reality. Each man experiences something different. One can feel something that is like a fan, another like a rope, another like a pillar, another like a wall. Imagine you were looking at a wall and someone told you it was a pillar. You would think they were insane.
The parable makes sense because we know the men are blind. None of them can see the whole elephant. But the point of the story is not that blind men cannot see. The point of the story is that we are all blind.
Just as one pair of hands cannot touch everything in the world, one pair of eyes cannot see everything in the world. One mind cannot know everything there is to know. We all can grasp some fragments of reality, but none of us have a grasp on reality as a whole.
This is not the same as saying everything is subjective. We can agree that there is a real world, an objective reality that we all share. At the same time, we must confront the fact that as human beings, the ways we experience that reality are inherently unique and subjective.
Einstein once said that it was his religion to believe in the existence of a real world, because he could not prove it.1
Let’s adopt Einstein’s religion and assume that we can agree that there is a valid, objective reality. We must still admit that any understanding we can gain of the world will be limited by our point of view. We all know some things, but nobody can know everything. Reality as a whole is unknowable.
For example, if I say the word elephant, I am conjuring an idea into your head. This idea is based on the sum total of your life experiences involving elephants. If you have lived or worked in close proximity to elephants for long periods of time, that idea is probably closer to reality than the idea of someone who has never seen an elephant.
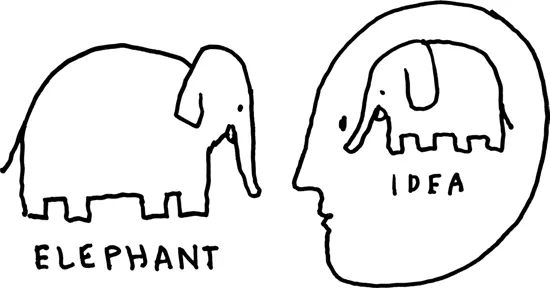
Having an idea of an elephant in your head is not the same thing as having a real elephant in your head! But we confuse our ideas about reality with the real thing all the time. Often, this is when we start arguing like those foolish blind men.
This is what the story of the blind men and the elephant is all about. We are all blind. Reality is like the elephant. We may be able to grasp pieces of the truth, but the whole truth about reality is unknowable.
Reality is something that is out there. It has a concrete existence, whether you believe it or not. A belief is something you hold in your mind, a kind of map or model of that external reality. But just as maps and models can be wrong, so can beliefs. And just as following the wrong map can get you into dangerous places, a wrong belief can get you into trouble.
When people confuse their beliefs with reality, they get into arguments and conflicts, sometimes even wars.
Have you ever had an argument with someone in your family—your spouse, your child, or your parent—over something you thought was obvious?
Have you ever seen two people read the same news article, only to get into a heated argument about whether it’s true, or what it means? This is especially common among people of different political persuasions. These arguments are based on different beliefs. But because people confuse their beliefs with reality, they say the other side is stupid, evil, or crazy. That’s a belief, too, and a very dangerous one.
Have you felt the frustration that the person you are arguing with must be obtuse, an idiot, or simply crazy, amazed that they just can’t see something that is blatantly evident and glaringly obvious?
You were engaging in a battle for the obvious.
Just because something seems obvious to you doesn’t necessarily mean it’s so. But in the heat of an argument, when your emotions are aroused, this is nearly impossible to see.
Beliefs are not reality. They are not facts. They are constructions. You construct your beliefs, even though for most people this is an unconscious process. By beliefs, I mean everything you know.
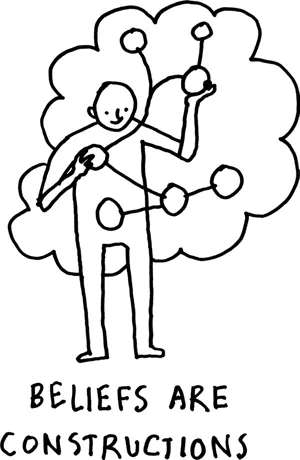
This does not mean that your beliefs are wrong, but it does not mean they are right either. In most cases, the question of whether a belief is right or wrong is a kind of distraction. Like the blind men and the elephant, it’s often the case that people see the same thing, but they see it differently, and the argument over who is right and wrong distracts them from learning or doing anything productive with the situation they find themselves in.
The obvious is not obvious.
Even the obvious. Especially the obvious.
All beliefs are approximations, because the whole of reality is unknowable. Any scientist who is worth her salt will tell you this. Beliefs may have some truth to them, but all of us are fallible, and so are our beliefs.
Buddha said his teachings were like a finger pointing at the moon. The finger is helpful if you want to see the moon, but you should not mistake the finger for the moon.
It’s the same with beliefs. They are like fingers pointing at the reality, which is the moon. Do not mistake the belief for the reality!

Liminal thinking is learning to see that there are many “obviouses”—and that what is obvious depends on your experiences and your point of view. It also means cultivating the ability to listen and to pay attention to “obviouses” that are different than yours. If one of the blind men had decided to move in a circle around the elephant, and felt what others were feeling, he would have been operating in a liminal way, challenging his own assumptions and beliefs.
The obvious is not obvious.
PRINCIPLE 1
Beliefs are models.
Beliefs seem like perfect representations of the world, but, in fact, they are imperfect models for navigating a complex, multidimensional, unknowable reality.
PRINCIPLE
2
Beliefs Are Created
The map is not the territory.
—Alfred Korzybski
Around noon on August 9, 2014, a hot summer day in Ferguson, Missouri, a young black man named Michael Brown was shot and killed by a white police officer named Darren Wilson.
Although there were several witnesses to the shooting, their stories about what happened varied widely.
In the following days and weeks, the mostly black population clashed with the mostly white police force of Ferguson in an escalating series of protests, riots, and police clamp-downs.
This is not a new pattern in the United States. It is a recurring one that has been happening for years. Even as I write this, a similar pattern is unfolding in Baltimore, after a young black man named Freddie Gray died of a broken neck while in police custody.
Every time something like this happens, a battle for the obvious unfolds in the news media, in living rooms, on social media, and elsewhere.
In one narrative, police are the frontline enforcers of a racist society that systemically oppresses black people, where poverty and hopelessness generate legitimate frustration and anger.
In another narrative, racism may be a real problem, but poor people are responsible for their own poverty and for pulling themselves out of it. The police are just doing their job, and unfortunately, sometimes people get hurt. If people didn’t break laws and resist arrest, they wouldn’t be hurt by the cops.
There are other narratives, too—many of them, too many to go into here.
The competing narratives are so different that they seem like different versions of reality, which is exactly what they are.
You can see similar battles for the obvious in media and politics all over the world, in debates about taxes, guns, religion, immigration, health ca...