ISTE Standards
This chapter addresses several ISTE Standards for Educators.
1. Learner
Educators continually improve their practice by learning from and with others and exploring proven and promising practices that leverage technology to improve student learning. Educators:
a. Set professional learning goals to explore and apply pedagogical approaches made possible by technology and reflect on their effectiveness.
5. Designer
Educators design authentic, learner-driven activities and environments that recognize and accommodate learner variability. Educators:
a. Use technology to create, adapt and personalize learning experiences that foster independent learning and accommodate learner differences and needs.
6. Facilitator
Educators facilitate learning with technology to support student achievement of the 2016 ISTE Standards for Students. Educators:
b. Manage the use of technology and student learning strategies in digital platforms, virtual environments, hands-on makerspaces or in the field.
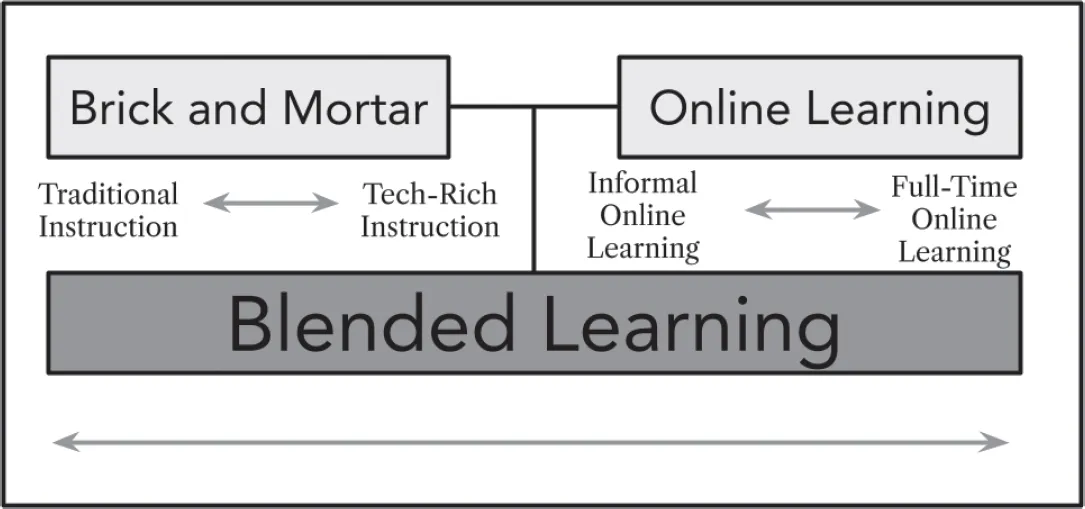
Models of Blended Learning
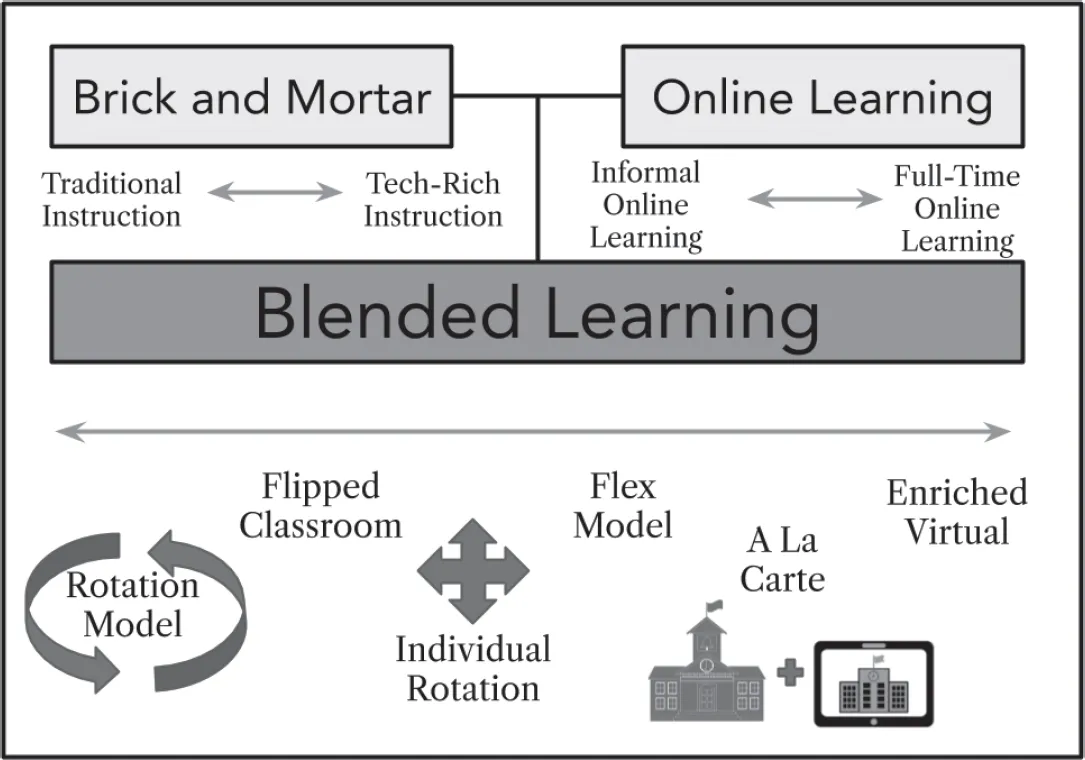
A leader in blended and personalized learning research, the nonprofit Clayton Christensen Institute focuses on the tools and strategies necessary to solve problems we face in the modern classroom. In research studying the various ways blended learning was being implemented around the country, for example, the Clayton Christensen Institute found that most blended classrooms follow one of seven models (Horn & Staker, 2014). Although a basic understanding of these models and the various ways you can blend your classroom is important, don’t become bogged down trying to replicate any specific model exactly. Feel free to embrace the flexibility of blended learning and to combine pieces of the models described below with your own ideas to create the perfect blend for your students.
Station Rotation
The Station Rotation Model is one that will feel familiar to many elementary school teachers. In this model, the teacher sets up stations for groups of students to move through during class time. The teacher determines the group members and time spent at each station. The number of stations that students move through can vary. Generally, at least one station should be devoted to small group instruction with the classroom teacher. A teacher can incorporate online learning into one of the stations. Students can do partner and group work, projects, or other offline activities at the remaining stations.
Lab Rotation
The Lab Rotation Model incorporates traditional, face-to-face classroom instruction with online instruction that happens in a lab. Students move on a teacher-determined schedule. At least one of the stops on a student’s schedule is a computer lab. In the computer lab, students can work on online learning. In many examples of a Lab Rotation Model, paraprofessional staff members help facilitate the lab, while certified staff provide instruction in other classrooms.
Students move from classroom to classroom receiving face-to-face instruction and online instruction in the computer lab. This model is similar to the Station Rotation Model, with the primary difference being in the physical location of the learning.
Individual Rotation
Another model that is similar to the Station Rotation Model, the Individual Rotation Model once again features stations, one of which features online learning. However, in this model, students do not move with a set group of peers. They each have an individual, personalized schedule. Students move to different stations on a set schedule, but they may not go to all of the stations. This is a highly personalized experience for the students that requires a great deal of planning on the part of the teacher if technology is not available to automate this scheduling.
One of the greatest benefits of this model is the customization based specifically on student needs. Unlike the previous models, students do not have to go through every modality for every lesson. They get exactly the kind of instruction they need at exactly the right time (Reading Horizons, 2019).
Flipped Classroom
The Flipped Classroom Model is based on the concept of flipped learning, one of the first forms of blended learning that became popular in traditional classrooms. The basic premise of flipped learning is that online learning is used as a homework tool, freeing up the teacher during class time to help with student application. The online learning portion of the instruction could be as simple as a video lecture that students watch at home. Students could work through more sophisticated online lessons at home as well.
Online learning is used in this instance as a way to make the best use of the teacher’s classroom instruction time. In a traditional model, homework is how students get dedicated time to practice a skill. The inherent problem with this is the absence of the teacher when a student does not fully understand. In the worst-case scenario, students practice something the wrong way, making it even more difficult for them to eventually master the skill.
Under the Flipped Classroom Model, instead of spending class time providing basic instruction, teachers are able to essentially replicate themselves. The teacher moves the basic instruction online in a carefully crafted assignment and is “present” when the student is learning at home. The teacher then dedicates subsequent in-class time to helping students apply that learning, avoiding the homework practice dilemma.
Flex
The Flex Model of blended learning is very similar to the Individual Rotation Model with two main differences: Online learning plays a heavier role in the Flex Model, and the teacher’s role in this environment is different as well. The teacher provides much of the instruction online and creates offline supports for the students.
According to the Clayton Christensen Institute (2019), “the Flex Model lets students move on fluid schedules among learning activities according to their needs.” Additionally, students have a greater amount of control in this particular environment. Many classrooms using the Flex Model look more like neighborhood coffee shops than traditional classroom spaces, with flexible seating to replicate the student choice that is a part of this model.
A La Carte
The A La Carte Model uses online learning in a much different capacity. Instead of integrating traditional instruction with online instruction within the same course, this type of model blends a student’s schedule. A school or district can offer individual courses online to supplement a student’s course schedule at a brick-and-mortar school. Some classes can be taken completely online, and others are taken completely face-to-face.
Enriched Virtual
The Enriched Virtual Model uses online learning as the primary vehicle for instructional delivery. This method of instruction allows the students to complete the majority of their work outside of a traditional brick-and-mortar setting. Because it is still a blended learning model and not fully online, students are asked to come for face-to-face learning sessions at specific times. Onl...