![]()
—— 1 ——
Introduction:
The Contextual Framework
Think in anticipation, today for tomorrow, and indeed, for many days. The greatest providence is to have forethought for what comes.
—Baltasar Gracian, Spanish Jesuit
It is the last lesson of modern science, that the highest simplicity of structure is produced, not by few elements, but by the highest complexity.
—Ralph Waldo Emerson Goethe; or, the Writer (1850)
It has become commonplace to describe today’s organizational environment as messy, frenzied, disordered, and even chaotic. At the simplest level, observers attribute this condition to the increasing pace of change, often citing advances ranging from new applications for robotics and laser technologies to the emergence of nanotechnologies to the potential benefits of quantum computers and genetic engineering. Indeed, there is near unanimity that the world has entered an era of unparalleled turbulence, reflecting the entwined forces of technological, biotechnological, and communication advances. It is not unusual for managers to note the vagaries and increased competition of a new global marketplace along with the unrelenting demands by customers for improved quality accompanied by their limited loyalty to their service and product providers. Yet other observers and practitioners note the challenges of recruiting, developing, and managing the new workforce, characterized by greater diversity in ethnicity, age, and education, and exacerbated by worker demands for new experiences and increased responsibility. Still others highlight the ongoing redesign of organizations to be more responsive to their environments, the management of knowledge, and the importance of continuous reinvention and transformational leadership. As projected by Senge et al. (1999:3):
Look ahead twenty or thirty years. Does anyone expect the next twenty years to be less tumultuous than the last twenty years? Given the changes expected in technology, biology, medicine, social values, demography, the environment and international relations, what kind of world might humanity face? No one can say for sure, but one thing is reasonably certain: Continuing challenges will tax our collective abilities to deal with them. Failure to rethink our enterprises will leave us little relief from our current predicaments.
Equally important, as put forth by Mazmanian (2004:1), the impact is far-reaching:
The dynamic forces of technological innovation, market orientation, increased mobility, global competition, deregulation, and changing public expectations and needs are affecting every major aspect of the economic, political, and social spheres of society. This is profoundly challenging those in business, government, and civic society to adapt or be relegated to the sideline of history. There are winners and losers emerging from the transformation between old- and new-age businesses, innovative and traditional governments, between works within and across industries, between different regions of the nation and around the globe, between professions and those with different skill sets, and between those with the talents and aptitude to succeed in the more rapidly changing world of information and technology than the more stable arrangement of the past age.
Operating in such an environment tends to be emotionally and physically taxing, akin to Vaill’s (1989: ch. 1) observation that we have entered a world of “permanent white water,” where the old operational rules are inadequate and leaders are asked to take on greater responsibility for what is less and less controllable. As asserted by Lissack and Roos in The Next Common Sense (2000:inside flap), organizational environments have shifted from being complicated to being complex:
The old common sense was about how to deal with the separate and freestanding units of a complicated world. The next common sense is about mastering the complex swirl of interweaving events and situations around us…. The new world is a complex one of arrows rather than boxes, of interactions rather than entities.
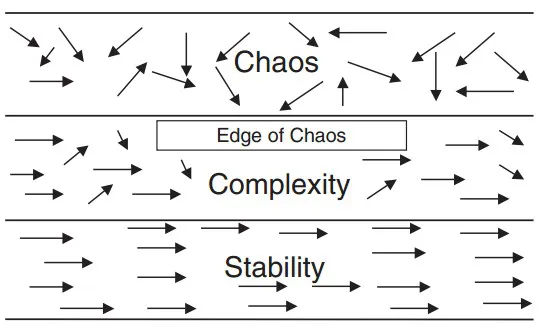
Figure 1.1
Organizational Environments
It is argued that today’s leaders must abandon organizational designs and accompanying processes based on the Newtonian concept of an orderly, predictable universe that assumes an understanding of each component leads to an explanation of the whole; rather, leaders must embrace the emergent complexity sciences and accept the notion of nonlinear systems where subtle, perhaps unobservable, events can dramatically impact their organizations (c.f., Stacy et al., 2002; Marion, 1999; Brown and Eisenhardt, 1998; Wheatley, 1992). It negates the view that stability is a primary metric for organizational excellence (Stacy, 1992:43–44).
We have adopted the phrase turbulent times to capture both the increasing pace of change and the uncertainty or dynamics of organizational environments.1 As shown in Figure 1.1, turbulence (as demonstrated by the arrows) occurs in two worlds: Chaos, where we intellectually know that order exists, but we also understand that we cannot discern that orderly state within the organizational environment, and (2) Complexity, bounded by stability on one side and chaos on the other, where overall directional order is identifiable, but the organization continually experiences unexpected “lightning bolts” from or “stochastic shocks” within the environment. As explained by an executive friend from the consumer products industry:
It seems that nearly every day I receive surprising information about a competitor’s new or improved product, or a distributor’s logistical problems, or a major customer’s unhappiness with our service, or even a legal action that requires my involvement—it is very, very difficult to stay focused on our strategic initiatives…. I have simply accepted that I live with continuous uncertainty; I live on the edge of chaos … and that my job is to make sure that others do not lose sight of the ends we seek.
From our perspective, this statement describes the world where today’s leaders must increasingly make their strategic choices. And, as noted by Weick (2001:153), “stochastic environments represent a moving target for learning because they can change faster than people can accumulate knowledge about them. When recurrence is scarce, so is learning.”
Defining Turbulence
Environmental turbulence, as defined by academe, is an extension of environmental uncertainty, which is typically defined by two factors:
1. Environmental complexity: This refers to the number, strength, and dissimilarity of external forces or pressures (e.g., competitive actions, technological advances, economic conditions) affecting an organization (Child, 1972). The greater the number and heterogeneity of these forces, the more complex the environment and, consequently, the more difficult to predict and control.
2. Dynamism: This refers to (a) the predictability with which the aforementioned forces are changing and (b) the actual rate of change of the forces (Miller and Friesen, 1983). A dynamic environment occurs when the forces shift quickly and/or abruptly with little or no warning (Jurkovich, 1974; Dess and Beard, 1984; Duncan, 1972).
The more complex and dynamic an organization’s environment, the more uncertain it becomes. When multiple forces in an organization’s environment change simultaneously, the environment is said to be turbulent (Daft, 1998; McCann and Selsky, 1984). We need to note, however, that individuals can experience the same environment differentially. As summarized by Hatch (1997:89), “The same environment might be perceived as certain by one set of managers and uncertain by another … environments do not feel uncertain, people do.” In fact, McCann and Selsky (1984:461) assert that only when the environmental conditions make an individual’s continued adaptation survival uncertain, can the label turbulent be truly applied. And, as McCann and Selsky also note (1984:460), sometimes the environment becomes hyperturbulent, that is, the environmental forces are beyond the adaptive capacity of the organization’s management.
Therefore, to understand strategy making in turbulent times, it is necessary to understand the individual perspective on the environment. If Einstein believed that time is relative to the entities experiencing it, would it not be the same for turbulence?
A Cross-Sector Phenomenon
Since the publication of books such as Managing in Turbulent Times (Drucker, 1993), Hypercompetition (D’Aveni, 1994), Blur (Myer and Davis, 1998), and Competing on the Edge: Strategy as Structured Chaos (Brown and Eisenhardt, 1998), there has been a tendency to attribute this era of turbulence primarily to the private sector, particularly high-technology organizations. Such a conclusion would be wrong! In the public sector, for instance, Peters and Savoie (2001:3, 6–7) foresee a disordered future for government:
The si...