![]()
1
Some Demographic Fundamentals
1.1 Introduction
Demography is the study of population structure and change. With the increasing complexity of modern society, it is becoming ever more important to be able to measure accurately all aspects of change in the size and composition of the population, and to be able to make estimates of what the future size and composition of the population might be. Demographers are the professionals who carry out this task.
This book attempts to describe and explain the methods which demographers use to achieve their aim. It considers the particular processes which are within the purview of demography. It shows how these processes may be measured, and how their operation in different populations, and in the same population over time, may be compared.
The subject matter of this book is sometimes referred to as formal demography, to distinguish it from the broader field of population studies. The latter field involves not only the measurement of demographic processes but also the study of their relationships to economic, social, cultural and biological processes. Readers who are interested in this broader field will find a good introduction in Daugherty and Kammeyer (1995).
This introductory chapter sets the scene for what is to follow. In Section 1.2 the fundamental demographic processes are listed. In Section 1.3 we show how the operation of demographic processes can be viewed in terms of people making transitions between a relatively small number of definable states, or conditions. Section 1.4 describes how demographers typically measure the speed at which people are making these transitions. In Section 1.5 the idea of population heterogeneity is introduced.
The analysis of demographic change relies on the availability of accurate data about the relevant population characteristics and processes. In Section 1.6 the main sources of data are briefly described. We shall not devote a lot of space to a general description of data sources. There are a number of good introductions available elsewhere (see the list of further reading towards the end of this chapter). In later chapters, however, the characteristics and limitations of particular sources in the context of specific applications of demographic analysis will be discussed.
1.2 The basic demographic equation
One of the fundamental facts about population change is that populations only change because of a limited, countable, number of events. For example, consider the population of a country. Suppose that this country at some time t contains Pt persons, and that 1 year later it contains Pt+X persons. Then we can write down the following equation:
Pt+1 = Pt + Bt − Dt + It − Et(1.1)
where Bt and Dt are respectively the number of births and deaths occurring in the population between times t and t + 1, and It and Et are respectively the number of immigrants to and emigrants from the country during the same period.
The quantity Bt− Dt is known as the natural increase (if the number of deaths exceeds the number of births, then we have Dt> Bt, which implies negative natural increase, or natural decrease). The quantity It— Et is known as the net migration.
Equation (1.1) is often referred to as the basic demographic equation, or sometimes as the demographic balancing or accounting equation. It says that a country’s population size can only change because of three types of event: births, deaths and migration. These three events are known as components of population change.
The process by which a population bears children is known as its fertility, and the process by which the members of the population are reduced by death is known as mortality. Fertility, mortality and migration are, therefore, the three fundamental demographic processes. Chapters 2–6 of this book consider the analysis of mortality, Chapters 8–11 are concerned with the analysis of fertility, and Chapter 15 is an introduction to the analysis of migration. Fertility, mortality and migration are, however, not the only processes of interest to demographers. Other processes which are studied include, for example, marriage and divorce, which we consider in Chapter 7.
1.3 Demographic processes as transitions between states
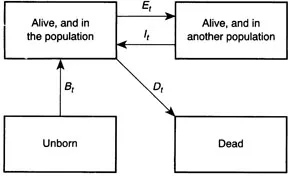
One way of representing the components of population change is to view them as a set of transitions made by individuals between various states. The basic demographic equation may, in this way, be represented by four states: ‘alive, and in the population’; ‘alive, but in another population’; ‘not yet born’; and ‘dead’.
The components of demographic change are then represented by transitions between these states (Figure 1.1). Notice that in some cases, transitions between two states can take place in both directions, whereas in other cases a transition in only one direction is possible. A state which people can never leave (for example, ‘dead’) is called an absorbing state.
Figure 1.1 Multiple-state representation of the basic demographic equation; Bt, Dt Et and It represent transitions (see text for definition of symbols)
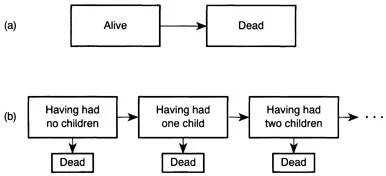
Figure 1.2 Two further examples of multiple-state representations
This way of viewing demographic processes may be called a multiple-state representation. Multiple-state representations are increasingly popular in demography, and often help demographers to understand complex processes.
Two further examples, drawn respectively from the analysis of mortality and the analysis of fertility, illustrate their usefulness in enabling demographers to conceptualize the processes they wish to study. First, mortality may be viewed as a single transition from the state ‘alive’ to the state ‘dead’ (Figure 1.2a). Second, women who are in the process of bearing children can be viewed as moving successively through the states ‘having had no children’, ‘having had one child’, ‘having had two children’, and so on (Figure 1.2b). Multiple-state representations will be used from time to time during this book.
1.4 Demographic rates
Understanding population change involves measuring and analysing its components: in the multiple-state representation it involves measuring the ‘speed’ with which the population is making the transitions between various states.
The simplest measure of any transition is the number of events which occur in a given time period. However, this is of little use for practical purposes since it is heavily influenced by the number of people who are around to experience those events. Clearly, the more people there are, the more births and deaths there are likely to be. For comparative work, what is needed is a way of measuring the number of the transitions in relation to the population size.
Demographers therefore measure events in terms of rates. A demographic rate is normally defined as
It is sometimes referred to as an occurrence/exposure ratio, because the numerator is the number of occurrences of an event (within a given period), and the denominator measures the population exposed to the risk of experiencing that event. Reflecting this, the denominator of a rate is often called the exposed-to-ri...