![]()
Chapter 1
The microelectronic system
Introduction
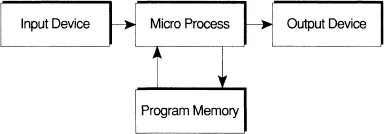
This book provides an introduction to microelectronic systems, and one of the best ways to learn about them is to study not just microelectronics, but the architecture, use and programming of a microcomputer system. It will soon become obvious what the differences between the two are, and how a micro-electronic system can be set up to do a specific job. A microelectronic system can be represented as shown in Figure 1.1. Many people now have a personal computer (PC), and those who don't will probably know what one is. A PC is an example of a microelectronic system, specially configured as a micro-computer, with a ‘typewriter style’ keyboard, video display unit (VDU) and disc drive as a minimum.
Figure I.1 A basic microprocessor system.
In the system shown, there is no keyboard, VDU or interfaces for tape or floppy disc storage. It does not (necessarily) represent a microcomputer system (although it could do) because a microelectronic system is dedicated to performing a particular task programmed into its memory. It doesn't (usually) need a keyboard or VDU since it might be designed to control a motor car or a washing machine, for example.
To get the system to perform a different routine requires that the memory device be reprogrammed or substituted by a device with a different program in it. The microprocessor used in the car could be exactly the same as the one used in the washing machine; it is simply controlled by a different program and once programmed, the system performs one specific task.
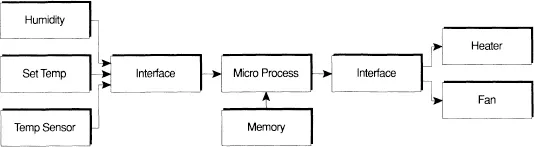
A more detailed microelectronic system is shown in Figure 1.2. This is a simple central heating and air-conditioning system. There are three input devices: a humidity detector, a temperature setting control and a temperature sensor. The output consists of a heater and a fan. Both input and output devices require interfaces, electronic circuits which adapt the outputs of the input devices to make them suitable for inputting to the microprocessor, and adapt the outputs of the microprocessor to enable them to drive the fan and the heater. The memory chip holds the program which tells the microprocessor what to do.
Figure 1.2 A microprocessor controlled heating system.
The program may turn the fan on only when the humidity reaches a specific level; the heater may be turned on when the temperature drops below a specific level and so on. The great flexibility of this system is demonstrated by the fact that the addition of more input sensors, or output devices, and the conditions under which they operate, can all be accommodated by changing the program in the memory.
Some program memories are on a silicon ‘chip’ which can be reprogrammed (e.g. an EPROM – erasable programmable read only memory); others are permanent. The choice of which to use depends upon the application and this will be discussed later.
The silicon chip
Most people will have heard of the ‘silicon chip’. There are many such devices, but the words are usually taken to mean a microprocessor. The heart of any computer is something called a central processing unit (CPU), the microprocessor (MPU) is simply a CPU which has been considerably reduced in size using modern integrated circuit technology. This ‘computer on a piece of silicon’ is so small, it's probably no bigger than the nail on your little finger. How the microprocessor functions and how it is ‘programmed’ is what we are about to investigate. Machine code programming will be discussed – this is the code that the microprocessor actually ‘understands’.
Some home computer users program in ‘BASIC but this is only for the users’ convenience. An interpreter inside the computer converts the BASIC program into machine code. This slows down program execution hundreds of times and increases the cost of the system. Hence, using machine code programming speeds up operation dramatically and uses less ‘firmware’.
The hardware
The book will be most useful to readers who have access to a microprocessor system such as the L J Technical Systems ‘MARC (Z80) or ‘EMMA’ (6502) Microcomputer (an ‘embedded system’), but this is not essential. Much of the text refers to the Z80 CPU, and so can be read in conjunction with any Z80-based system, such as the simple ‘Micro Professor’, or a comparable 6502 system. Most IBM PCs can run Z80 emulators which are software packages enabling machine code programs to be created and run on a PC.
Alternatively, manufacturers such as L J Technical Systems supply micro-processor-based controllers as ‘target systems’ for a host PC. This means that the Z80/6502-based system is connected to the PC which is then used to create and run machine code programs. We concentrate on Z80 and 6502 CPUs simply because they are now the most widely used 8-bit processors in education and industry. They are commonly available at minimal cost and are adequate for thousands of applications where the increased s...