Welding Metallurgy
Sindo Kou
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Welding Metallurgy
Sindo Kou
Informazioni sul libro
Discover the extraordinary progress that welding metallurgy has experienced over the last two decades
Welding Metallurgy, 3 rd Edition is the only complete compendium of recent, and not-so-recent, developments in the science and practice of welding metallurgy. Written by Dr. Sindo Kou, this edition covers solid-state welding as well as fusion welding, which now also includes resistance spot welding. It restructures and expands sections on Fusion Zones and Heat-Affected Zones. The former now includes entirely new chapters on microsegregation, macrosegregation, ductility-dip cracking, and alloys resistant to creep, wear and corrosion, as well as a new section on ternary-alloy solidification. The latter now includes metallurgy of solid-state welding. Partially Melted Zones are expanded to include liquation and cracking in friction stir welding and resistance spot welding. New chapters on topics of high current interest are added, including additive manufacturing, dissimilar-metal joining, magnesium alloys, and high-entropy alloys and metal-matrix nanocomposites.
Dr. Kou provides the reader with hundreds of citations to papers and articles that will further enhance the reader's knowledge of this voluminous topic. Undergraduate students, graduate students, researchers and mechanical engineers will all benefit spectacularly from this comprehensive resource.
The new edition includes new theories/methods of Kou and coworkers regarding:
· Predicting the effect of filler metals on liquation cracking
· An index and analytical equations for predicting susceptibility to solidification cracking
· A test for susceptibility to solidification cracking and filler-metal effect
· Liquid-metal quenching during welding
· Mechanisms of resistance of stainless steels to solidification cracking and ductility-dip cracking
· Mechanisms of macrosegregation
· Mechanisms of spatter of aluminum and magnesium filler metals,
· Liquation and cracking in dissimilar-metal friction stir welding,
· Flow-induced deformation and oscillation of weld-pool surface and ripple formation
· Multicomponent/multiphase diffusion bonding
Dr. Kou's Welding Metallurgy has been used the world over as an indispensable resource for students, researchers, and engineers alike. This new Third Edition is no exception.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Part I
Introduction
1
Welding Processes
1.1 Overview
1.1.1 Fusion Welding Processes
- (a) Gas welding: Oxyacetylene welding (OAW)
- (b) Arc welding: Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW)Gas−tungsten arc welding (GTAW)Plasma arc welding (PAW)Gas−metal arc welding (GMAW)Flux‐cored arc welding (FCAW)Submerged arc welding (SAW)Electroslag welding (ESW)
- (c) High‐energy beam welding: Electron beam welding (EBW)Laser beam welding (LBW)
- (d) Resistance spot welding: Resistance spot welding (RSW)
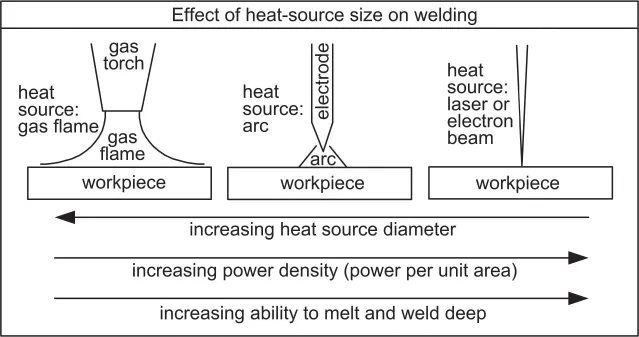
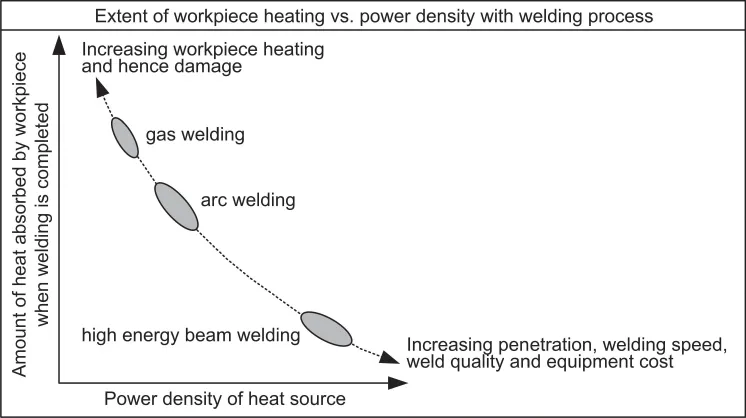
1.1.1.1 Power Density of Heat Source