
eBook - ePub
Epidemiology of Diabetes
Jahangir Moini
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 210 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Epidemiology of Diabetes
Jahangir Moini
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
Epidemiology of Diabetes addresses the patterns, risk factors and prevention tactics for the epidemic of diabetes in the US population. Diabetes is a costly and common disease that needs serious attention and awareness. Diabetes causes devastating consequences, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, nephropathy and vasculopathy. This succinct reference focuses on current data and research on diabetes, and is essential reading for diabetes care providers, as well as health care decision-makers. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has reported that more than 100 million US adults are living with diabetes or prediabetes, hence this is a timely resource on the topic.
- Serves as a starting point for medical professionals who are addressing the patterns, risk factors, prevention and treatment of the epidemic of diabetes in the US population
- Discusses the epidemic and prevalence of diabetes in the United States, covering the disability, burden and mortality of diabetes
- Covers the epidemiology of nutrition and diet, addressing carbohydrates and fiber, fats, protein, alcohol and nutritional intervention
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Epidemiology of Diabetes è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Epidemiology of Diabetes di Jahangir Moini in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Medicina e Endocrinología y metabolismo. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
MedicinaCategoria
Endocrinología y metabolismoChapter 1
Introduction and History of Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States. Its two primary forms are: type 1, in which no insulin is secreted by the pancreas, and type 2, in which the body can no longer normally produce or utilize insulin. Diabetes has been studied since the 5th century BC, though it was named in 1674, based on the sweetness of urine in diabetics. Both type 1 and 2 diabetes originate from autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic beta cells. There are also other less common forms, including gestational diabetes, which develop during pregnancy. The three primary signs of diabetes are: polydipsia, polyphagia, and polyuria.
Diabetes may cause many different conditions. These include diabetic foot and ketoacidosis, eye damage, heart disease, kidney and nerve damage, nonketotic hyperosmolarity, poor wound healing, and infections of various body tissues. Over time, excellent methods of diagnosis of diabetes have been developed. Unfortunately, prevalence of the disease has greatly increased in the United States, as well as in other countries. In the early 20th century, treatment for diabetes became more effective when insulin was first isolated. As a result, the lives of many diabetic patients are longer and more fulfilling than in previous years.
Keywords
Acromegaly; antiinsulin; Cushing syndrome; cystic fibrosis; glucokinase; hyperosmolar; hypoglycemia; hypothyroidism; insidious onset; osmotic diuresis; peripheral insulin resistance; pheochromocytoma; polycystic ovary disease; vitiligo; zedoary seed
Diabetes is very common in the United States, with more than 30 million Americans having the disease. This makes up 9.4% of the country’s population. Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States. The condition known as diabetes mellitus is characterized by high fasting blood glucose. This is tested by taking a blood sample following an overnight period in which the patient has not consumed any types of food.
There are two primary forms of diabetes, which are known as diabetes type 1 and diabetes type 2. In type 1, the beta (ß) cells of the pancreas can no longer secrete insulin. As a result, blood glucose levels become elevated to a condition called hyperglycemia. Almost 75% of type 1 diabetes cases are diagnosed in people under the age of 18 years. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the beta cells of the pancreas can no longer allow glucose to enter in order to produce energy. Studies have shown that the risks of developing type 2 diabetes are higher in people who have a family history, are inactive, and are overweight or obese.
Diabetes has become much more widely understood since the early 1980s, though the disease has existed for much longer. The perception is that a “newer” disease surrounds the components of the modern diet and lifestyle. Diabetes mellitus is related to less-than-adequate physical activity, increased caloric intake, and the resulting factor of obesity being much more common than in previous times. This situation occurs all over the world. Written records about diabetes have existed for thousands of years, in many different countries.
History
The first recorded record of diabetes mellitus comes from India, during the 5th century BC. Descriptions of the disease included the terms emaciation, excessive urination with a sweet odor, and thirst. In ancient Egypt (approximately 460 and 1550 BC), the disease was described as including excessive urination, but there was no description of a “sweet odor.” In China (475–221 BC and AD 229) diabetes was described similarly to the Indian description, and it is believed that the people who wrote the symptoms down were describing patients with type 2 diabetes. They linked it with the following risk factors: large quantities of calories, eating of cereal, rice, and sweets, and as being more common in rich people—meaning that they could better afford these kinds of foods.
The actual term “diabetes” is credited to Demetrius of Apameia (approximately the 1st or 2nd century BC). The term is derived from the Greek language, originally meaning “to siphon” or “to empty.” The first clinical description of diabetes came from Aretaeus of Cappadocia (approximately AD 81–138). In his book called Therapeutics of Chronic Diseases, he even described a “cure” for the disease.
Both Aretaeus and Galen of Pergamum (approximately AD 129–200) believed that the kidneys were the source of urine, and that diabetes was a rare form of kidney disease. Galen (Fig. 1.1) experimented on dogs to substantiate his findings. Both of them did not use any term describing the “sweetness” of urine. It is possible that they were actually describing diabetes insipidus, which is caused by lack of antidiuretic hormone or antidiuretic hormone, and not diabetes mellitus.
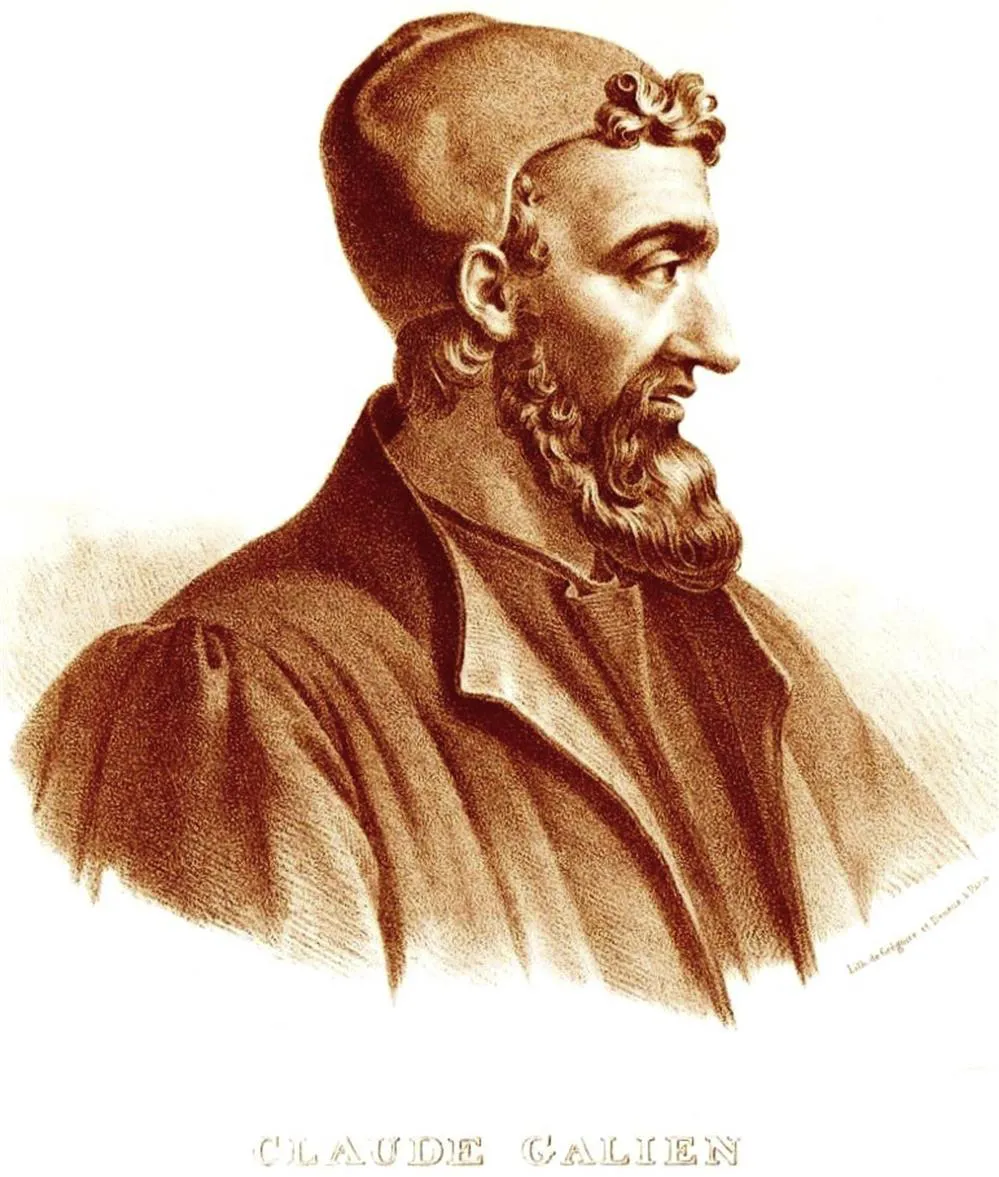
For the next 500 years, Greek physicians were very approving of Galen’s work concerning diabetes. They added new medical writings focused mostly on treatments for the condition, which included bloodletting, medicinal herbs, and even various types of wine. The first diagnostic test for diagnosing diabetes was by actually tasting urine. The sweet taste was written about by the Asians, Egyptians, and Indians. In AD 229, Chang Chung-Ching commented that the urine was so sweet that dogs liked it. In the 5th century, medical texts from the Hindu culture described the urine as being like sugarcane or sweet honey. In AD 630, Theodore Protospatharios recommended that diagnosis of diabetes should include examination of th...