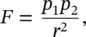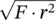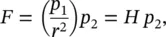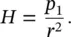Magnetic Memory Technology
Spin-transfer-Torque MRAM and Beyond
Denny D. Tang, Chi-Feng Pai
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Magnetic Memory Technology
Spin-transfer-Torque MRAM and Beyond
Denny D. Tang, Chi-Feng Pai
Informazioni sul libro
STAY UP TO DATE ON THE STATE OF MRAM TECHNOLOGY AND ITS APPLICATIONS WITH THIS COMPREHENSIVE RESOURCE
Magnetic Memory Technology: Spin-Transfer-Torque MRAM and Beyond delivers a combination of foundational and advanced treatments of the subjects necessary for students and professionals to fully understand MRAM and other non-volatile memories, like PCM, and ReRAM. The authors offer readers a thorough introduction to the fundamentals of magnetism and electron spin, as well as a comprehensive analysis of the physics of magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) devices as it relates to memory applications.
This book explores MRAM's unique ability to provide memory without requiring the atoms inside the device to move when switching states. The resulting power savings and reliability are what give MRAM its extraordinary potential. The authors describe the current state of academic research in MRAM technology, which focuses on the reduction of the amount of energy needed to reorient magnetization.
Among other topics, readers will benefit from the book's discussions of:
- An introduction to basic electromagnetism, including the fundamentals of magnetic force and other concepts
- An thorough description of magnetism and magnetic materials, including the classification and properties of magnetic thin film properties and their material preparation and characterization
- A comprehensive description of Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) and tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) devices and their equivalent electrical model
- Spin current and spin dynamics, including the properties of spin current, the Ordinary Hall Effect, the Anomalous Hall Effect, and the spin Hall effect
- Different categories of magnetic random-access memory, including field-write mode MRAM, Spin-Torque-Transfer (STT) MRAM, Spin-Orbit Torque (SOT) MRAM, and others
Perfect for senior undergraduate and graduate students studying electrical engineering, similar programs, or courses on topics like spintronics, Magnetic Memory Technology: Spin-Transfer-Torque MRAM and Beyond also belongs on the bookshelves of engineers and other professionals involved in the design, development, and manufacture of MRAM technologies.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
1
Basic Electromagnetism
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Magnetic Force, Pole, Field, and Dipole