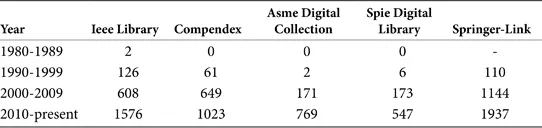
Multi-Component Force Sensing Systems
Qiaokang Liang
- 80 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Multi-Component Force Sensing Systems
Qiaokang Liang
Informazioni sul libro
Multi-Component Force Sensing Systems focuses on the design, development, decoupling, and applications of multi-component force sensing systems. Force and moment information can be used as feedback to form an automatic control system to accomplish efficient manipulation. The origins of force measurement and control can be traced back to the late 1970s. Since then, multi-component F/M (force/moment) sensing systems have been widely known and intensively studied. In the past few years, force measurement practices have been significantly affected by new tools (such as digital force gauges, virtual instrumentation, high speed data acquisition systems, etc.) as well as sophisticated measurement methods such as mechano-magnetic, mechano-optical, etc. However, this is the first book to provide an overview of the topic. It will be a useful reference for students in physics and engineering working with robotic sensing systems and robotic systems, in addition to researchers and those working within industry. This work was supported in part by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (NSFC 62073129 and 61673163).
Features:
• Explores the development of force/torque sensing systems
• Provides real applications of the multi-component force/torque sensing systems
• Contains executable code for decoupling algorithms
About the Author:
Qiaokang Liang is an Associate Professor with the College of Electrical and Information Engineering, Hunan University. He is currently the vice director of the Hunan Key Laboratory of Intelligent Robot Technology in Electronic Manufacturing and serving as the assistant director of the National Engineering Laboratory for Robot Vision Perception and Control. He received his Ph.D. degree in control science and engineering from the University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, in 2011. His research interests include robotics and mechatronics, biomimetic sensing, advanced robot technology, and human–computer interaction.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni
Introduction
1.1What is a Multi-Component Force Sensing System?
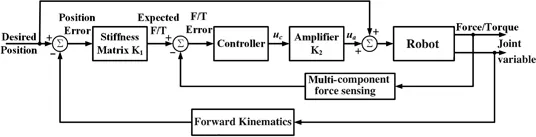
- Multi-component force transducer consists of an elastic structure and corresponding measuring elements. The applied load (force and/or torque along an arbitrary axis) acts on the elastic structure, and the measuring element and circuit will transform corresponding physic variations (such as wavelength shift, displacement, strain, potential, etc.) occurred on the elastic structure into the electrical quantity.
- The obtained electrical quantities such as changes in voltage and current are usually small; therefore, instrumentations with amplification function are adopted, which are always placed close to the measuring circuit.
- Data acquisition devices with functions such as analog-to-digital conversion, signal conditioning (filtering, isolation, temperature compensation, linearization, creep correction, etc.) are equipped as the interface between the multi-component force transducer and a computer or an embedded microcomputer system.
- The computer or microcomputer system is adopted to processing (calculation, calibration, and software filtering), storing, and visualizing the measured force information.
1.2Classification of Multi-Component Force Sensing Systems
Sensing Principle | Transduction Effect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
Magnetoelectric | hall effect | wide dynamic range; low power consumption; high reliability | poor interchangeability; large nonlinear error; low resolution |
Capacitive | capacitance variation due to a load | high sensitivity and resolution; large bandwidth; robustness; drift-free; durability; | complex electronic circuits; stray capacitance; edge effect |
Resistive | conductivity variation due to a load | theoretical maturity; adjustable resolution; high reliability; maintenance-free | higher power consumption; rigid and fragile; scarce reproducibility |
Inductive | magnetic coupling variation due to a load | high sensitivity and resolution; linear output; | lower-frequency response; poor reliability |
Optoelectronic | refractive index variation due to a load | good reliability; wide detection range; noncontact | non-conformable; hard to construct dense arrays |
Piezoelectric | piezoelectric effect | High-frequency response; higher accuracy; high sensitivity and dynamic range; high stiffness | charge leakages; poor spatial resolution; deteriorations of voltages or drifts in the presence of static forces |
1.3State of the Art and Trends in Multi-Component Force Sensing Systems