
eBook - ePub
Neurology E-Book
An Illustrated Colour Text
Geraint Fuller, Mark R. Manford
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 144 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Neurology E-Book
An Illustrated Colour Text
Geraint Fuller, Mark R. Manford
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
An introductory textbook of neurology in the Illustrated Colour Text series, making full use of all the usual features of the series - double page spreads, short paragraphs, summary boxes, attractive use of colour etc.
- Clear explanation of neurological examination - often found very taxing by students.
- Demonstrates how to approach common neurological presentations, such as blackouts and numbness, before moving on to a comprehensive coverage of syndromes and diseases.
- Concentrates on the core curriculum which the medical student really needs to know.
- Updated management in the light of new evidence and new drugs most notably in Parkinson's disease, epilepsy and multiple sclerosis.
- Images, particularly MRI scans, updated with more modern and higher resolution images.
- Includes a new double-page spread on Sleep.
- Extra material added on giddiness to include the head thrust test and Epley's manoeuvre.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Neurology E-Book è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Neurology E-Book di Geraint Fuller, Mark R. Manford in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Medicine e Internal Medicine & Diagnosis. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Organization of the nervous system
The practice of clinical neurology depends on an appreciation of the structure and function of the nervous system. However, a detailed knowledge of neuroanatomy is not essential. This section will outline some of the important neuroanatomy needed for clinical neurology. Some areas, for example the anatomy of the visual system, will be described in the relevant section.
The levels of the nervous system
The nervous system is very complicated, in terms of both its structure and its physiology. Fortunately, when things go wrong they can be categorized on the basis of a relatively simple scheme of neuroanatomy. The nervous system can be thought of as having different levels (Fig. 1). The distribution and type of the clinical problem will often point to the affected level. For example, a patient who is confused must have a disturbance affecting the cerebral hemispheres. There are some situations when the level cannot immediately be determined: for example, a patient with foot drop could have a problem in the peripheral nerve, nerve root, spinal cord or cerebral hemisphere. Terminology used to describe disturbances at different levels is given in Box 1.
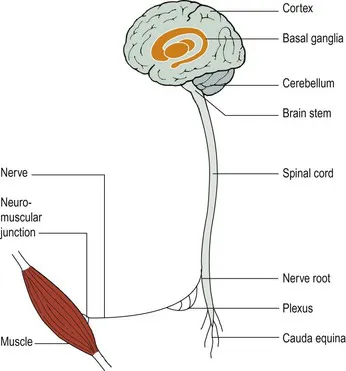
Fig. 1 Levels of the nervous system.
Box 1 Terminology
Abnormalities in the different levels of the nervous system can be referred to according to different terms. One commonly used system is described here. The suffix -opathy can be replaced by -itis if there is thought to be an inflammatory basis to the disturbance.










These terms can be combined with one another or other qualifiers to produce descriptions such as focal encephalopathy, or meningoencephalomyelitis (inflammation of the meninges, brain and spinal cord).
The central nervous system
The cerebral hemispheres
The cerebral hemispheres contain the apparatus of higher function. The dominant hemisphere (left in right-handed people) controls speech and the non-dominant hemisphere provides more spatial awareness. Different lobes undertake different functions (Fig. 2):




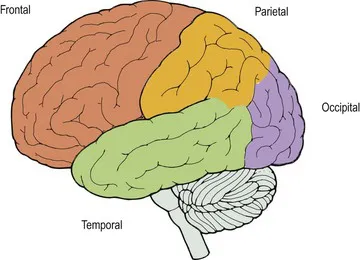
Fig. 2 Lobes of the brain.
The basal ganglia
The basal ganglia are interconnected deep nuclei including the putamen, caudate, globus pallidum and substantia nigra with complicated interrelations. They are involved in the integration of motor and sensory ...