Bioactive Steroids from Marine Organisms
Marina P. Savić1, *, Marija N. Sakač1, Jovana. J. Ajduković1 1 Department of Chemistry, Biochemistry and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Sciences, University of Novi Sad, Trg Dositeja Obradovića 3, 21000 Novi Sad, Serbia
Abstract
Natural products have played a key role in cancer drug discovery, as well in other therapeutic fields. In the past decades, marine organisms have proven to be a primary source of new potentially bioactive natural products for drug discovery. By reviewing the literature describing marine organisms and isolated metabolites, we can notice a large increase in the number of studies today compared to the end of the 20th century. The number of structures isolated each year has almost doubled over the past 20 years. Because of their topicality, we have focused on natural bioactive steroids isolated from marine organisms. In the chapter ‘Bioactive Steroids from Marine Organisms’, an overview of the new steroid compounds isolated from marine sponges, macroalgae and cucumbers, described in the relevant literature in the period from 2011 to 2020, is given. To provide a comprehensive introduction in the field of marine bioactive steroids, we highlighted typical molecules grouped according to their structural characteristics with additional reference to their biological activity. The structures of the new compounds, their natural origin (species of the organism) and their rich biological activities are presented and described in detail. In addition, biological tests performed on known compounds during this time period are also described. Some of the compounds possess multiple activities and have been tested only in a limited number of biological assays, which means that the full potential and significance of these compounds may only be discovered in the future.
Keywords: Bioactivity, Biosynthetic origin, Marine cucumber, Marine macroalgae, Marine sponges, Natural steroids, Structural characterization.
* Corresponding author Marina P. Savić: Department of Chemistry, Biochemistry and Environmental Protection, Faculty of Sciences, University of Novi Sad, Trg Dositeja Obradovića 3, 21000 Novi Sad, Serbia; Tel: +381 2148 5273 3; E-mail:[email protected] INTRODUCTION
The American, Werner Bergmann, was one of the first scientists who started the chemical investigation of marine organisms. He reported the isolation of unusual nucleosides from the sponge Cryptotethia crypta collected near the coast of Florida [1] and his discovery was followed by the development of the very first marine-derived drug, Cytarabine, which destroys cancer cells by blocking DNA
polymerase function [2]. In 1969, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved this drug for the treatment of leukemia. Currently, there are six FDA-approved marine-derived drugs in the market and several compounds in different phases of the clinical trials [3].
Steroids are a major class of natural compounds with an important biological role. They have attracted great attention over the years from medicinal chemists in the search for new drugs. Their function involves the constitution of the membrane, hormonal function, protective functions and many others. Steroid-based compounds are widely used in medicine as drugs with anti-inflammatory, anabolic, contraceptive or anticancer activities [4].
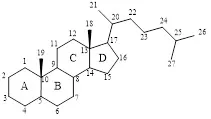
The term ‘steroid’ covers a wide variety of compounds based on a partially cyclized isoprenoid skeleton. These molecules are structurally defined by their 17-carbon tetracyclic (cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene) core containing three cyclohexane rings (A, B, and C) and one cyclopentane (D ring). The numbering of the steroid nucleus is presented in the example of a cholestane-type compound, which is structurally the most representative (Fig. 1).
Fig. (1)) The structure and the numbering of a cholestane-type compound.
The chapter ‘Bioactive Steroids from Marine Organisms’ covers the literature published in the period from 2011 to 2020 relating to the new steroid compounds isolated from marine sponges, macroalgae and cucumbers. The chapter contains three subchapters, each relating to one of the groups of marine organisms. Within these subchapters, steroid compounds are grouped according to their common structural characteristics, while their biological activity is additionally described, as well as their biosynthetic origin. Also, new biological activity for known steroid compounds is described.
BIOACTIVE STEROIDS FROM MARINE SPONGES
The sponges are the simplest and probably oldest group of animals that have separated from other metazoans. They are sessile organisms that do not possess true tissues, organs or nerve structures [5]. Sponges are important within the fields of marine biotechnology and marine pharmacology. They are considered the best resources for highly active therapeutic molecules amongst other marine invertebrates.
Marine sponges are the source of a large number of compounds with unusual carbon frameworks and functionalities. Various compounds with a unique structure, such as secosteroids or steroids with sugar moiety on the side chains of steroid compounds, are often present [6, 7].
In the literature, novel compounds, particularly steroids with a diverse range of conventional and unconventional side chains and nuclei with various biological activities have been described as secondary metabolites of sea sponges [8]. Due to their significant potential, steroid compounds isolated from sponges will be described in this sub...