eBook - ePub
Special Economic Zones in the Indonesia–Malaysia–Thailand Growth Triangle
Opportunities for Collaboration
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 172 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Special Economic Zones in the Indonesia–Malaysia–Thailand Growth Triangle
Opportunities for Collaboration
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
This publication explains why Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand need to ramp up cooperation to boost their special economic zones (SEZ) and spur sustainable growth. Mapping out and assessing the economic performance of SEZs across the subregion, it highlights the threats they face from factors including growing competition for foreign investment, international trade disputes, and the rise of digital technologies. The publication stresses the need for policymakers and stakeholders to intensify their strategic collaboration in order to make their SEZs more competitive. Against the backdrop of COVID-19, it details a range of practical steps designed to increase trade, create jobs, and build economic resilience across the three countries.
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Special Economic Zones in the Indonesia–Malaysia–Thailand Growth Triangle è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Special Economic Zones in the Indonesia–Malaysia–Thailand Growth Triangle di in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Politics & International Relations e Local & Regional Planning Public Policy. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Introduction
Background
Since its inception in 1993, the Indonesia–Malaysia–Thailand Growth Triangle (IMT-GT) subregional program has attained remarkable economic growth and shared regional prosperity through concerted policy interventions. Yet, there is a mismatch between the actual achievements and declared objectives. The midterm review of the IMT-GT Implementation Blueprint 2012–2016 observes that the gains in terms of intra-subregional trade and investment are particularly modest, suggesting the limited success of the member states in leveraging on their comparative advantages to make it a well-positioned regional production base (Asian Development Bank [ADB] 2015). To address this gap, the IMT-GT Vision 2036 (Centre for IMT-GT Subregional Cooperation [CIMT] 2017a) supported by the IMT-GT Implementation Blueprint 2017–2021 (CIMT 2017b) adopts the spatial approach that accords a high priority to the development of regional and cross-border production networks in the IMT-GT areas using special economic zones (SEZs), special border economic zones (SBEZs), and other production sites as the key tools. The IMT-GT Vision 2036 places the five priority IMT-GT economic corridors at the center to facilitate cross-border connectivity of these production sites backward with resources and forward with markets and maximize the economic network externalities. The objective is to foster diversification and sophistication of manufacturing, agribusiness, and tourism chains for “an integrated, innovative, inclusive and sustainable subregion by 2036” (CIMT 2017a, 43). However, very little is known about whether and how economic corridors are being leveraged for setting up SEZs, SBEZs, and other production hubs and how successful they have been in generating network externalities in the subregion through regional cooperation. Bearing this in mind, ADB, a regional development partner to IMT-GT since 2006, has conducted this study on a collaborative approach to SEZ development in the IMT-GT subregion at the request of the member states under the technical assistance project titled Enhancing Effectiveness of Subregional Programs to Advance Regional Cooperation and Integration in Southeast Asia.
The study’s main objectives are to take stock of the IMT-GT SEZs and other economic zones, review the extent to which these are integrated into national development agendas of the member states, review their performance, identify challenges, and offer recommendations for policy makers to support their active clustering and specialization efforts in the subregion. One of the study’s objectives is to map the universe of SEZs and other industrial zones in a comparative framework to harmonize the data on economic zones in the three member countries. Harmonization of data means transforming the data of varying zone types and naming conventions into one cohesive data set by developing a framework for zone typology. To my best knowledge, no earlier studies have assessed the implementation of the subregional agenda from the perspective of economic zones and/or attempted to harmonize the regional economic zone data. This study is the first to address this gap. The study makes three major contributions to the existing literature on economic zones, particularly SEZs. First, it harmonizes the data on economic zones in the IMT-GT member countries. Second, it develops a framework to assess the mainstreaming of the subregional agenda into national and subnational development agendas and proposes a strategy to implement it successfully. Third and most important, it proposes a strategic framework for the success of economic zones in the subregion. While doing so, it underlines the relevance of the collaborative approach for the subregional economic zones and highlights how the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic has further underscored the need for the collaborative approach to economic zones. Typically, economic zones are set up as a competitive tool to attract investment and generate employment. However, this study identifies the transborder subregion with a hybrid zone and proposes a coopetition (a combination of collaboration and competition) strategy to improve the attractiveness of the subregional economic zones.
Objectives and Scope
The study sets out the following specific objectives:
The study’s ultimate objective is to strengthen the strategic relevance of economic zones in the subregional initiative and identify actions for promoting them.
While the study proposal was designed to cover only SEZs and SBEZs, all other economic zones have been included in the study for three reasons. First, there has been a proliferation not only of SEZs but also of other economic zones in the region; any study based only on SEZs would, therefore, present a partial view of trade and investment activity along the economic corridors. Second, the distinction between SEZs and other economic zones is becoming blurred, with many of the advantages of SEZs also being offered in other economic zones. Third, the ultimate goal of the zones, irrespective of the type, is to promote industrial clustering and production networks, one of the planks on which the Vision 2036 strategic framework is based.
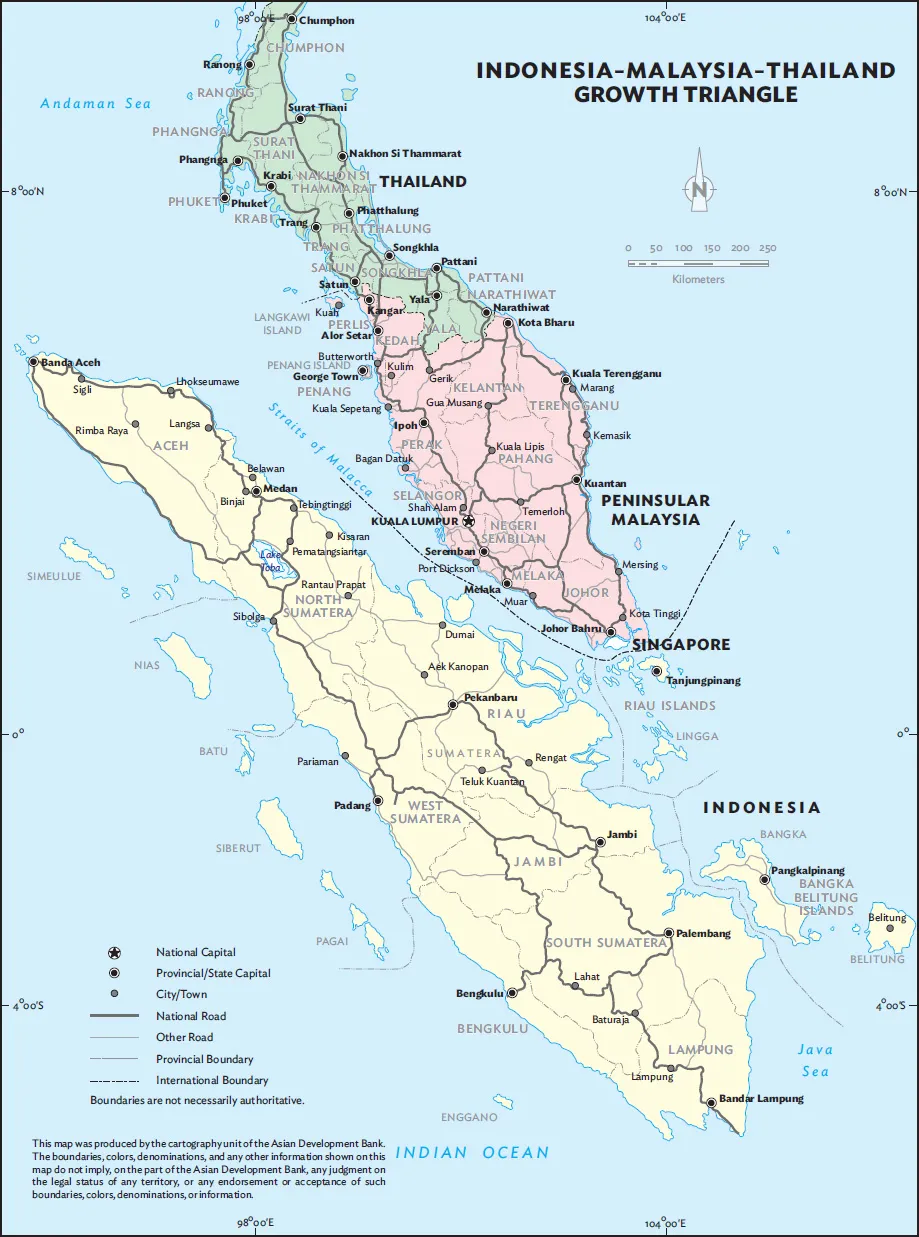
The geographical scope of the study covers all 32 provinces and states under the IMT-GT (Map 1):
Methodology
The methodology employed in this study involves a combination of secondary and primary research. Extensive country consultations were conducted during July and August 2019. Using semi-structured questionnaires, a study team comprising of the author and project management team of ADB conducted face-to-face interviews with key informants such as government officials at the national and subnational levels, administrative officials of SEZs and other economic zones, the Centre for IMT-GT Subregional Cooperation (CIMT) management team, and private sector entities across the subregion. The field-based consultations offered crucial insights into the implementation of the subregional agenda at the national level. Country consultations were also filled with presentations by various government agencies, discussions, and site visits, yielding rich information on the existing and proposed economic zones in these countries. The primary data gathered during field trips were then combined with the secondary data, encompassing an enormous range of sources, including nationally and internationally published studies; development plan documents of the three countries since the 1960s; texts of the relevant acts, decrees, and regulations; government reports and press releases; academic and news articles; blogs and books; and websites of investment promotion agencies such as the Malaysian Investment Development Authority (MIDA), Indonesian Investment Coordinating Board, Industrial Estate Authority of Thailand (IEAT), and Board of Investment of Thailand (BOI).
The data were assessed using the descriptive, exploratory, and explanatory approaches. The descriptive element includes the mapping of economic zones in the three IMT-GT countries and their policy frameworks. The exploratory part analyzes the linkages between the zones and national development agendas, and reviews the subregional economic performance. The explanatory approach explains the relevance of the subregional program using both theoretical arguments and empirical evidence, discusses the challenge, and suggests approaches to strengthen the subregional economic zones.
Organization of the Study
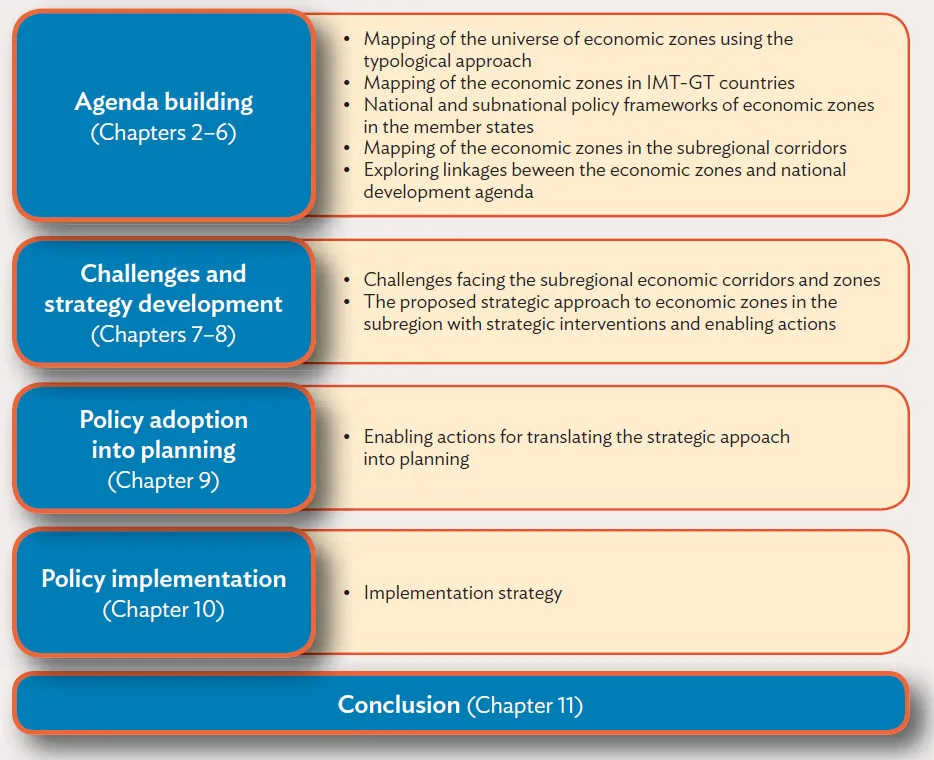
Since the study’s ultimate objective is to identify policy actions for promoting economic zones created within the subregional economic corridors, it is structured using the “stages model framework” of the public policy literature. According to this model, the process of producing public policies can be divided into five to seven stages. This report uses the Howlett and Ramesh model (Howlett and Ramesh 2003), which proposes five stages of public policy: agenda building, policy formulation, adoption, implementation, and evaluation. The agenda building stage establishes the relevance of an issue or topic for public intervention. Policy formulation means strategy building to address the issue. In policy adoption, the third phase of the policy process, policies are adopted by government bodies for implementation. Implementation involves putting the policies into effect.
Evaluation, the final stage, requires an impact assessment of the policy. In the present study, these stages are adapted and reorganized into four stages: agenda building, strategy development, policy adoption into planning, and policy implementation. The fifth stage of monitoring and evaluation (M&E) is grouped into the implementation stage as part of the implementation strategy. The rest of the study is organized into 10 sections covering these four stages and concluding remarks, as illustrated in Figure 1.
Chapter 2
Understanding the Concept of Economic Zones: The Conceptual Framework
Typological Framework of Economic Zones
Economic zones are geographically delimited areas created to offer well-developed industrial spaces with or without special rules and incentives. While the underlying principle for economic zones is clustering general or specialized firms and generating agglomeration economies, they are different from industrial or economic cl...