
eBook - ePub
Pattern Cutting
Second Edition
Dennic Chunman Lo
This is a test
Condividi libro
- 300 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
eBook - ePub
Pattern Cutting
Second Edition
Dennic Chunman Lo
Dettagli del libro
Anteprima del libro
Indice dei contenuti
Citazioni
Informazioni sul libro
This practical guide explains how to take accurate measurements, introduces key tools and takes you from simple pattern-cutting ideas to more advanced creative methods. Step-by-step illustrations show how to create and then fit basic bodice, sleeve, skirt, dress, and trouser blocks, and how to adapt these to create patterns for original designs. New material includes advice on fitting toiles and working with stretch fabrics. There is also a fully updated chapter dedicated to digital technology. New to this edition: Access to 32 instructional videos
Domande frequenti
Come faccio ad annullare l'abbonamento?
È semplicissimo: basta accedere alla sezione Account nelle Impostazioni e cliccare su "Annulla abbonamento". Dopo la cancellazione, l'abbonamento rimarrà attivo per il periodo rimanente già pagato. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
È possibile scaricare libri? Se sì, come?
Al momento è possibile scaricare tramite l'app tutti i nostri libri ePub mobile-friendly. Anche la maggior parte dei nostri PDF è scaricabile e stiamo lavorando per rendere disponibile quanto prima il download di tutti gli altri file. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui
Che differenza c'è tra i piani?
Entrambi i piani ti danno accesso illimitato alla libreria e a tutte le funzionalità di Perlego. Le uniche differenze sono il prezzo e il periodo di abbonamento: con il piano annuale risparmierai circa il 30% rispetto a 12 rate con quello mensile.
Cos'è Perlego?
Perlego è un servizio di abbonamento a testi accademici, che ti permette di accedere a un'intera libreria online a un prezzo inferiore rispetto a quello che pagheresti per acquistare un singolo libro al mese. Con oltre 1 milione di testi suddivisi in più di 1.000 categorie, troverai sicuramente ciò che fa per te! Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Perlego supporta la sintesi vocale?
Cerca l'icona Sintesi vocale nel prossimo libro che leggerai per verificare se è possibile riprodurre l'audio. Questo strumento permette di leggere il testo a voce alta, evidenziandolo man mano che la lettura procede. Puoi aumentare o diminuire la velocità della sintesi vocale, oppure sospendere la riproduzione. Per maggiori informazioni, clicca qui.
Pattern Cutting è disponibile online in formato PDF/ePub?
Sì, puoi accedere a Pattern Cutting di Dennic Chunman Lo in formato PDF e/o ePub, così come ad altri libri molto apprezzati nelle sezioni relative a Design e Design generale. Scopri oltre 1 milione di libri disponibili nel nostro catalogo.
Informazioni
Argomento
DesignCategoria
Design generaleCHAPTER 1
PREPARATION
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
• List the four main decisions needed before pattern cutting can begin.
• Outline the different size charts and how they apply to a variety of pattern-cutting scenarios.
• Explain the difference between woven and stretch fabrics, and describe the effects of grainline, gravity and suppression on a garment.
• Discuss the relationship between a two-dimensional pattern and a three-dimensional garment.
• Recognize the elements and requirements of a working drawing.

INTRODUCTION
Common sense is the key to pattern cutting. When trying to make something – whether it is a pillowcase, a cushion cover, a tablecloth, an apron or even a simple quilted case for a laptop – you need to know four things before beginning:
1. The measurements.
2. The intended material.
3. The techniques that will be used to make it; for example, machine stitching, hand stitching, taping, gluing, overlocking, zipping, buttoning and so on.
4. Finally, and perhaps this is the most important point, whether you want to make more than one. If so, you will need to keep a record.
To translate the above in terms of pattern cutting for the garment industry:
1. Before beginning you need to know the measurements required and the sizing system you need to work to.
2. You need to know the fabric from which the garment will be made because this will affect the method you apply to cut the pattern and will also determine the seam allowances in terms of width and method of finishing.
3. To be a good pattern cutter, you also need to understand construction. Pattern cutting is not only working out the shape, it is also about engineering the pieces to fit together to form a garment. To understand how to do this you need to acquire garment construction skills such as sewing or knitting.
4. To make more than one garment you need to be able to record the shape in the form of papter pattern. This is done by perfecting the shape first through a draft pattern and then through toiling and alteration. The resulting pattern(s) can be reused many times throughout the production process.
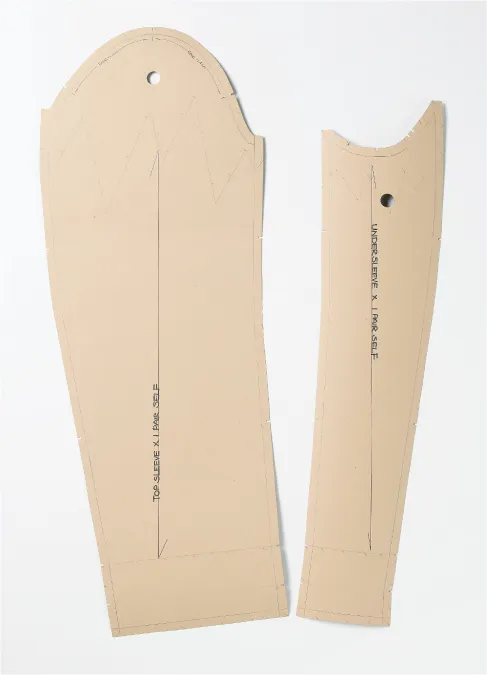


You will mainly use either pattern card or spot-and-cross paper, but in practical terms you can use almost any type of paper for pattern cutting. Recycled newspaper, for example, might make an economical and interesting set of paper patterns (see here), but only if you can read any marks you might make through the newsprint and the paper does not tear too readily.
An experienced pattern cutter will be able to draft the pattern directly onto real fabric with chalk from a set of measurements. This needs experience, confidence, practice and a lifetime of dedication to one skill. This method, however, can only really be used in home dressmaking or bespoke tailoring because there is no mass production and therefore no need to make a record. For mass production in the garment industry, patterns must be used. These are usually made from plain paper or soft card, card being more durable. However, digital patterns, which are more user-friendly and sustainable, are becoming more prevalent.
Patterns record the shape of the garment accurately. Each part of the garment is drafted separately: sleeve, collar, front, back, yoke, lapel and so on. Sets of paper patterns should be stored, recorded or even archived systematically so they can be reused over a period of time. In the case of computerized pattern cutting, the sets of patterns are stored in digital format and can be plotted, shared by e-mail and reproduced at the click of a button.
Having established the need to record the garment in the form of a pattern, the next stage is usually the creation of a block, which is a basic garment shape from which a pattern for a specific garment can be drafted. You will learn how to draft a block in Chapter 3. Before we begin, however, we will further explore the first two premises listed opposite – measurements and sizing systems and the effect of different fabrics on pattern cutting. There is also a third item a pattern cutter needs before beginning to draft the block or pattern, and that is an idea of the garment they are to create. This comes in the form of a working drawing, which will be explored at the end of the chapter.

MANNEQUINS & MEASUREMENTS
Before you start to cut a block or produce a paper pattern for a garment, you must consider the person for whom you are making the garment. Is it:
1. a garment for yourself? (home dressmaking)
2. a garment for a particular person? (couture/bespoke tailoring)
3. a garment for an assignment at college? (using a mannequin)
4. a garment for a fashion show? (aesthetic based)
5. a garment made professionally for the industry? (realistic, to fit the general public)
Each of these different scenarios will require a different size chart and the selection of a different mannequin for fitting. Please see Chapter 3 for advice on taking measurements.
PERSONAL SIZE CHART
When making a garment for yourself or for a specific person, you can create a unique size chart containing the following measurements:
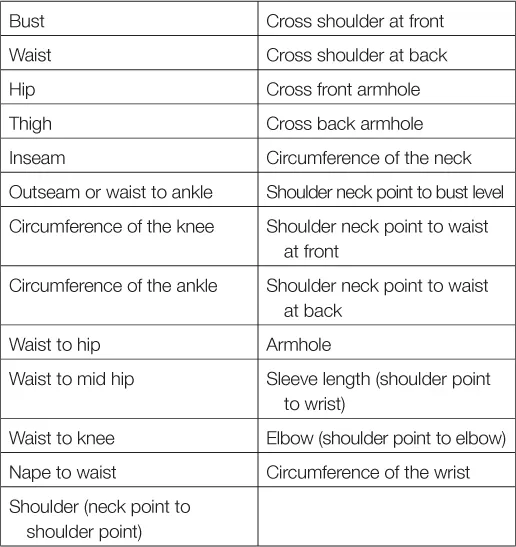
BNW = Centre back of neck to waistline, or nape to waist (Courtesy Kennett and Lindsell Ltd)
Using a personal size chart will ensure a made-to-measure fit, which is virtually impossible using any other kind of size chart. Tailors, bridalwear designers and haute couturiers not only produce each garment to the exact measurements of their clients, but also use custom-made mannequins (or forms) sized for their most loyal customers; Hardy Amies had a special mannequin for Queen Elizabeth II, as did Givenchy for Audrey Hepburn. Rather than relying on personal measurements alone (no matter how many you take), the best practice when cutting a pattern for one person is to spend time actually fitting the toile to that person.
MANNEQUIN SIZE CHART
Most colleges use a European size 12 mannequin as a standard size, though some are now using a size 10 as the ideal shape slims down on the catwalk. Using a size 10 mannequin is increasi...