Greenhouse Gas Emission and Mitigation in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants
Fundamentals and a Guide to Experimental Research
Xinmin Zhan, Zhenhu Hu, Guangxue Wu
- 160 pagine
- English
- ePUB (disponibile sull'app)
- Disponibile su iOS e Android
Greenhouse Gas Emission and Mitigation in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants
Fundamentals and a Guide to Experimental Research
Xinmin Zhan, Zhenhu Hu, Guangxue Wu
Informazioni sul libro
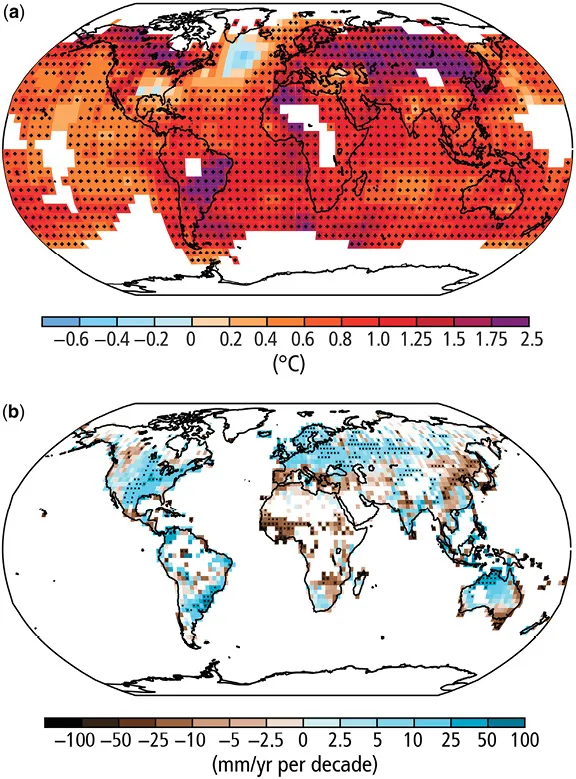
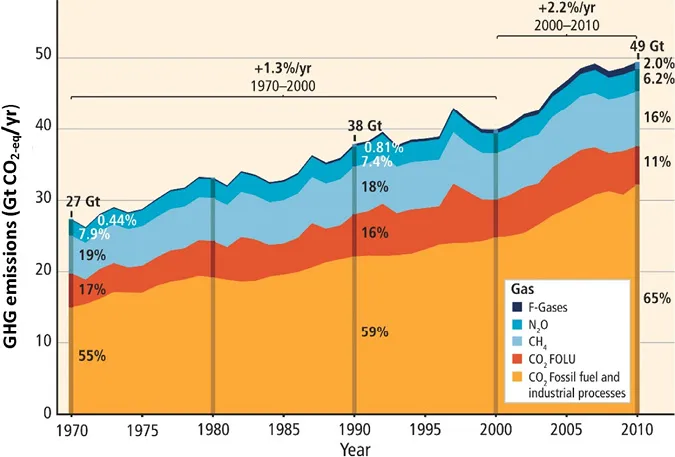
Advanced wastewater treatment processes and novel technologies are adopted to improve nutrient removal from wastewater so as to meet stringent discharge standards. Municipal wastewater treatment plants are one of the major contributors to the increase in the global greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and therefore it is necessary to carry out intensive studies on quantification, assessment and characterization of GHG emissions in wastewater treatment plants, on the life cycle assessment from GHG emission prospective, and on the GHG mitigation strategies.Greenhouse Gas Emission and Mitigation in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants summarises the recent development in studies of greenhouse gases' (CH4 and N2O) generation and emission in municipal wastewater treatment plants. It introduces the concepts of direct emission and indirect emission, and the mechanisms of GHG generations in wastewater treatment plants' processing units. The book explicitly describes the techniques used to quantify direct GHG emissions in wastewater treatment plants and the protocol used by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) to estimate GHG emission due to wastewater treatment in the national GHG inventory. Finally, the book explains the life cycle assessment (LCA) methodology on GHG emissions in consideration of the energy and chemical usage in municipal wastewater treatment plants. In addition, the strategies to mitigate GHG emissions are discussed.The book provides an overview for researchers, students, water professionals and policy makers on GHG emission and mitigation in municipal wastewater treatment plants and industrial wastewater treatment processes. It is a valuable resource for undergraduate and postgraduate students in the water, climate, and energy areas; for researchers in the relevant areas; and for professional reference by water professionals, government policy makers, and research institutes.
Domande frequenti
Informazioni